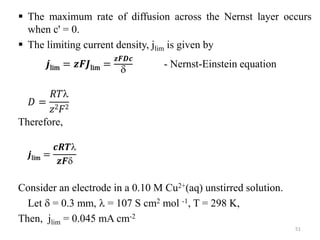
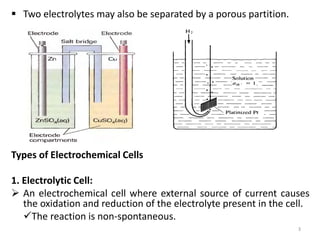
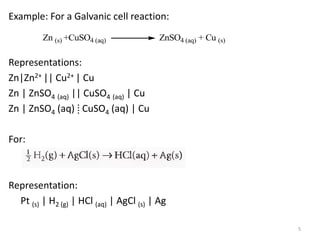
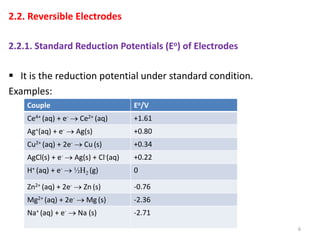
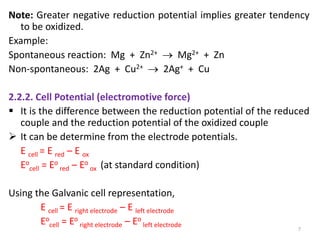
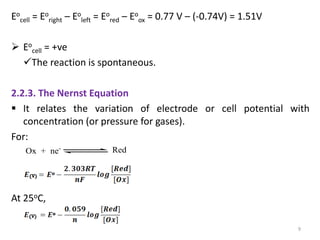
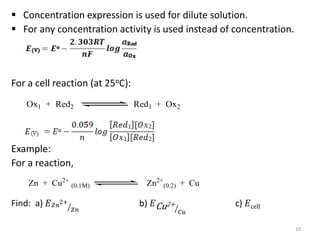
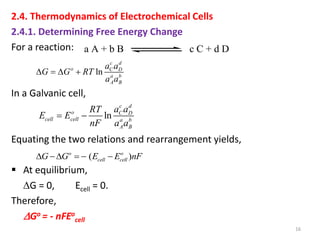
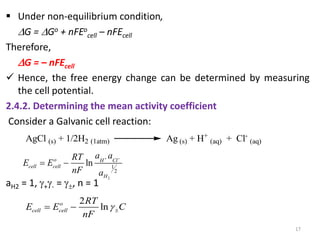
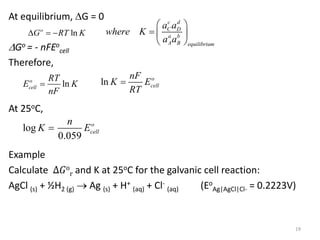
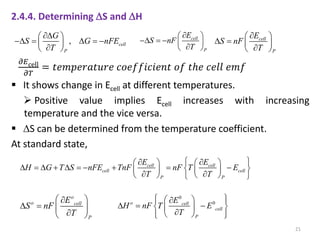
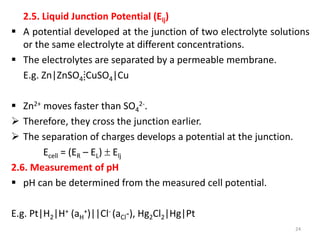
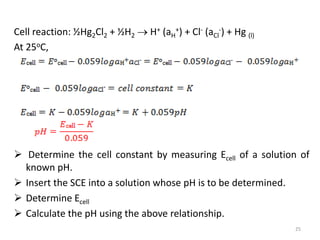
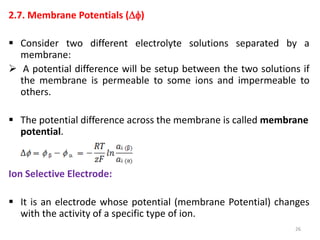
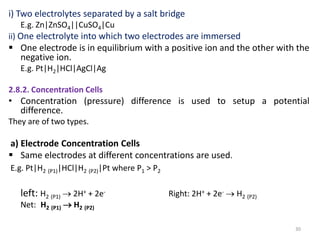
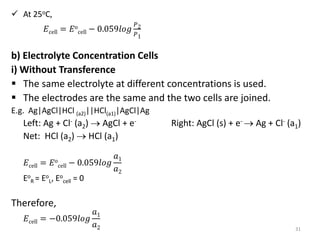
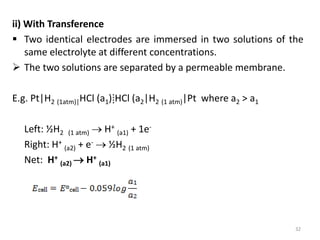
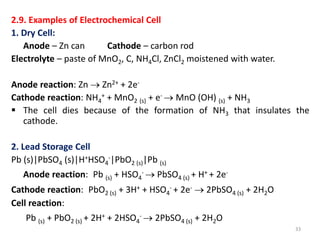
This document provides information about electrochemical cells. It begins by defining an electrochemical cell as consisting of two electrodes in contact with an electrolyte, with each electrode and electrolyte comprising an electrode compartment. It describes the two main types of electrochemical cells - electrolytic cells, where an external current causes non-spontaneous oxidation and reduction, and galvanic cells, where a spontaneous chemical reaction produces electricity. It then discusses standard reduction potentials, cell potentials, the Nernst equation, types of electrodes, and methods for determining standard electrode potentials, free energy changes, and equilibrium constants from cell potentials.




![Solution
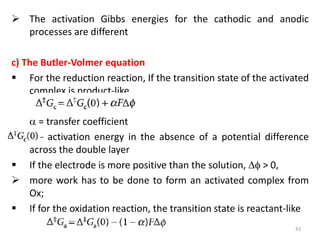
b)
𝑬𝑪𝒖2+/𝑪𝒖 = 𝑬𝑪𝒖2+/𝑪𝒖
𝒐
−
𝟎. 𝟎𝟓𝟗
𝟐
𝒍𝒐𝒈
𝑪𝒖
𝑪𝒖2+
= 𝟎. 𝟑𝟒 −
𝟎. 𝟎𝟓𝟗
𝟐
𝒍𝒐𝒈
𝟏
𝟎. 𝟏
= 𝟎. 𝟑𝟏𝑽
11
2 2
2 2
0 0 0
2 2
/ /
0.059 [ ][ ] 0.059 [ ][ ]
) log ( ) log
[ ][ ] [ ][ ]
0.059 0.2
(0.34 ( 0.76) log 1.09
2 0.1
cell cell Cu Cu Zn Zn
Zn Cu Zn Cu
c E E E E
n Zn Cu n Zn Cu
V
Re 0.31 ( 0.78 ) 1.09
cell d Ox
Or E E E V V V
2 2 2
/ /
0.059 [ ] 0.059 1
) log 0.76 log 0.78
[ ] 2 0.2
o
Zn Zn Zn Zn
Zn
a E E V
n Zn
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-231216084426-e37f29a7/85/Chapter-2-pdf-11-320.jpg)
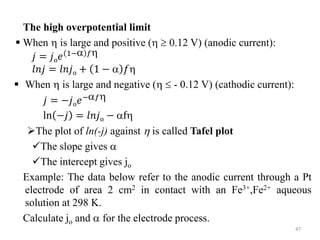
![2.2.4. Types of Electrodes in Galvanic Cells
1. Metal – metal ion electrode: A metal rod is dipped in a solution
containing the ion of he metal.
Mn+ + ne- M
E.g. Ag+|Ag
2. Gas – ion electrode: The gas is allowed to mix with a solution
containing its ions. Inert metal is used for the passage of electrons.
E.g. 2H+ + 2e- H2 Or H+ + e- ½H2
3. Metal – insoluble salt – anion of salt electrode: A metal coated
with its insoluble salt is dipped in a solution containing the anion
of the salt.
12
/ /
0.059 1
log
[ ]
n n
o
n
M M M M
E E
n M
2
2 2
( )
2
/ /
0.059
log
[ ]
H atm
o
H H H H
P
E E
n H
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-231216084426-e37f29a7/85/Chapter-2-pdf-12-320.jpg)
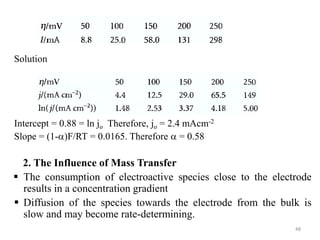
![E.g.1 Ag|AgCl(s)|Cl-
AgCl (s) + e- Ag + Cl-
𝐸Ag/AgCl/Cl- = 𝐸o
Ag/AgCl/Cl- −
0.059
1
log
[𝐶𝑙-]
E.g.2 Saturated calomel electrode (SCE): Hg|Hg2Cl2 (s)||Cl-
Hg2Cl2 (s) + 2e- 2Hg (l) + 2Cl-
𝐸Hg/Hg2Cl2/Cl- = 𝐸o
Hg/Hg2Cl2/Cl- −
0.059
2
log 𝐶𝑙− 2 = 𝐸o
Hg/Hg2Cl2/Cl- − 0.059log
[𝐶𝑙−]
4. Amalgam electrode: Na (Hg)|Na+
Na+ + e- + Hg Na (Hg)
13
( )/ ( )/
0.059 ( )
log
1 [ ]
o
Na Hg Na Na Hg Na
Na Hg
E E
Na
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-231216084426-e37f29a7/85/Chapter-2-pdf-13-320.jpg)
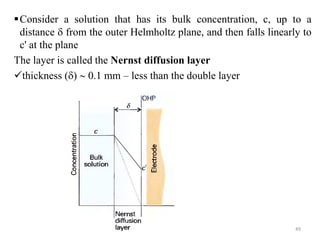
![5. Oxidation – Reduction Electrode
There are two ions one of which is reduced to the other.
E.g. Pt|Fe3+, Fe2+
Fe3+ + e- Fe2+
2.3. Determination of Standard Electrode Potential
Consider the Galvanic cell: Pt|H2|HCl|AgCl|Ag
Cell reaction:
½H2 (1atm) + AgCl Ag + H+ (aH
+) + Cl- (aCl
-)
At 25 oC,
𝑬cell = 𝑬o
cell − 𝟎. 𝟎𝟓𝟗𝒍𝒐𝒈𝒂H
+𝒂Cl−
14
3 2 3 2
2
3
, ,
0.059 [ ]
log
1 [ ]
o
Fe Fe Fe Fe
Fe
E E
Fe
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-231216084426-e37f29a7/85/Chapter-2-pdf-14-320.jpg)
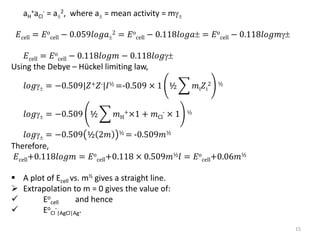








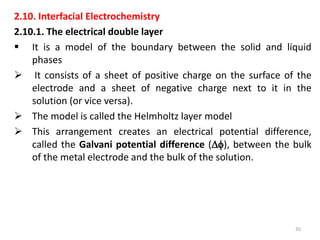
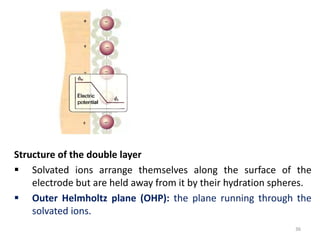
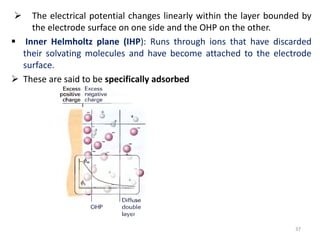
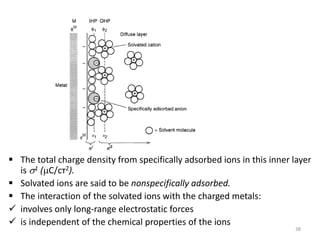
![ Because of thermal agitation, the nonspecifically adsorbed ions
are distributed in a diffuse layer, which extends from the OHP into
the bulk of the solution
The excess charge density in the diffuse layer is d
The thickness of the diffuse layer depends on the total ionic
concentration in the solution;
for concentrations greater than 10~2 M, the thickness is less than
~100 Å.
The structure of the double layer can affect the rates of electrode
processes
2.10.2. Electrochemical kinetics
1. Kinetics of Simple electrode reactions
a) The rate laws
Rate of reduction of Ox: Ox = 𝑘c[𝑂𝑥]
Rate of oxidation of Red: Red = 𝑘a[𝑅𝑒𝑑]
39](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-231216084426-e37f29a7/85/Chapter-2-pdf-39-320.jpg)