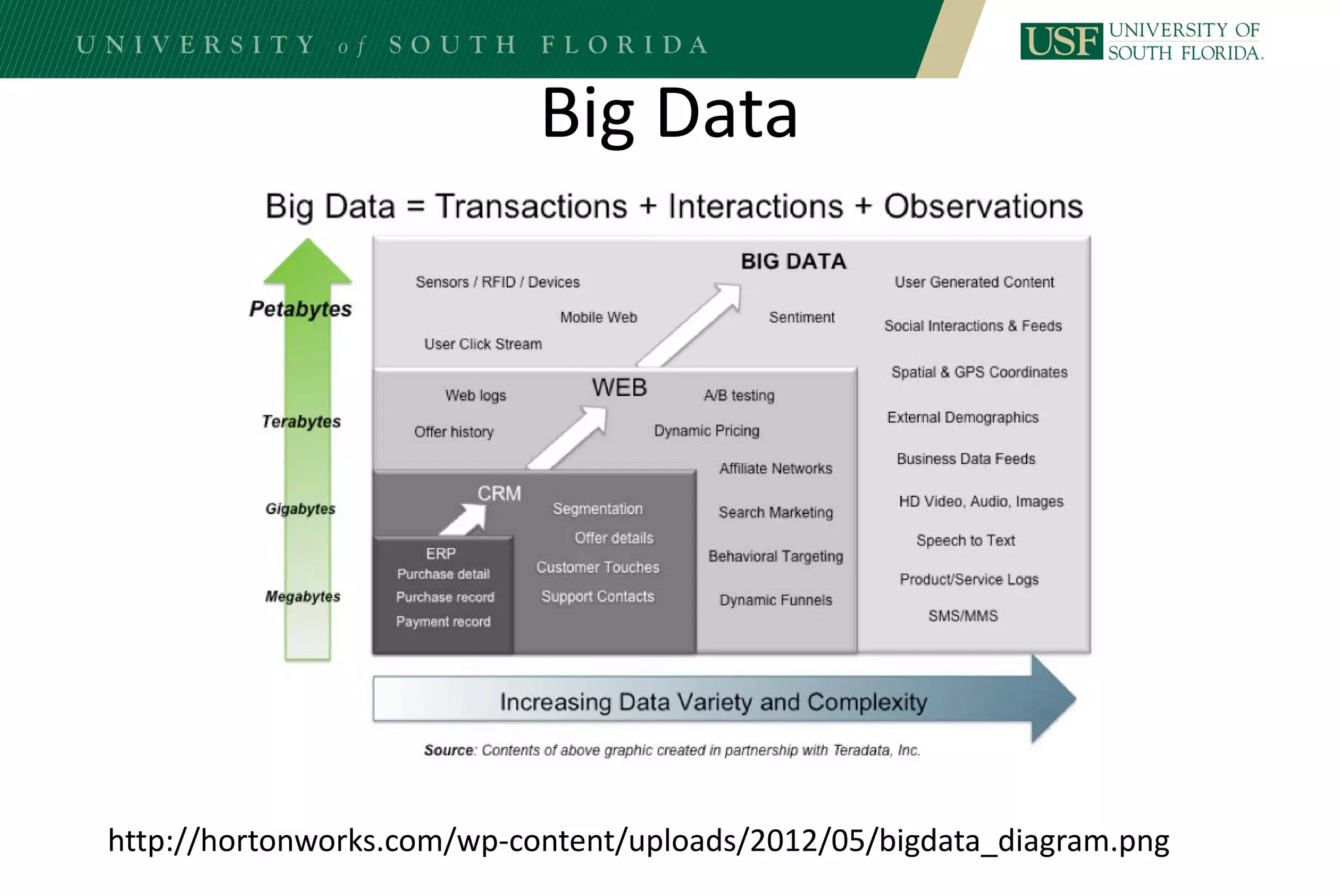
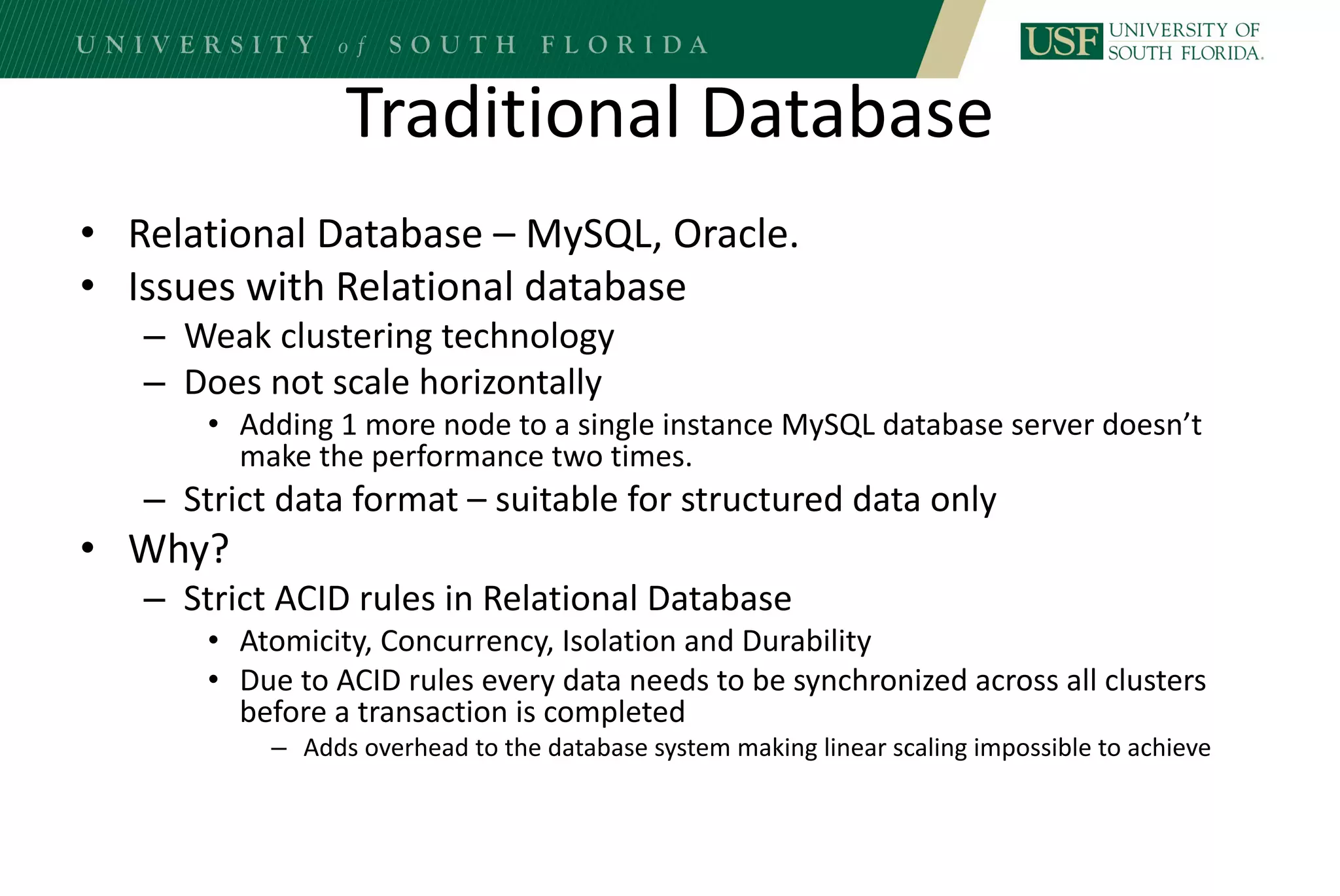
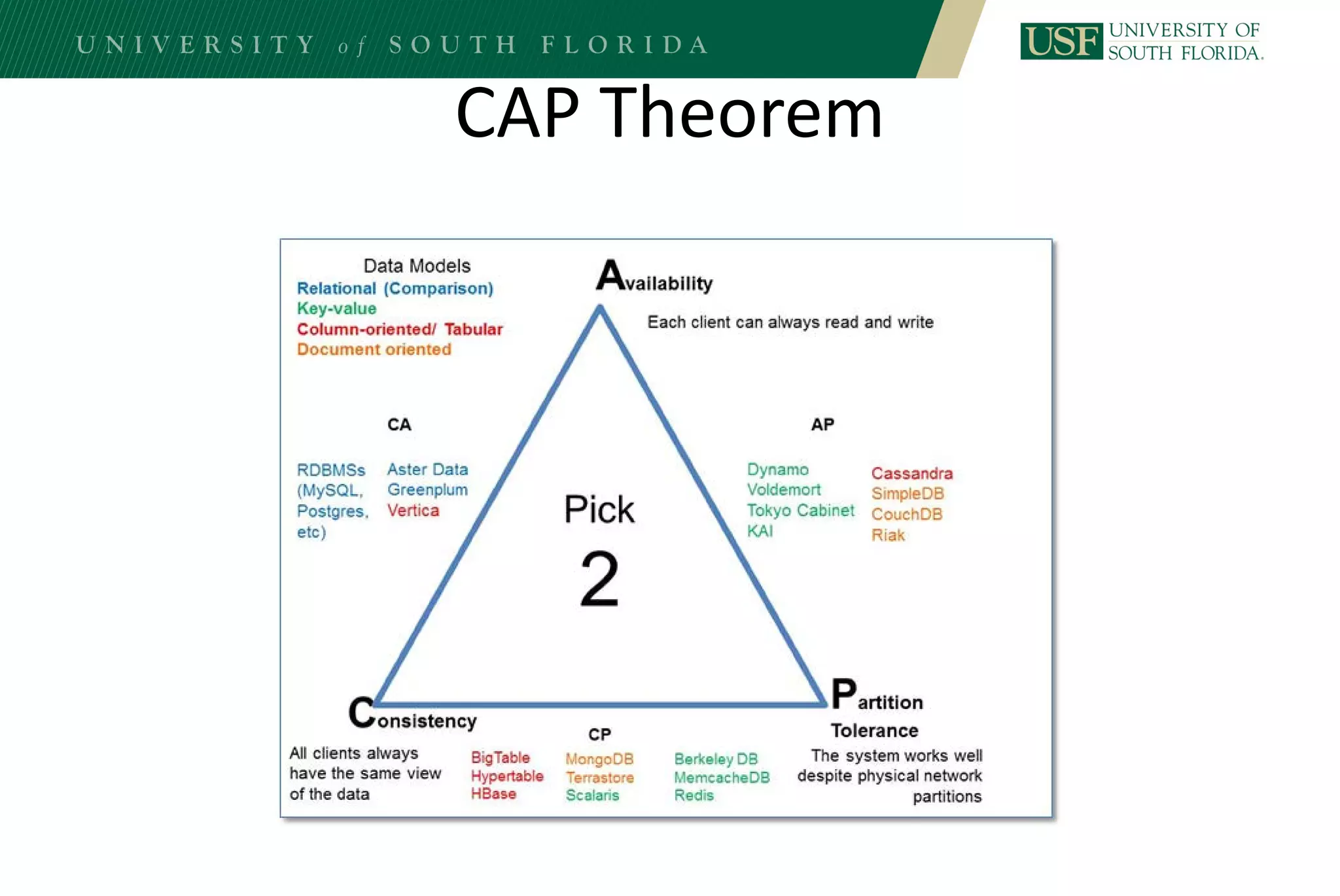
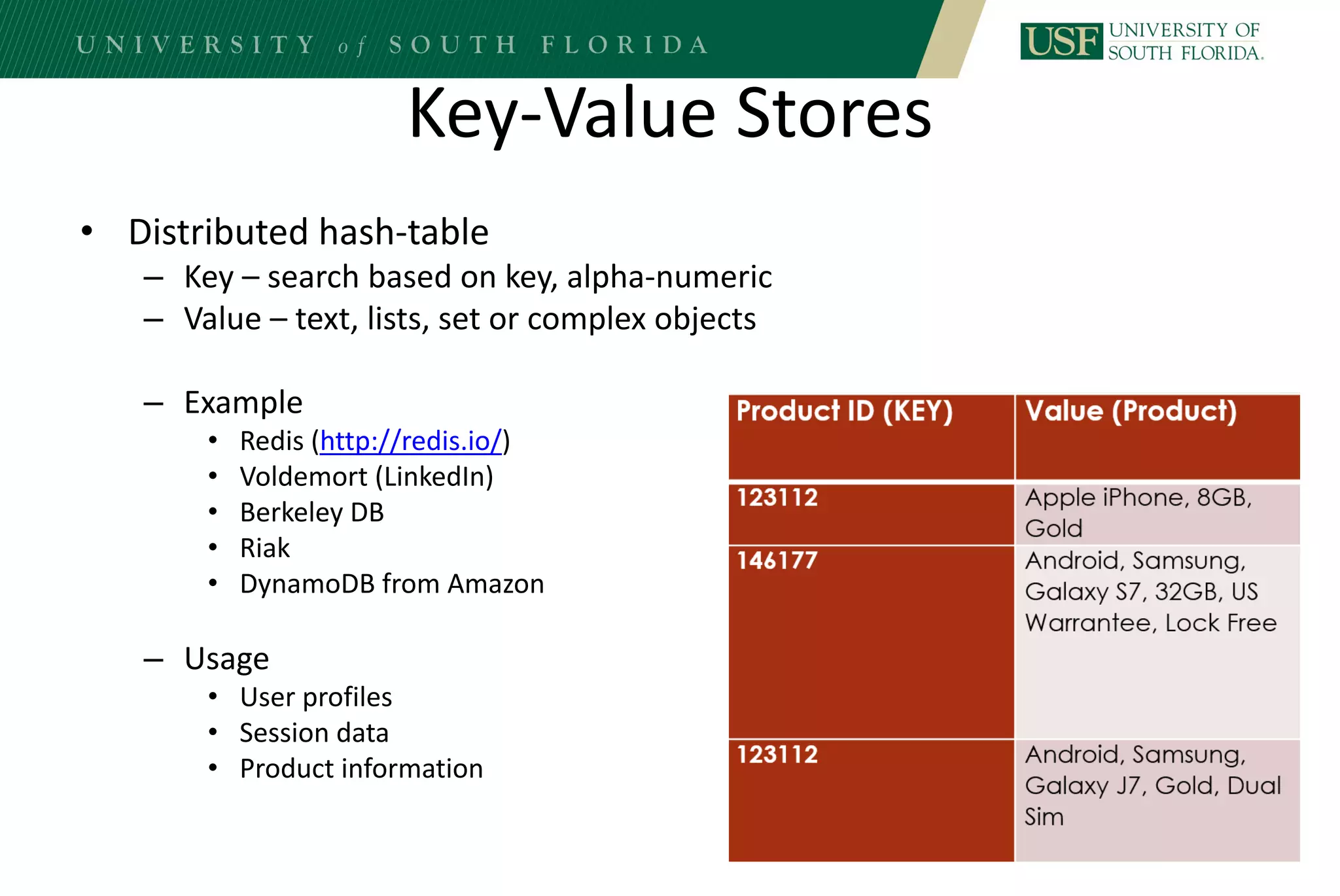
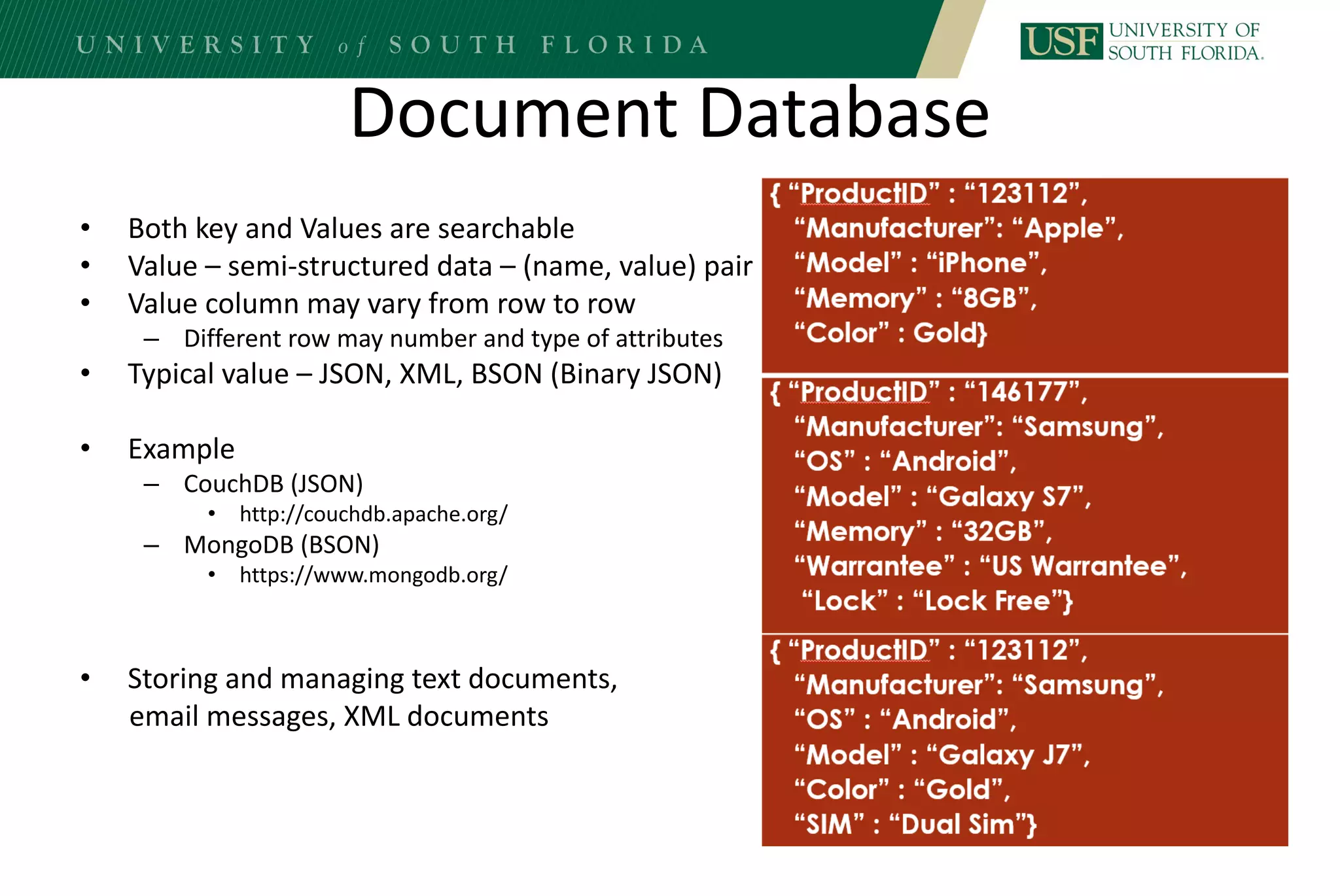
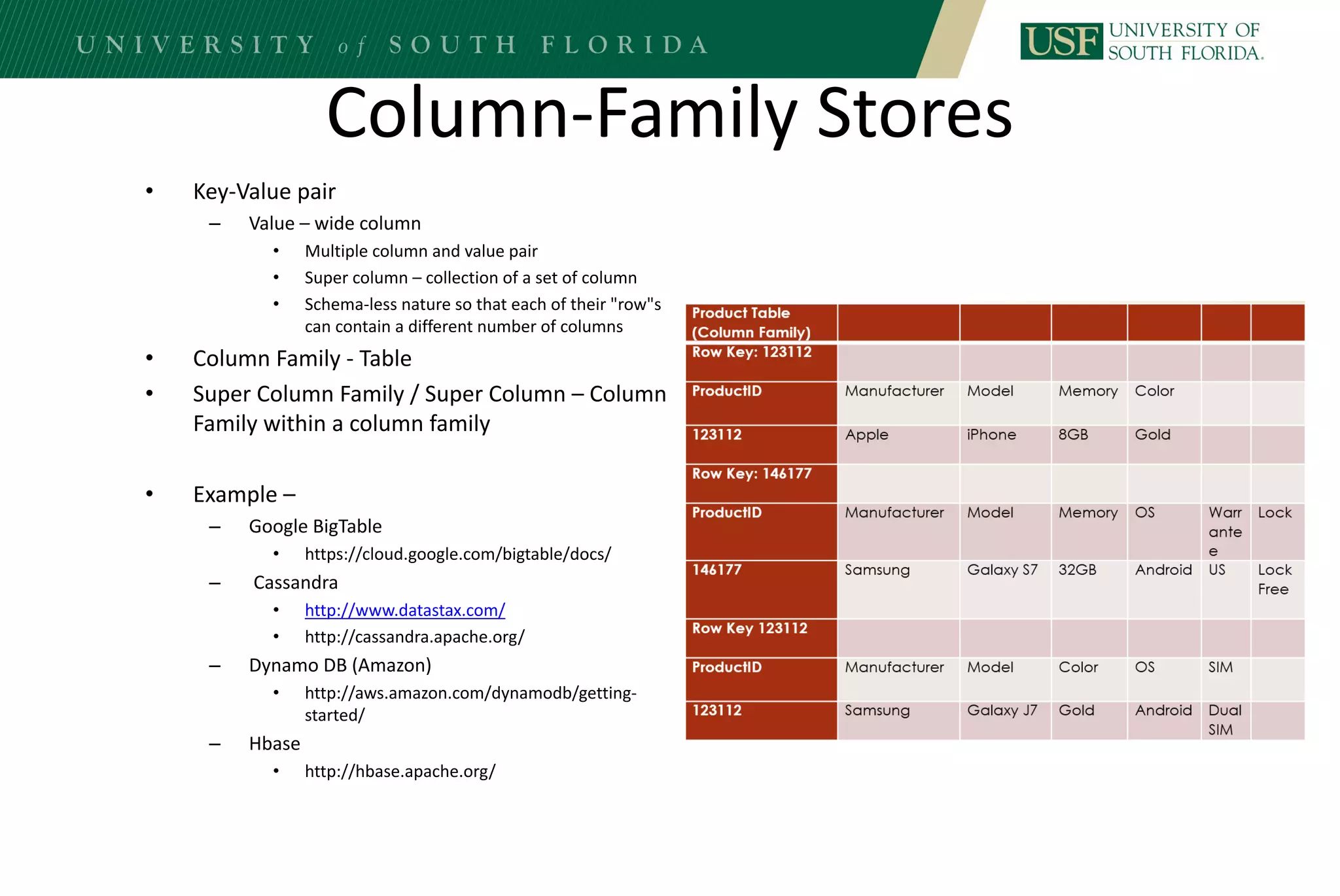
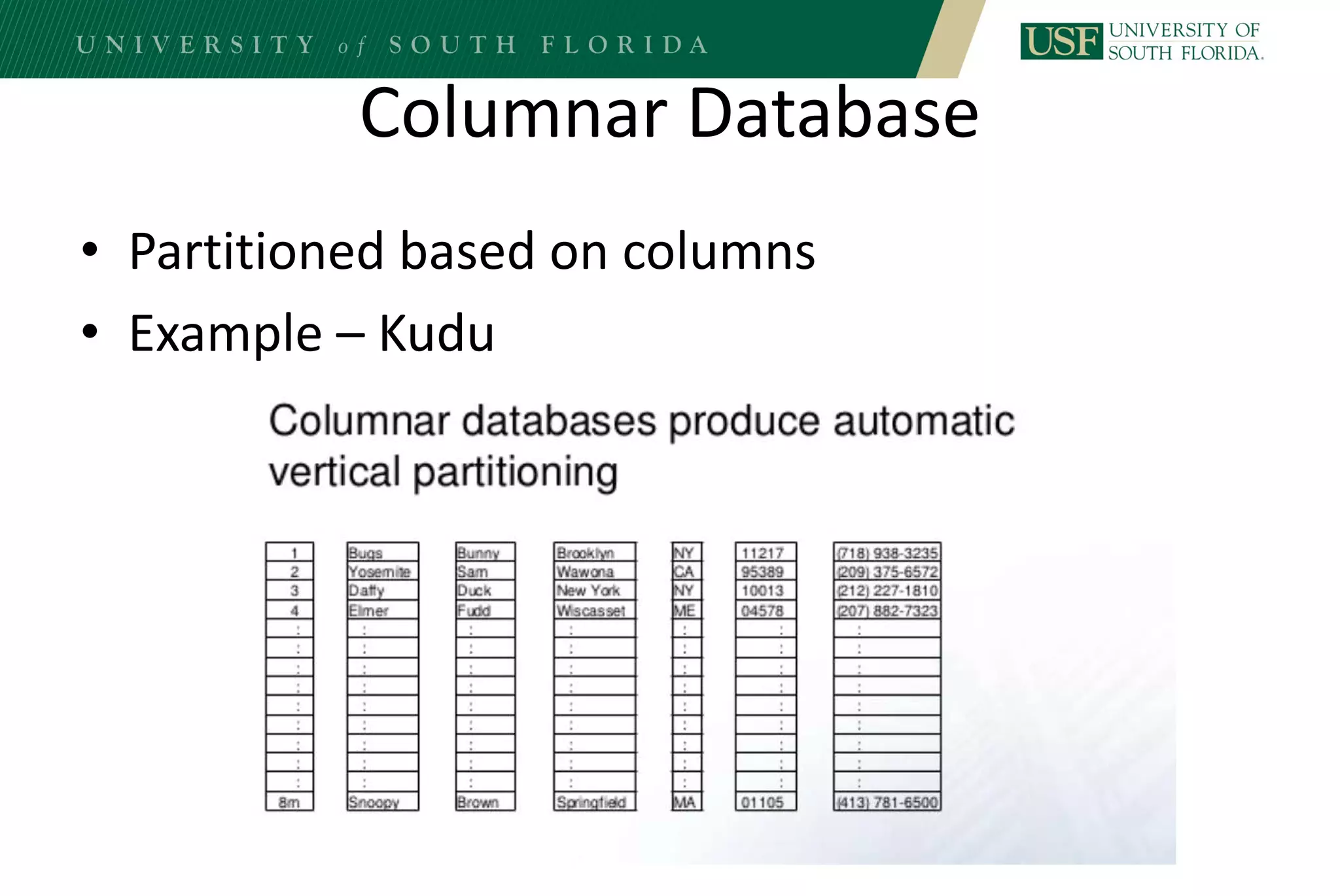
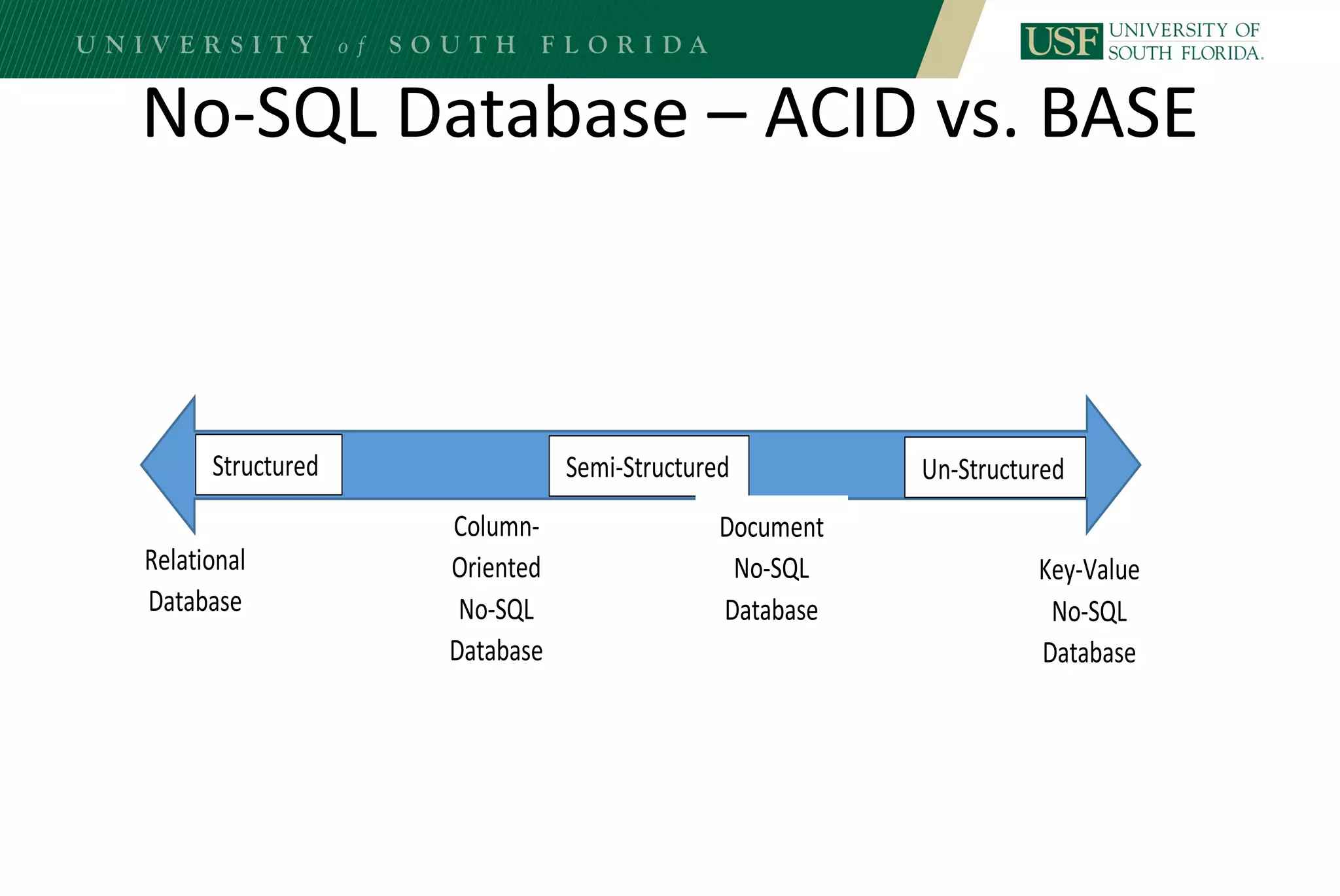
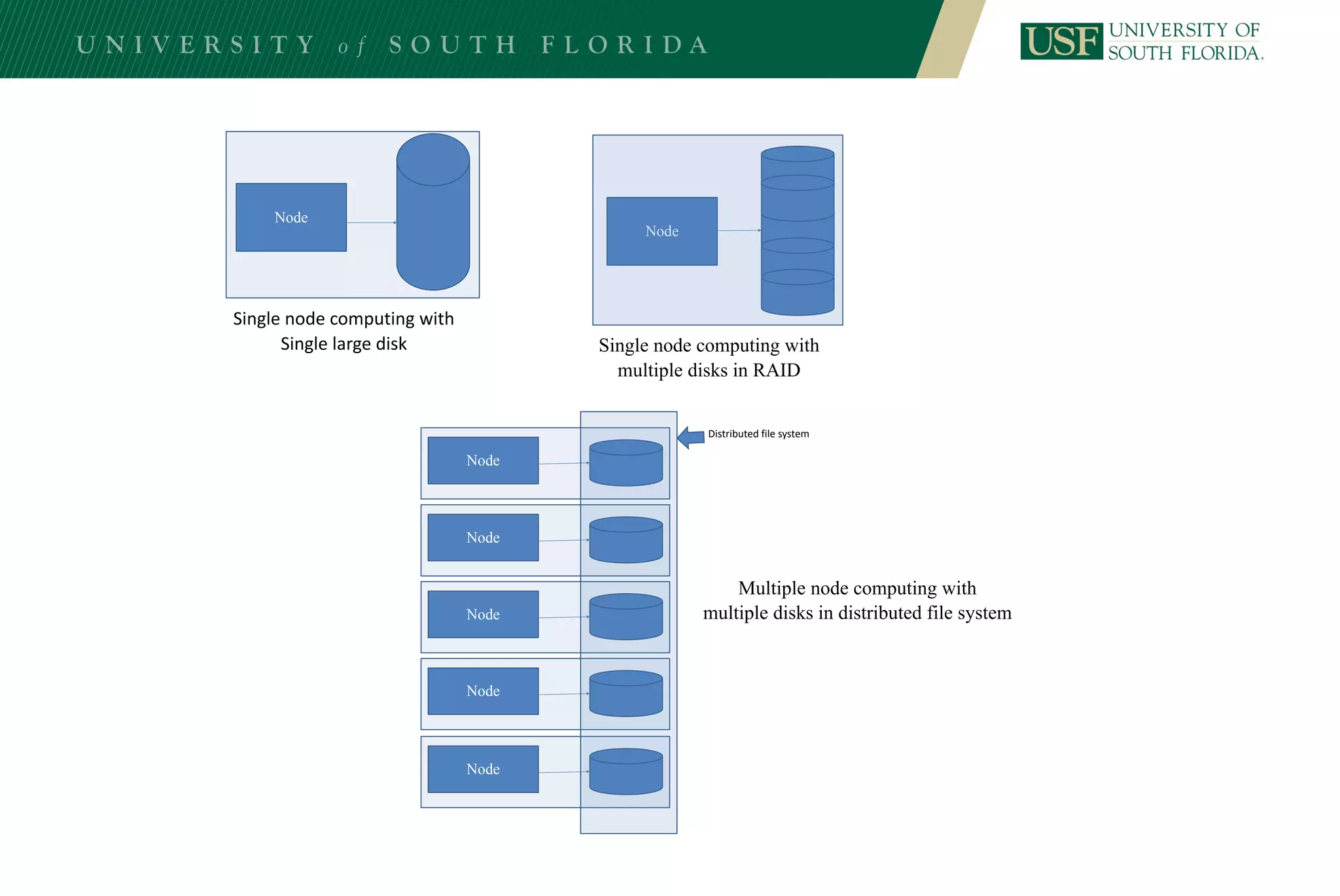
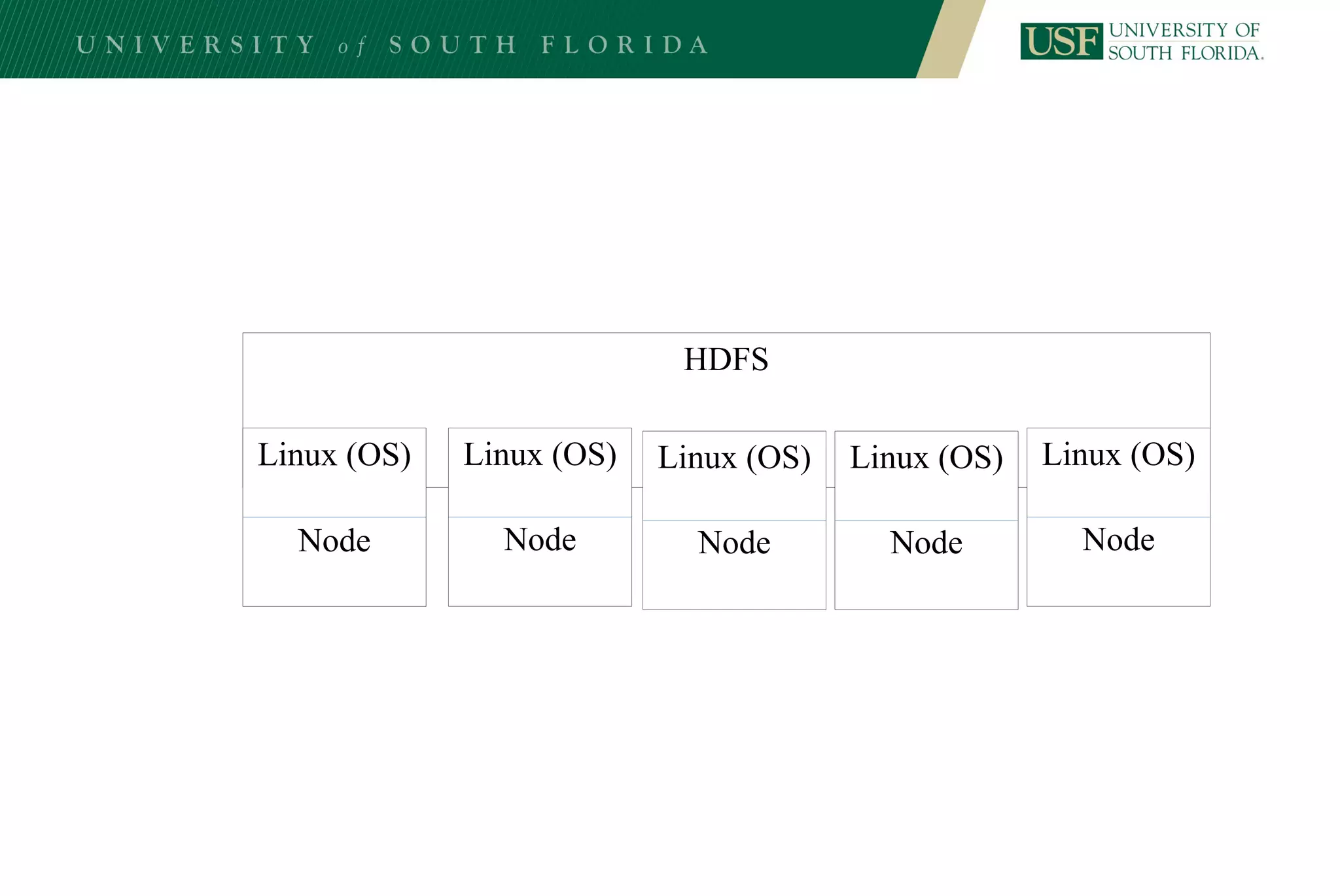
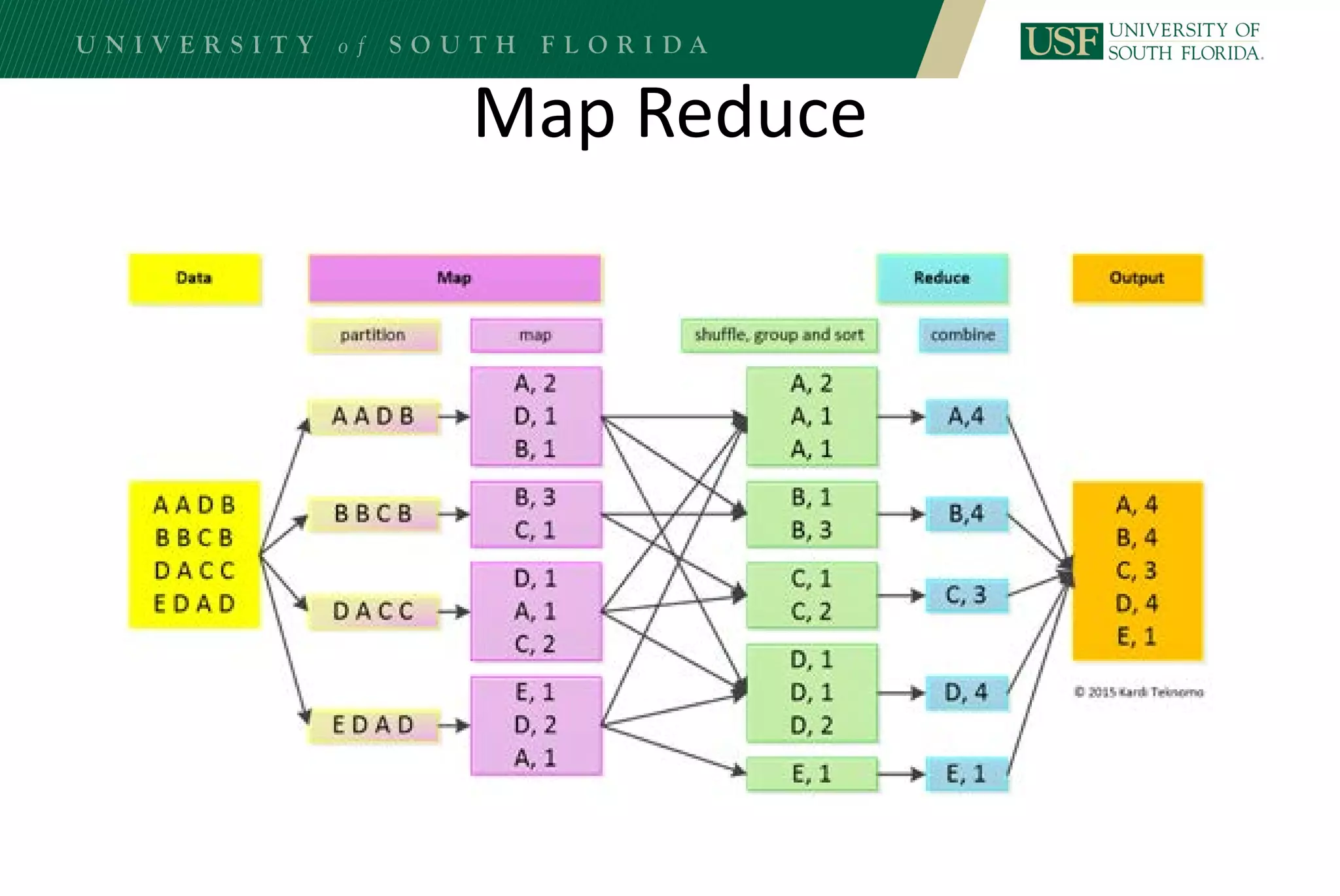
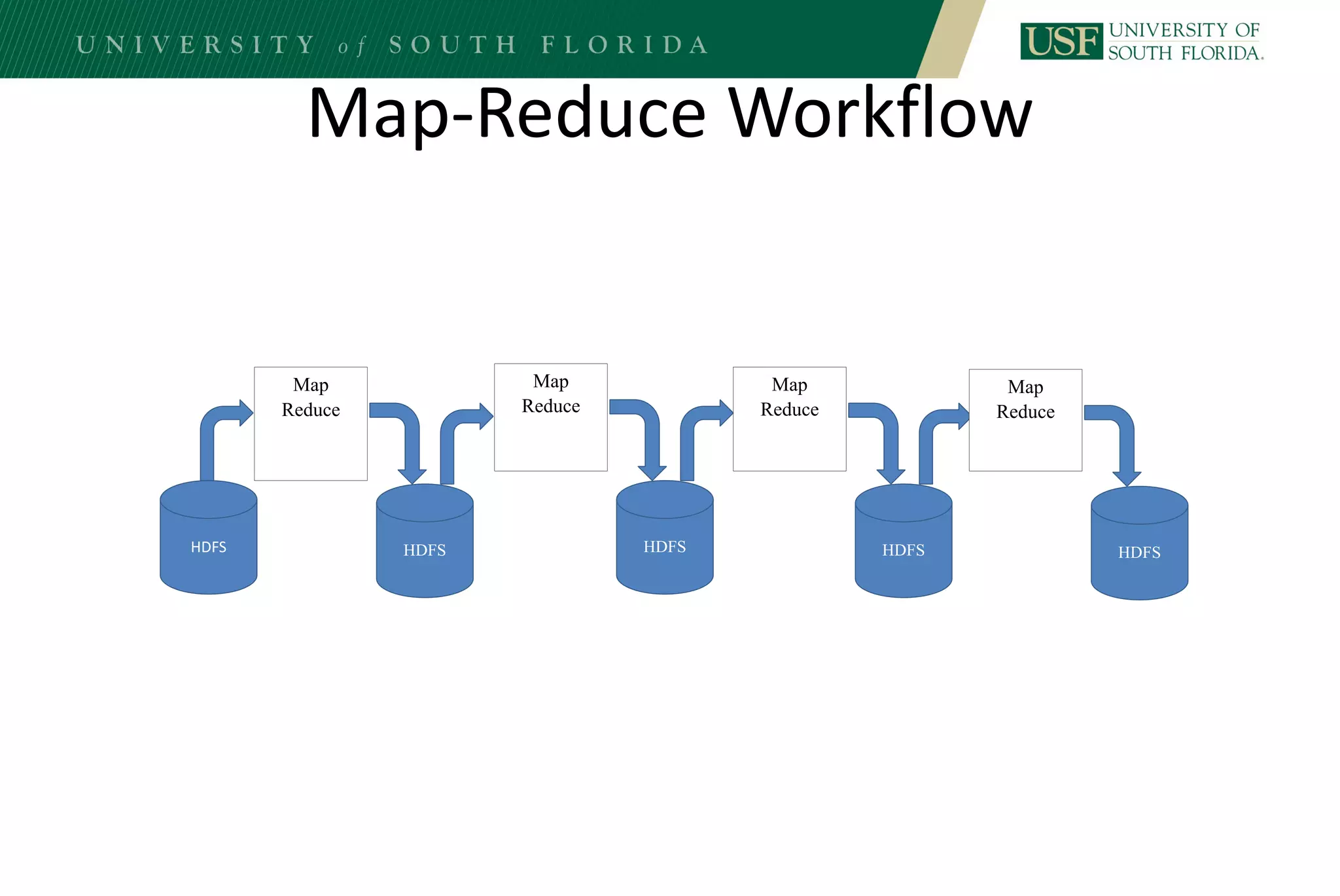
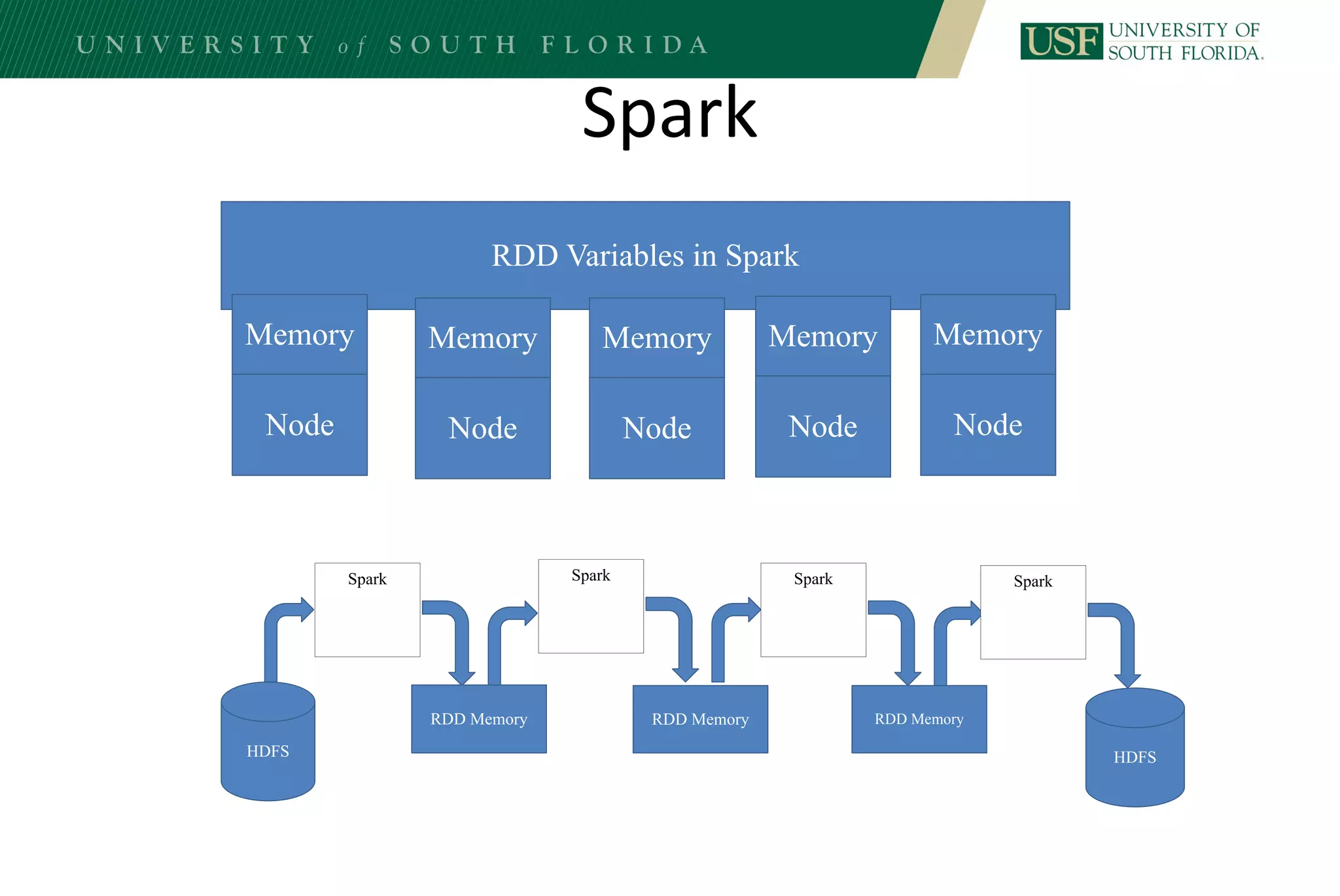
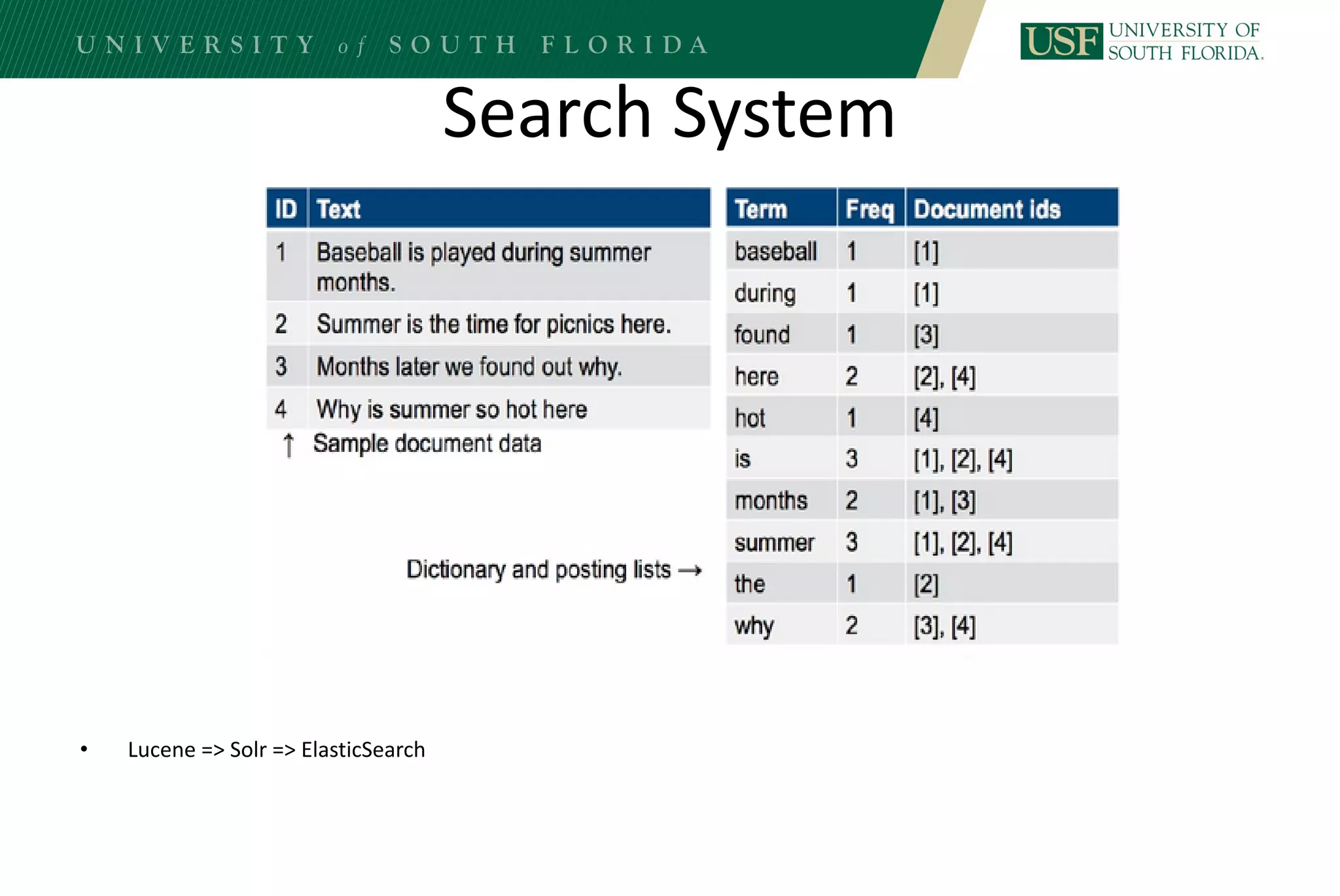
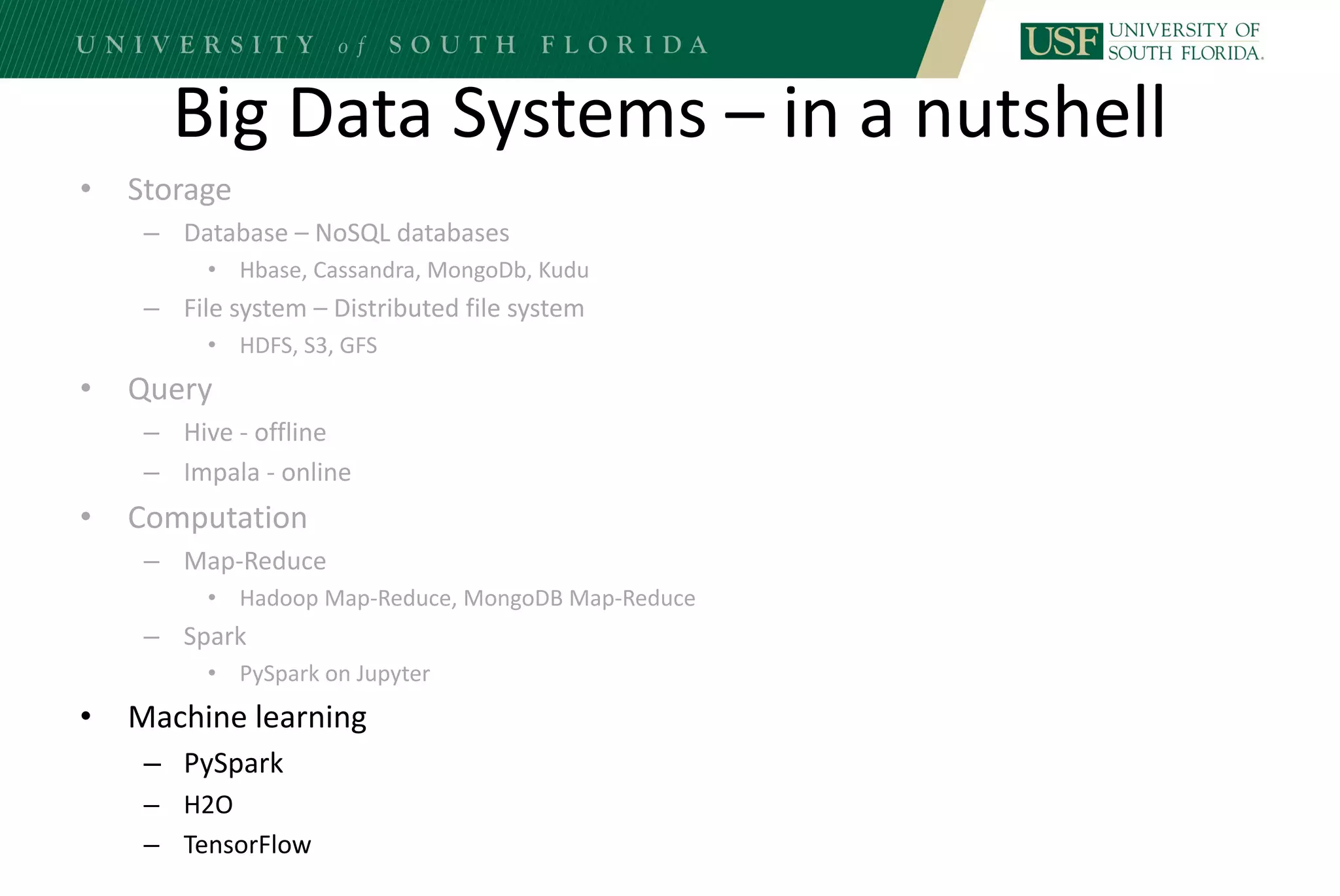
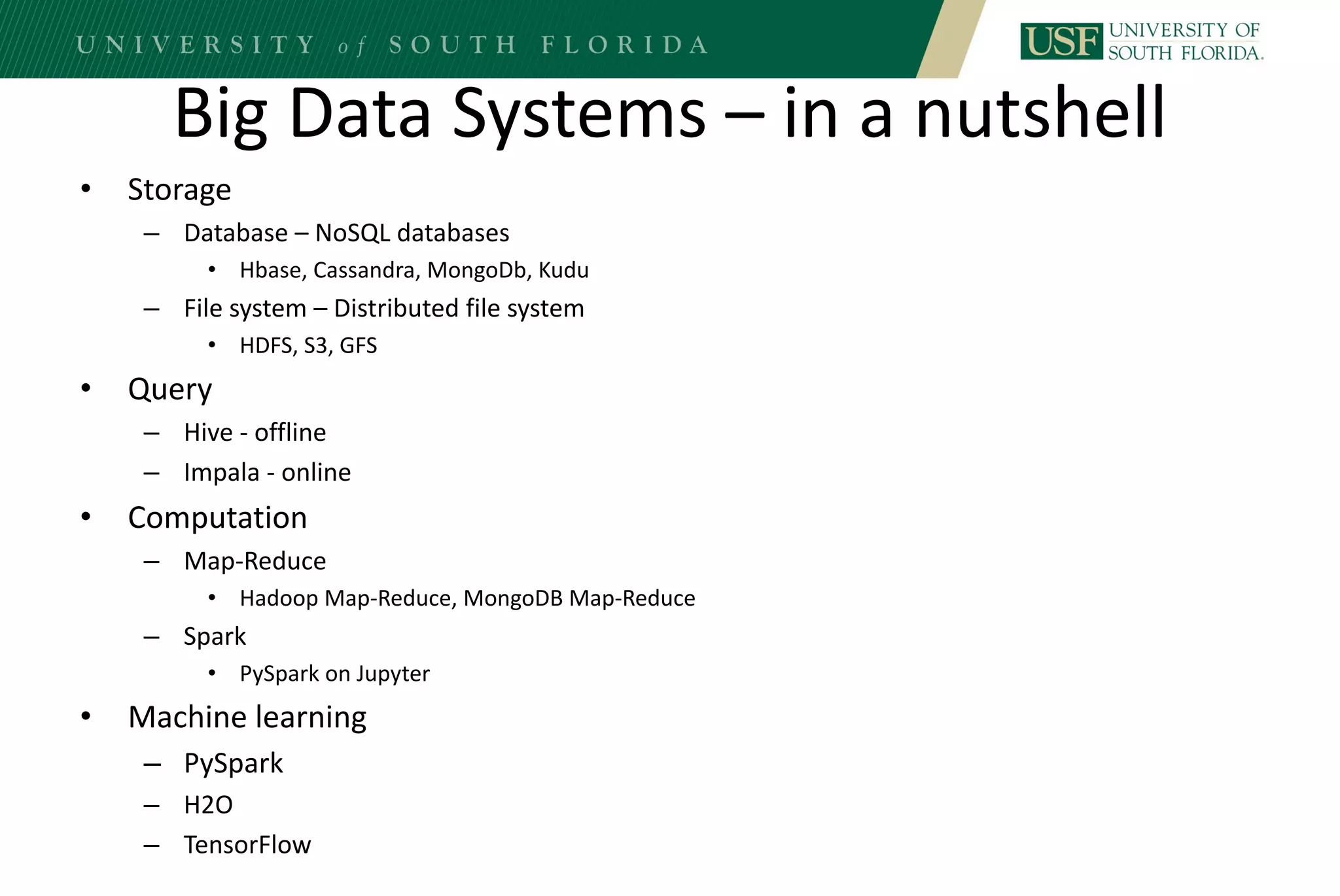
The document discusses data management for analytics. It describes how traditional relational databases do not scale well for big data due to strict structure and synchronization requirements. It then summarizes NoSQL databases as more scalable alternatives that trade strict structure for flexibility and relax synchronization. Specific NoSQL databases discussed include key-value stores, document databases, wide-column stores, and columnar databases. Distributed file systems like HDFS are also covered.