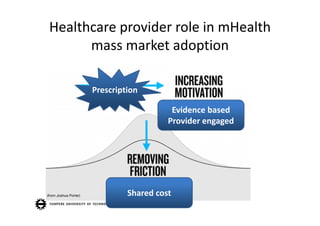
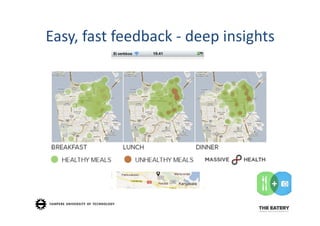
The document discusses the potential of mHealth in addressing chronic disease management and lifestyle-related health challenges. It highlights the significant adoption of health monitoring apps and wearable technologies, noting the need for behavioral changes and citizen responsibility in health. Additionally, it emphasizes the necessity of integrating mHealth into healthcare practices to facilitate mass market adoption and make healthy choices more accessible.





![Ease‐to‐use connected sensors
everywhere
169.5 million wearable wireless health and fitness sensors sold in 2017,
up from 21 million in 2011.
~90% supporting mobile phone connectivity, compared to 5% currently
[ABI Research]
NFC and Low Energy Bluetooth 4.0 technologies deployed
in the majority of smartphones by the end of 2012
Tapping – new, intuitive way to interact
Wearable wireless sensors with long operating times
Nike+ Fuelband VTT HearMeFeelMe](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datadrivenmedicine-perspectivesonmhealth-120927032804-phpapp01/85/Data-driven-medicine-Perspectives-on-mHealth-6-320.jpg)



![mHealth adoption curve?
Get through the day 11%
Not right now 24%
I need a plan 20%
Value Independence 19%
In it for Fun 17%
Leading the Way 10%
Health & Wellness segmentation in US
[The Future Company] Diffusion of innovations
[Rogers]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datadrivenmedicine-perspectivesonmhealth-120927032804-phpapp01/85/Data-driven-medicine-Perspectives-on-mHealth-14-320.jpg)