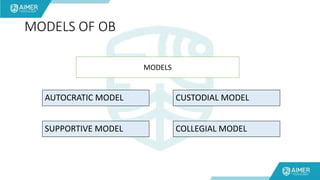
This document provides an introduction to organizational behaviour. It defines organizational behaviour as the study and application of knowledge about how individuals and groups act within organizations. It identifies the key elements of organizational behaviour as people, structure, technology, and environment. It then describes four common models of organizational behaviour: the autocratic model, custodial model, supportive model, and collegial model. Finally, it outlines some of the benefits of studying organizational behaviour, such as understanding human behavior and leadership within organizations.