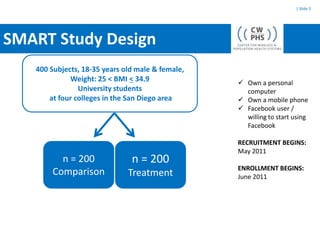
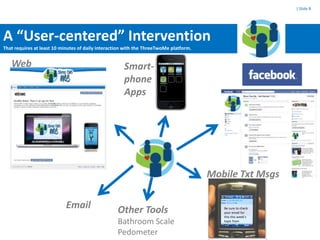
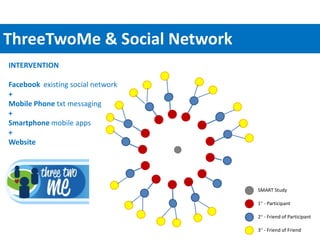
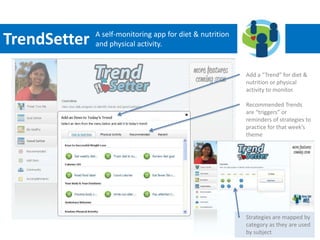
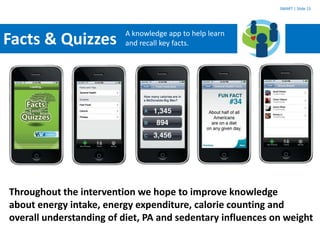
The SMART study aims to leverage mobile phones, social networks, and the web to promote weight loss among young adults ages 18-35. The study will enroll 400 subjects who will be randomly assigned to either a treatment group that receives the SMART intervention or a comparison group that receives standard health information. The SMART intervention utilizes existing social networks like Facebook combined with mobile apps, text messages, and a website to deliver behavior change strategies for diet, physical activity, and weight loss. Key challenges for evaluating the intervention include its evolving nature over time, potential contamination of control participants, clustering of participant social networks, and changes to platforms like Facebook.