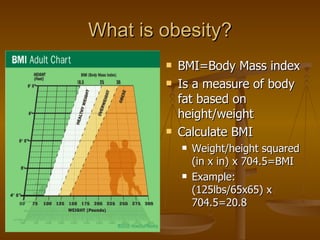
The document discusses obesity, defining it as a body mass index over 30. It notes the highest rates of obesity are in North America and Western Europe due to high-fat diets and sedentary lifestyles. About 55% of US adults are overweight or obese, straining the healthcare system. Obesity is associated with over 30 diseases and health risks. Children are also increasingly affected, with racial, gender and geographic patterns mirroring adults. Causes include genetics, diet, decreased physical activity, and sedentary lifestyles. Treatment involves lifestyle changes like diet, exercise and behavior therapy while prevention emphasizes healthy eating and active living.