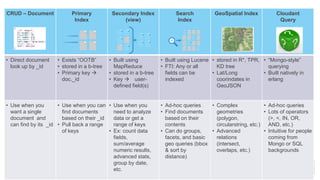
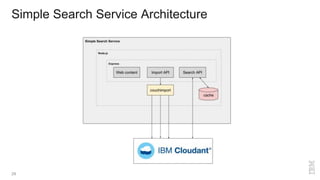
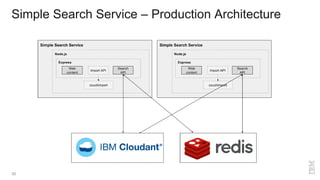
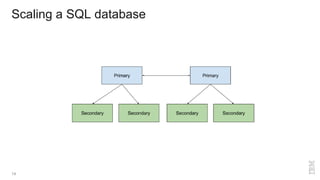
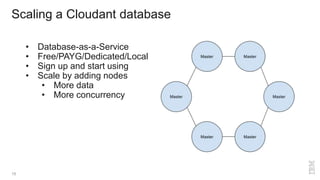
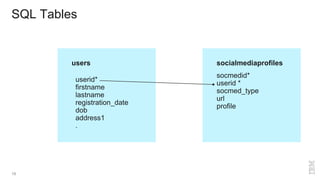
The document is a presentation by Glynn Bird, a Developer Advocate at IBM, focusing on NoSQL database systems as alternatives to traditional SQL RDBMS. It covers the differences between SQL and NoSQL, the types of NoSQL databases, scalability, querying, and data modeling, along with various applications such as search services and geo-spatial data. The presentation also emphasizes the ease of scaling NoSQL databases, their benefits for big data use cases, and the importance of replication for maintaining data integrity.







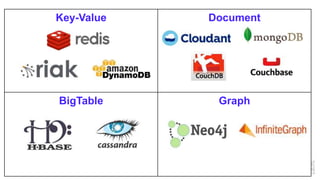






![NoSQL Data model
20
{
"firstname": "Glynn",
"lastname": "Bird",
"dob": "1986-10-02",
"registration_date": "2015-02-04",
"verified": true,
"address": { "address1": "10", "postcode": "W1A 1AA" },
"socialmedia": [
{ "type": "twitter", "handle": "glynn_bird" },
{ "type": "github", "username": "glynnbird" }
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nosqlforsqlusers-webinar-march20161-160316174058/85/NoSQL-for-SQL-Users-20-320.jpg)
![Cloudant Query
21
{
"selector": {
"$and": [
{ "registration_date" : { "$gt" : "2015-01-01" } },
{ "verified" : true },
{ "socialmedia" : true}
]
},
"sort": [
"registration_date:string"
]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nosqlforsqlusers-webinar-march20161-160316174058/85/NoSQL-for-SQL-Users-21-320.jpg)