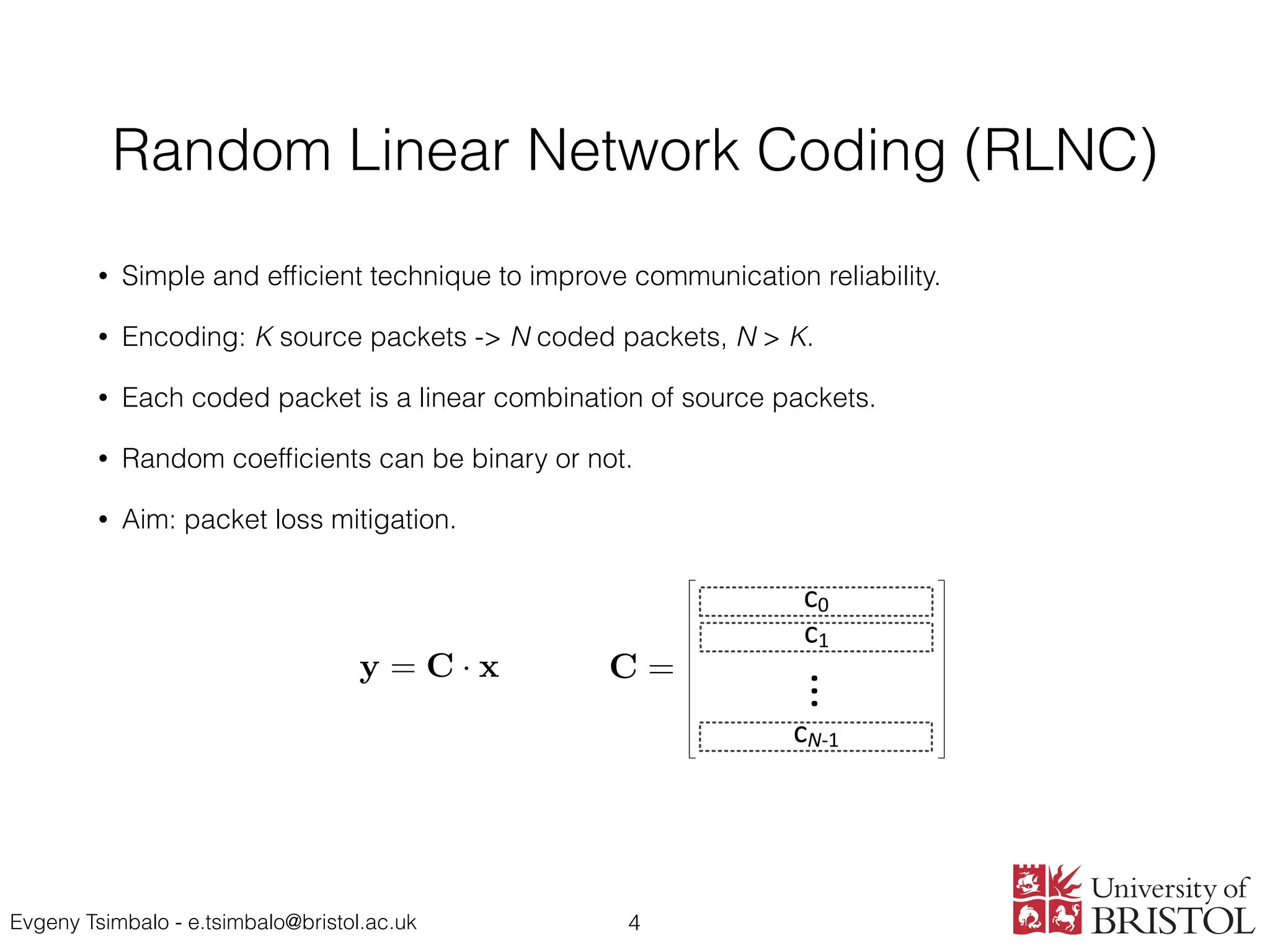
This document proposes a theoretical framework for analyzing the probability of successful decoding in single-relay networks using network coding. It defines key terms like random linear network coding and presents two theorems:
1) The probability that two randomly generated coding matrices at a source and relay are simultaneously full rank is given by a formula involving the dimensions and number of common rows of the matrices.
2) The probability of successful decoding at two destinations in a network defined by certain parameters is calculated as the sum of probabilities involving the coding matrices and dimensions at each stage of transmission through the source, relay, and destinations.
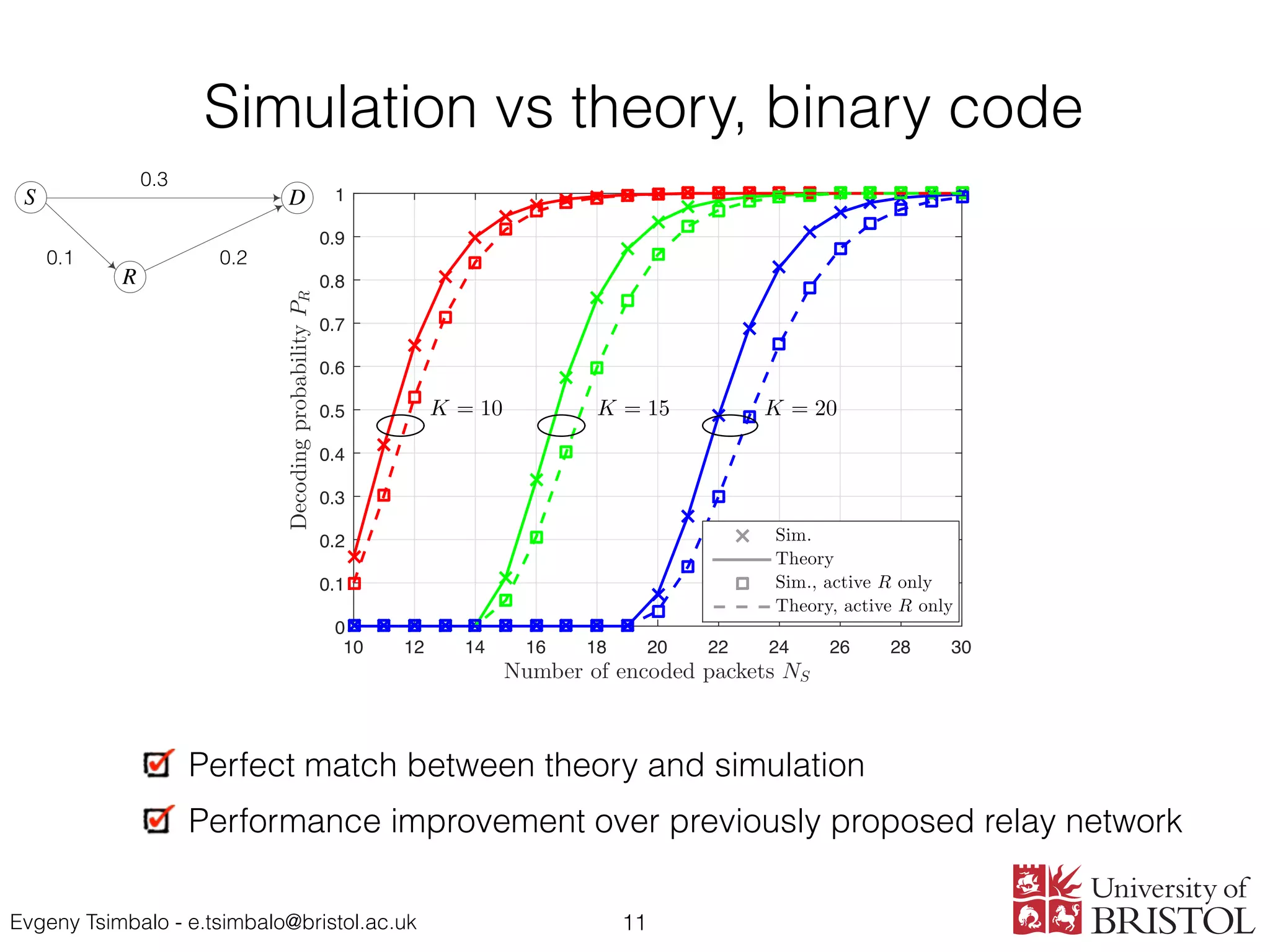
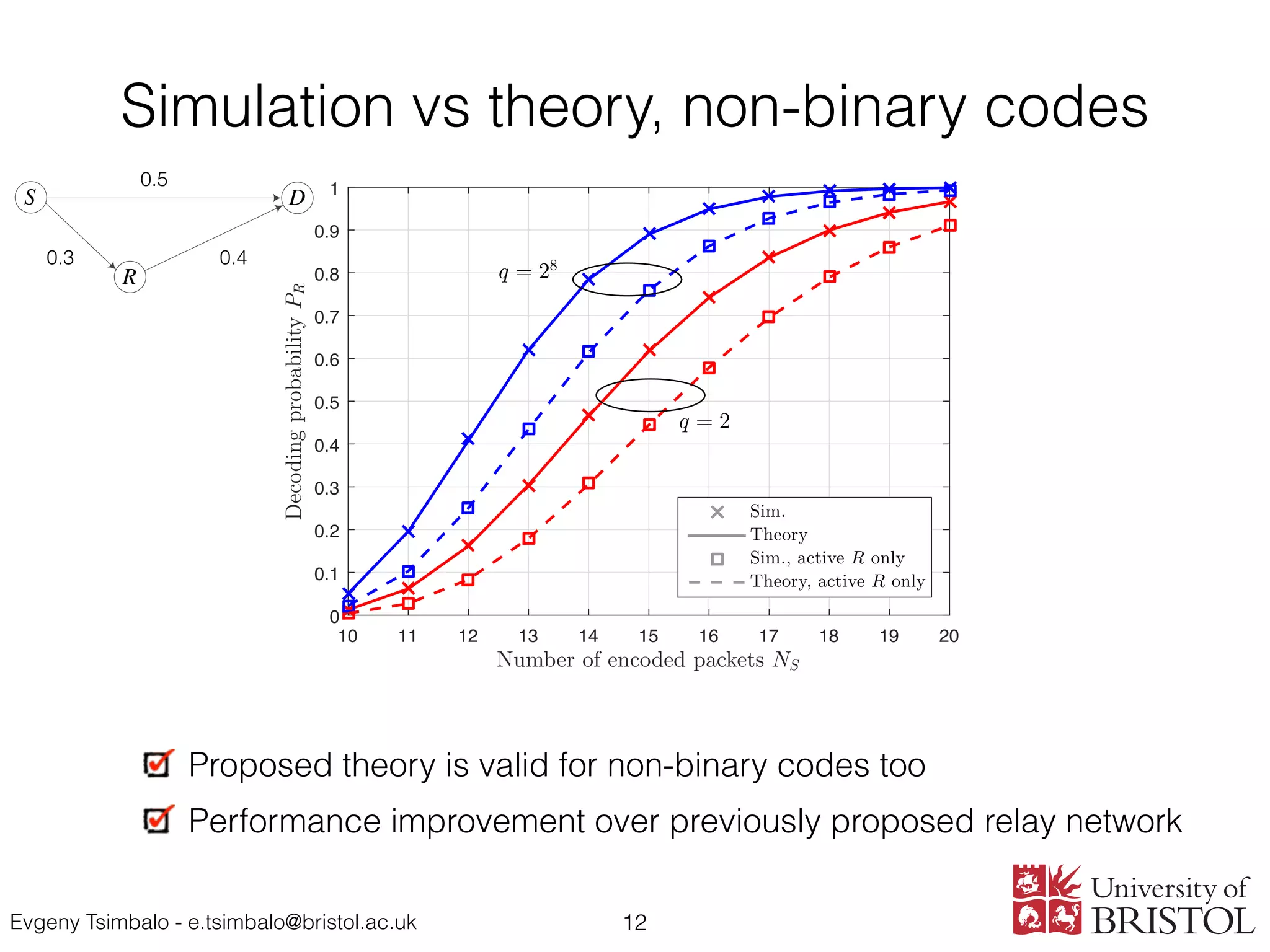
Numerical results are presented to validate the theoretical analysis.



![Evgeny Tsimbalo - e.tsimbalo@bristol.ac.uk
RLNC: point-to-point link
• Matrix should be invertible, i.e., full rank.
• What is the probability of successful decoding, given N, K and p?
5
c0
c1
cN-1
...
S D
p
latter are stacked together
ding matrix CR at the relay
atrix CD at the destination
the same packets from S,
ows. Let MRD denote the
t this point, the destination
to make its coding matrix
ecode the original message
d if the relay coding matrix
the original K packets and
erated random coefficients
d transmits them to D. In
case the active relay mode.
e source packets, it simply
he destination node, which
mode. In either mode, we
ng vectors reached D from
+ M0
D ⇥ K coding matrix
is different from the one
in the latter the relay node
ckets from the source node.
hould improve the decoding
fails to decode. In addition,
sis can be straightforwardly
ple sources, in which each
P(m, k) =
k 1Y
i=0
(1 qi m
). (5)
Furthermore, following the same train of thought used to
obtain (2) in the binary case, the probability (4) can be
generalized to the non-binary case as follows:
Pr(m, k) = q mk
G(m, k, r) (6)
=
1
q(m r)(k r)
r 1Y
i=0
(1 qi m
)(1 qi k
)
1 qi r
.
Consider now the application of RLNC to a point-to-
point link, with a source node encoding K source packets
and transmitting N coded packets to the destination. The
probability of successful decoding for such link characterized
by the PEP p can be given by [11]
Pptp(N, K, p) =
NX
M=K
B(M, N, p)P(M, K), (7)
where B(M, N, p) is the probability mass function (PMF) of
the binomial distribution:
B(M, N, p) =
✓
N
M
◆
(1 p)M
pN M
. (8)
In addition to the binomial distribution, we will also need
its generalized version - the multinomial distribution [14].
The PMF of such distribution describes the probability of
P(M, K) =
K 1Y
i=0
(1 qi M
).
Pr(M, K) = q MK
G(M, K, r)
=
1
q(M r)(K r)
r 1Y
i=0
(1 qi M
)(1 qi K
)
1 qi r
.
Pptp(N, K, p) =
NX
B(M, N, p)P(M, K),
y = C · x
r = ˜C · x
) x = ˜C 1
· r
C =
y = C · x
r = ˜C · x
) x = ˜C 1
· r
C =
y = C · x
r = ˜C · x
) x = ˜C 1
· r
C =
B⇤
(M, N, p) =
N
M12
N M12
M1 M12
N M1
M2 M12
·(1 p1)M1
pN M1
1
·(1 p2)M2
pN M2
2 (8)
and the summation is performed over the following values:
{ M 1 , M2 = K, . . . , N; M12 = max(0, M1 + M2 N), . . . , min(M1, M2). (9)
y = C · x
r = ˜C · x
1
Small letters in some equations were replaced with capitals, to make them
consistent and more understandable on the slides.
P(M, K) =
K 1Y
i=0
(1 qi M
). (1)
Pr(M, K) = q MK
G(M, K, r) (2)
=
1
q(M r)(K r)
r 1Y
i=0
(1 qi M
)(1 qi K
)
1 qi r
.
Pptp(N, K, p) =
NX
M=K
B(M, N, p)P(M, K) (3)
B(M, N, p) =
✓
N
M
◆
(1 p)M
pN M
. (4)
y = C · x
r = ˜C · x
) x = ˜C 1
· r
C =
all letters in some equations were replaced with capitals, to make them consistent and more understandable o
Pr[˜C is f.r.] =
X
M
Pr[M pkts rxd] Pr[˜C is f.r. | M pkts rxd]
P(M, K) =
K 1Y
i=0
(1 qi M
).
Pr(M, K) = q MK
G(M, K, r)
=
1
q(M r)(K r)
r 1Y
i=0
(1 qi M
)(1 qi K
)
1 qi r
.
NX](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/globecomslidesetsimbalo-170104092529/75/Novel-Performance-Analysis-of-Network-Coded-Communications-in-Single-Relay-Networks-5-2048.jpg)

![Evgeny Tsimbalo - e.tsimbalo@bristol.ac.uk
Preliminaries: multicast network
7
......
......
M12
M1
M2
D1
S
D2
p1 p2
P(M, K) =
K 1Y
i=0
(1 qi M
).
Pr(M, K) = q MK
G(M, K, r)
=
1
q(M r)(K r)
r 1Y
i=0
(1 qi M
)(1 qi K
)
1 qi r
.
Pptp(N, K, p) =
NX
M=K
B(M, N, p)P(M, K),
B(M, N, p) =
✓
N
M
◆
(1 p)M
pN M
.
X1 X2
GF(q) M1 ⇥ k M2 ⇥ K M1, M2 k M12
P⇤
(M, K) =
X
i
Pi(M12, k)P(M1 M12, K i)
· P(M2 M12, k i),
M = (M1, M2, M12)
i max(0, K M1 + M12, K M2 + M12) min(M12, K)
N, K p
PM (N, K, p) =
X
M
B⇤
(M, N, p)P⇤
(M, K),
B⇤
(M, N, p) =
✓
N
◆✓
N M12
◆✓
N M1
◆
Small letters in some equations were replaced with capitals, to make them
consistent and more understandable on the slides.
P(M, K) =
K 1Y
i=0
(1 qi M
). (1)
Pr(M, K) = q MK
G(M, K, r) (2)
=
1
q(M r)(K r)
r 1Y
i=0
(1 qi M
)(1 qi K
)
1 qi r
.
Pptp(N, K, p) =
NX
M=K
B(M, N, p)P(M, K) (3)
B(M, N, p) =
✓
N
M
◆
(1 p)M
pN M
. (4)
Theorem 1. The probability of two random matrices X1 and X2 generated over
GF(q) with dimensions M1 ⇥ k and M2 ⇥ K, M1, M2 k, and M12 common
rows being simultaneously full rank is given by
P⇤
(M, K) =
X
i
Pi(M12, K)P(M1 M12, K i)P(M2 M12, K i) (5)
where M = (M1, M2, M12) and the summation is performed over the values of
i from max(0, K M1 + M12, K M2 + M12) to min(M12, K).
Theorem 2. The probability of successful decoding for a two-destination mul-
ticast network defined by parameters N, K and p is given by
PM (N, K, p) =
X
M
B⇤
(M, N, p)P⇤
(M, K), (6)
where
✓ ◆✓ ◆✓ ◆
Pr(M, K) = q G(M, K, r) (2)
=
1
q(M r)(K r)
r 1Y
i=0
(1 qi M
)(1 qi K
)
1 qi r
.
Pptp(N, K, p) =
NX
M=K
B(M, N, p)P(M, K) (3)
B(M, N, p) =
✓
N
M
◆
(1 p)M
pN M
. (4)
Theorem 1. The probability of two random matrices X1 and X2 generated over
GF(q) with dimensions M1 ⇥ k and M2 ⇥ K, M1, M2 k, and M12 common
rows being simultaneously full rank is given by
P⇤
(M, K) =
X
i
Pi(M12, K)P(M1 M12, K i)P(M2 M12, K i) (5)
where M = (M1, M2, M12) and the summation is performed over the values of
i from max(0, K M1 + M12, K M2 + M12) to min(M12, K).
Theorem 2. The probability of successful decoding for a two-destination mul-
ticast network defined by parameters N, K and p is given by
PM (N, K, p) =
X
M
B⇤
(M, N, p)P⇤
(M, K), (6)
where
B⇤
(M, N, p) =
✓
N
M12
◆✓
N M12
M1 M12
◆✓
N M1
M2 M12
◆
(1 p1)M1
pN M1
1 (1 p2)M2
pN M2
2
and the summation is performed over the following values:
{ M 1 , M2 = K, . . . , N; M12 = max(0, M1 + M2 N), . . . , min(M1, M2). (7)
y = C · x
What is the
probability of
successful
decoding?
y = C · x
r = ˜C · x
) x = ˜C 1
· r
C =
⌦
NS, K, pSD) =
NX
M=K
B(M, NS, pSD)P(M, K) (8)
, p)
NRX
M0
D=1
B(M0
D, NR, pRD) [P⇤
(M0
, K) P⇤
(M, K)]
M0
R, pRD)[P(MD + M0
D, K) P(MD, K) P⇤
(M00
, K) + P⇤
(M, K)]
PR = PR,1 + PR,2 + PR,3 (9)
Pr[˜C1, ˜C2 are f.r. | M] :
Pr[M] :
1
1 2 1 2
y = C · x
r = ˜C · x
) x = ˜C 1
· r
C =
⌦
SD) =
NX
M=K
B(M, NS, pSD)P(M, K) (8)
X
=1
B(M0
D, NR, pRD) [P⇤
(M0
, K) P⇤
(M, K)]
RD)[P(MD + M0
D, K) P(MD, K) P⇤
(M00
, K) + P⇤
(M, K)]
PR,1 + PR,2 + PR,3 (9)
˜C1, ˜C2 are f.r. | M] :
Pr[M] :
1
PR,1 = Pptp(NS, K, pSD) =
NX
M=K
B(M, NS, pSD)P(M, K)
PR,2 =
X
M
B⇤
(M, NS, p)
NRX
M0
D=1
B(M0
D, NR, pRD) [P⇤
(M0
, K) P⇤
(M, K)]
M, NS, p)
M0
RX
M0
D=1
B(M0
D, M0
R, pRD)[P(MD + M0
D, K) P(MD, K) P⇤
(M00
, K) + P⇤
(M, K)]
PR = PR,1 + PR,2 + PR,3
Pr[˜C1, ˜C2 are f.r. | M] :
Pr[M] :
1
PR,1 = Pptp(NS, K, pSD) =
NX
M=K
B(M, NS, pSD)P(M, K
PR,2 =
X
M
B⇤
(M, NS, p)
NRX
M0
D=1
B(M0
D, NR, pRD) [P⇤
(M0
, K) P
PR,3 =
X
M
B⇤
(M, NS, p)
M0
RX
M0
D=1
B(M0
D, M0
R, pRD)[P(MD + M0
D, K) P(MD, K)
PR = PR,1 + PR,2 + PR,3
Pr[˜C1, ˜C2 are f.r. | M] :
Pr[M] :
1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/globecomslidesetsimbalo-170104092529/75/Novel-Performance-Analysis-of-Network-Coded-Communications-in-Single-Relay-Networks-7-2048.jpg)
![Evgeny Tsimbalo - e.tsimbalo@bristol.ac.uk
Relay network
• Stage 1: S transmits, R & D receive.
• If D can decode, success!
• If not:
• Stage 2: R attempts decoding and transmits to D.
• If R can decode, it re-encodes prior to
transmission;
• If R can’t decode, it just relays packets to D.
• Previous work [1]: active relay only.
8
pSD
S
R
D
pSR pRD
active relay
passive relay
What is the probability of
successful decoding at D?
[1] A. S. Khan and I. Chatzigeorgiou, “Performance Analysis of Random Linear Network Coding in Two-Source
Single-Relay Networks,” in Proc. of IEEE ICC 2015, (London, United Kingdom, UK), pp. 991–996, June 2015.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/globecomslidesetsimbalo-170104092529/75/Novel-Performance-Analysis-of-Network-Coded-Communications-in-Single-Relay-Networks-8-2048.jpg)
![Evgeny Tsimbalo - e.tsimbalo@bristol.ac.uk
Relay network
9
D decodes
directly from S
Active relay
Passive relay
pSD
S
R
D
pSR pRD
:
M
B⇤
(M, N, p) =
✓
N
M12
◆✓
N M12
M1 M12
◆✓
N M1
M2 M12
◆
(1 p1)M1
pN M1
1 (1 p2)M2
pN M2
2
ation is performed over the following values:
{ M 1 , M2 = K, . . . , N; M12 = max(0, M1 + M2 N), . . . , min(M1, M2). (7)
y = C · x
r = ˜C · x
) x = ˜C 1
· r
C =
PR,1 = Pptp(NS, K, pSD) =
NX
M=K
B(M, NS, pSD)P(M, K) (8)
PR,2 =
X
M
B⇤
(M, NS, p)
NRX
M0
D=1
B(M0
D, NR, pRD) [P⇤
(M0
, K) P⇤
(M, K)]
3 =
X
M
B⇤
(M, NS, p)
M0
RX
M0
D=1
B(M0
D, M0
R, pRD)[P(MD + M0
D, K) P(MD, K) P⇤
(M00
, K) + P⇤
(M, K)]
PR = PR,1 + PR,2 + PR,3 (9)
:
M
M
e
B⇤
(M, N, p) =
✓
N
M12
◆✓
N M12
M1 M12
◆✓
N M1
M2 M12
◆
(1 p1)M1
pN M1
1 (1 p2)M2
pN M2
2
he summation is performed over the following values:
{ M 1 , M2 = K, . . . , N; M12 = max(0, M1 + M2 N), . . . , min(M1, M2). (7)
y = C · x
r = ˜C · x
) x = ˜C 1
· r
C =
PR,1 = Pptp(NS, K, pSD) =
NX
M=K
B(M, NS, pSD)P(M, K) (8)
PR,2 =
X
M
B⇤
(M, NS, p)
NRX
M0
D=1
B(M0
D, NR, pRD) [P⇤
(M0
, K) P⇤
(M, K)]
PR,3 =
X
M
B⇤
(M, NS, p)
M0
RX
M0
D=1
B(M0
D, M0
R, pRD)[P(MD + M0
D, K) P(MD, K) P⇤
(M00
, K) + P⇤
(M, K)]
PR = PR,1 + PR,2 + PR,3 (9)
:
M
where
B⇤
(M, N, p) =
✓
N
M12
◆✓
N M12
M1 M12
◆✓
N M1
M2 M12
◆
(1 p1)M1
pN M1
1 (1 p2)M2
pN M2
2
and the summation is performed over the following values:
{ M 1 , M2 = K, . . . , N; M12 = max(0, M1 + M2 N), . . . , min(M1, M2).
y = C · x
r = ˜C · x
) x = ˜C 1
· r
C =
PR,1 = Pptp(NS, K, pSD) =
NX
M=K
B(M, NS, pSD)P(M, K)
PR,2 =
X
M
B⇤
(M, NS, p)
NRX
M0
D=1
B(M0
D, NR, pRD) [P⇤
(M0
, K) P⇤
(M, K)]
PR,3 =
X
M
B⇤
(M, NS, p)
M0
RX
M0
D=1
B(M0
D, M0
R, pRD)[P(MD + M0
D, K) P(MD, K) P⇤
(M00
, K) + P⇤
(M, K)]
PR = PR,1 + PR,2 + PR,3
1
{ M 1 , M2 = K, . . . , N; M12 = max(0, M1 + M2 N), . . . , min(M1, M2).
y = C · x
r = ˜C · x
) x = ˜C 1
· r
C =
PR,1 = Pptp(NS, K, pSD) =
NX
M=K
B(M, NS, pSD)P(M, K)
PR,2 =
X
M
B⇤
(M, NS, p)
NRX
M0
D=1
B(M0
D, NR, pRD) [P⇤
(M0
, K) P⇤
(M, K)]
X
M
B⇤
(M, NS, p)
M0
RX
M0
D=1
B(M0
D, M0
R, pRD)[P(MD + M0
D, K) P(MD, K) P⇤
(M00
, K) + P⇤
(M, K
PR = PR,1 + PR,2 + PR,3
Relay can decode
D
R
R
R
M12 = max(0, M1 + M2 N),
y = C · x
r = ˜C · x
) x = ˜C 1
·
C =
⌦
PR,1 = Pptp(NS, K, pSD) =
NX
M=K
B
PR,2 =
X
M
B⇤
(M, NS, p)
NRX
M0
D=1
B(M0
D, NR,
X M0
RX
All possible
outcomes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/globecomslidesetsimbalo-170104092529/75/Novel-Performance-Analysis-of-Network-Coded-Communications-in-Single-Relay-Networks-9-2048.jpg)