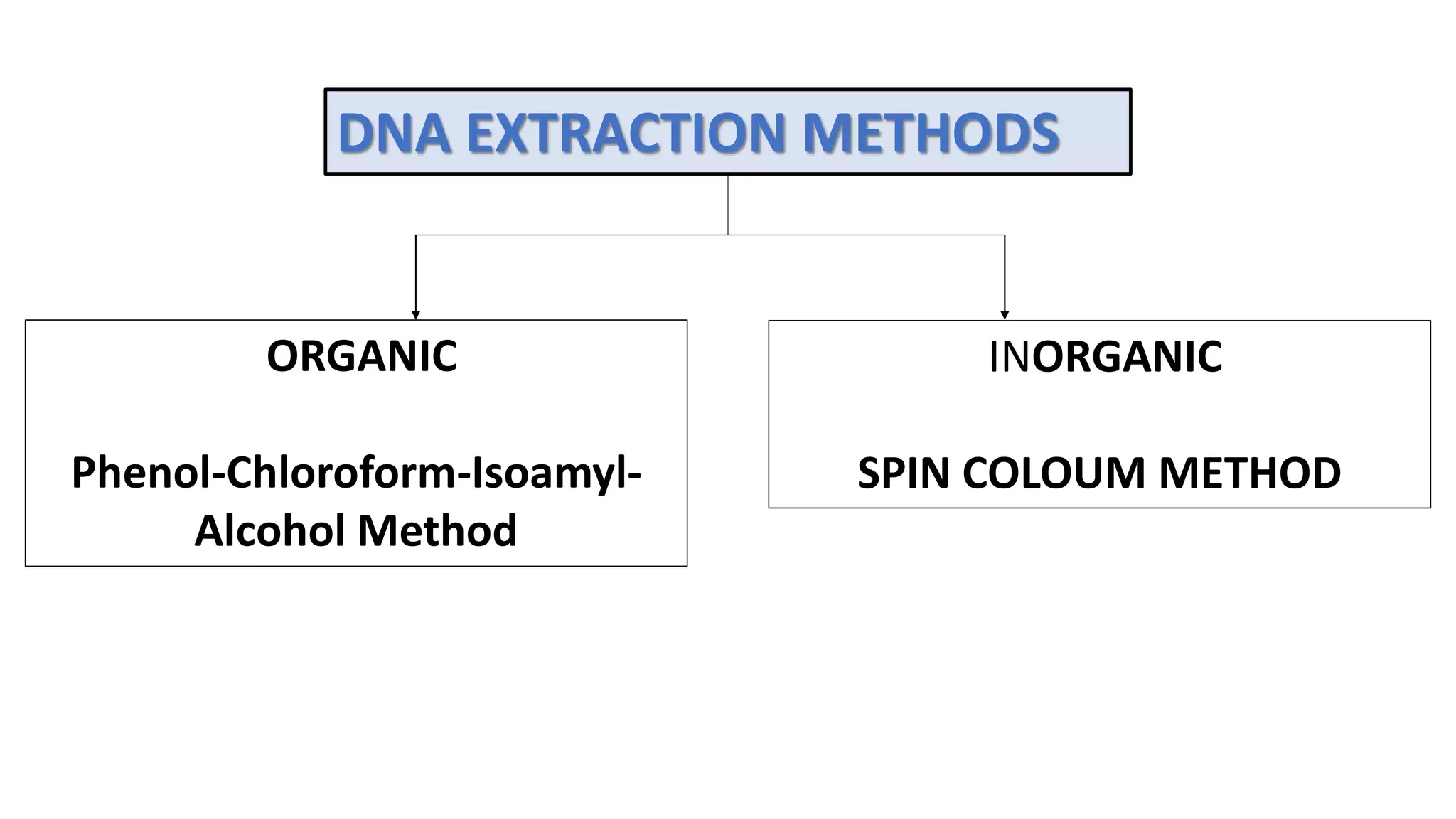
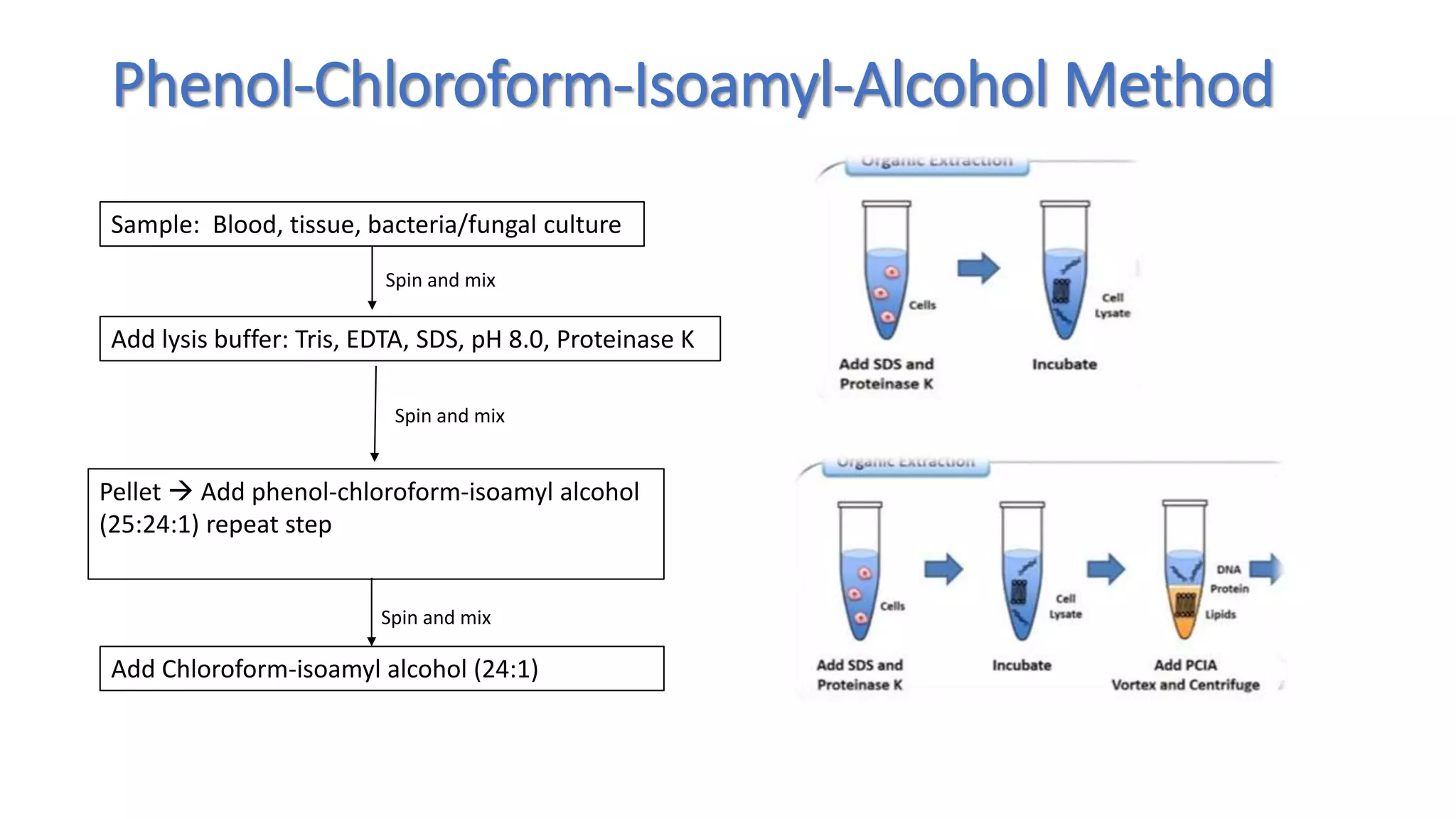
This document discusses nucleic acid extraction and purification methods. It outlines the organic phenol-chloroform-isoamyl alcohol extraction method. This method involves lysing the sample with Tris, EDTA, SDS, and proteinase K. Phenol-chloroform-isoamyl alcohol is added to separate the DNA into aqueous and organic layers. The DNA is then precipitated with sodium acetate and ethanol or isopropanol before being stored. The document also mentions inorganic spin column extraction and assessing DNA yield and purity.


![Purpose of NA Isolation?
Good yield [ ] of DNA
Good quality/pure free from
contamination](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nucleicacidextractionandpurification2023-230929211530-f04956db/75/NUCLEIC-ACID-EXTRACTION-AND-PURIFICATION-2023-pptx-3-2048.jpg)