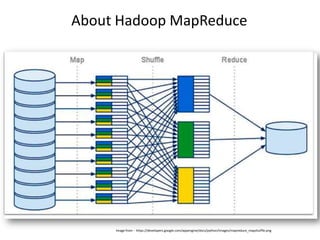
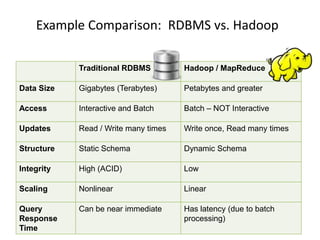
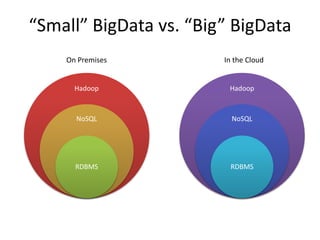
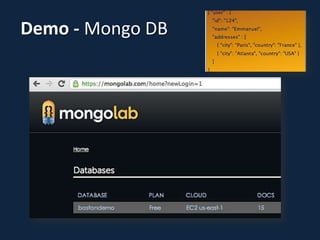
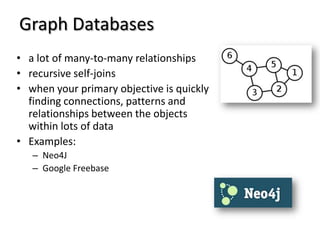
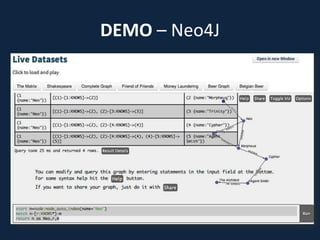
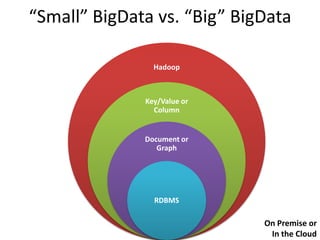
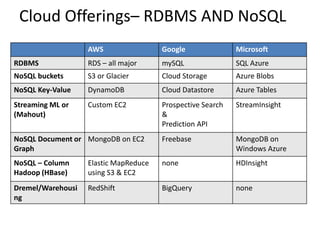
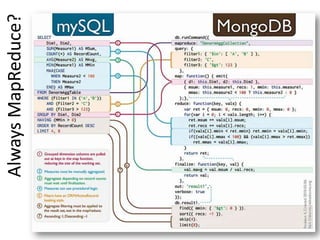
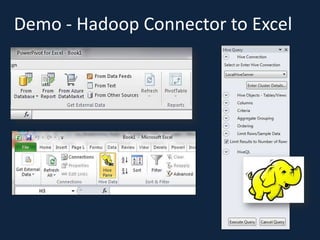
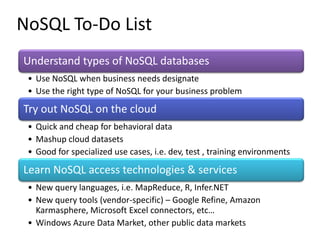
This document discusses database choices and provides an overview of different database technologies including relational databases, NoSQL databases, and Hadoop. It highlights key-value, columnar, document, and graph NoSQL databases and provides demos of technologies like DynamoDB, MongoDB, Neo4j, and Hadoop. The document also discusses using these database options on premises or in the cloud with providers like AWS, Google, and Microsoft and how to query data from NoSQL databases.














![• recipes)
www.TeachingKidsProgramming.org
•
•
Free Courseware (Java, Small Basic or C# [on Pluralsight])
Do a Recipe Teach a Kid (Ages 10 ++)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jan2014databasechoicesnosql-140118174701-phpapp02/85/Not-only-SQL-Database-Choices-44-320.jpg)