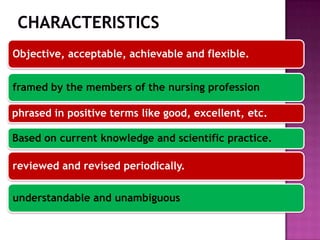
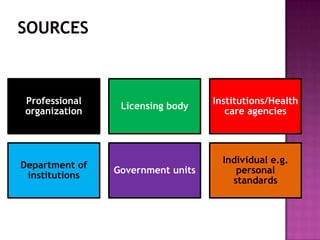
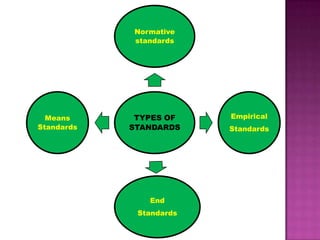
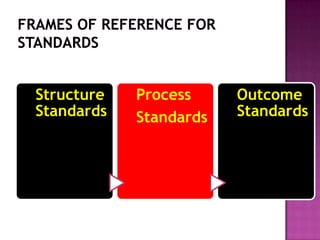
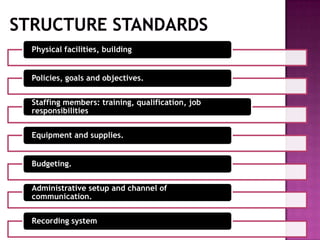
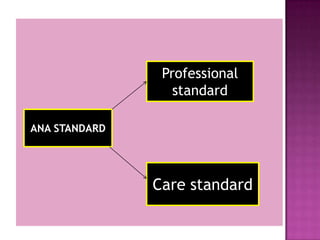
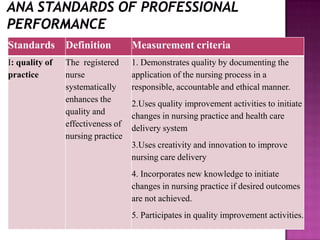
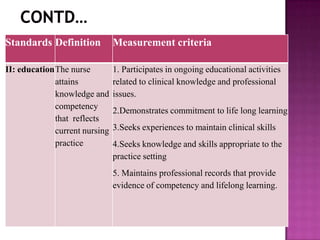
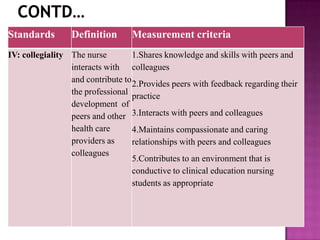
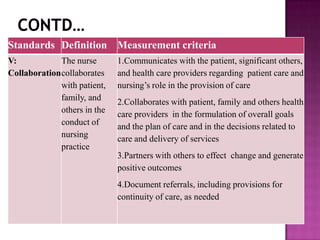
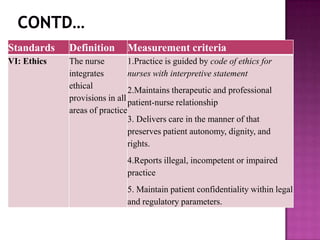
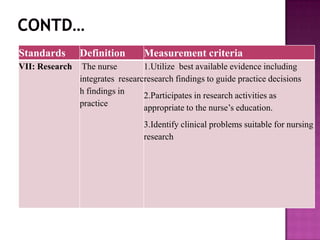
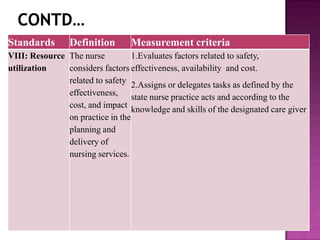
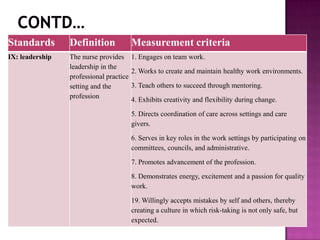
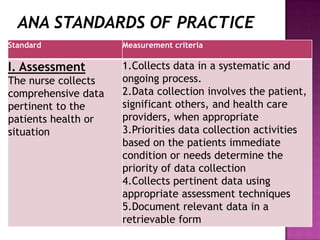
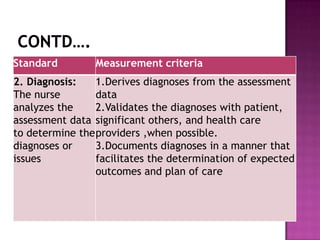
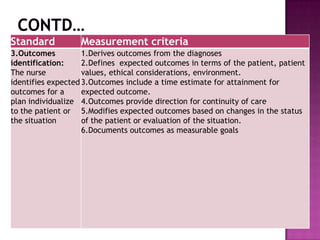
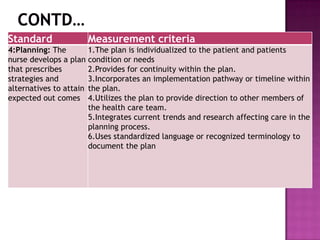
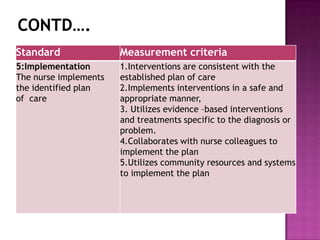
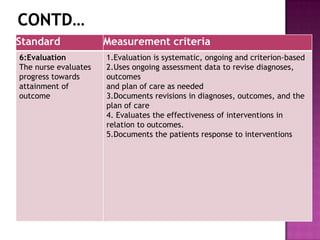
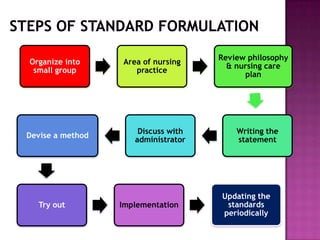
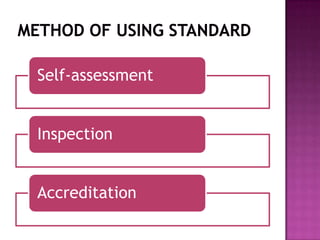
Nursing standards provide a framework for nursing practice and define expectations for nurses. Standards are developed by nursing professionals and reflect best practices. They promote high quality nursing care by establishing guidelines for areas like assessment, diagnosis, care planning, and evaluation. Standards are meant to be objective, achievable and reviewed over time. They are used for various purposes such as evaluating nursing performance, educating nurses, and informing the public about the nursing profession.