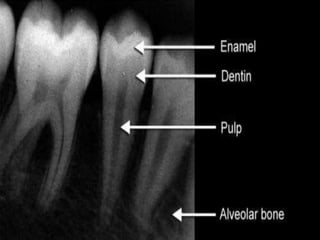
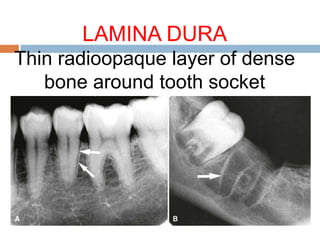
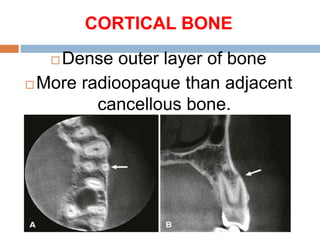
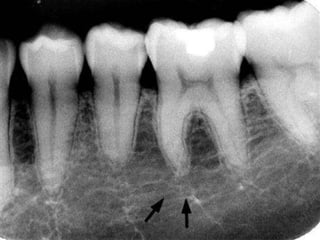
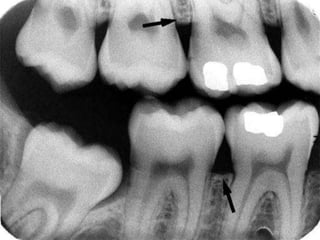
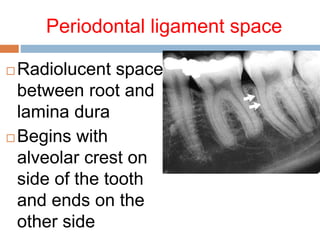
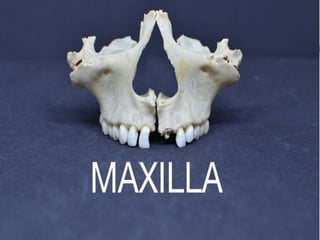
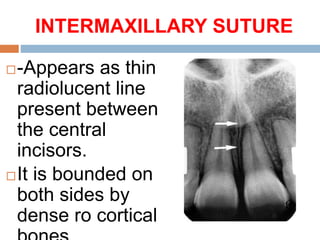
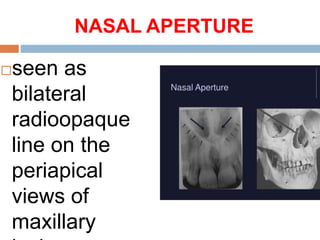
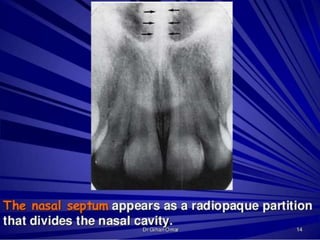
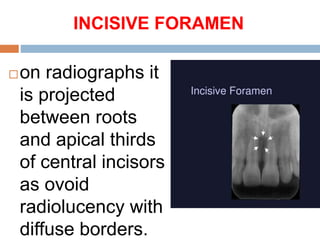
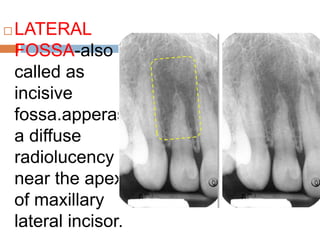
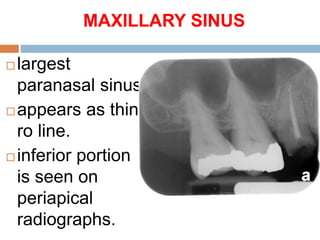
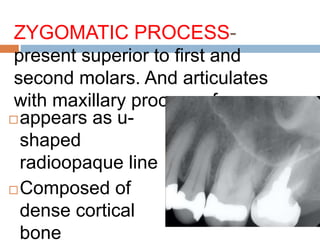
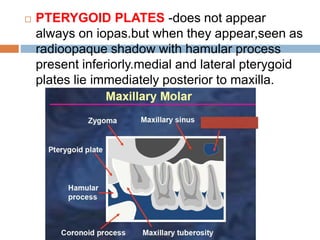
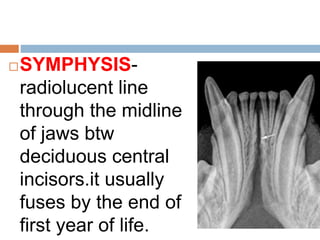
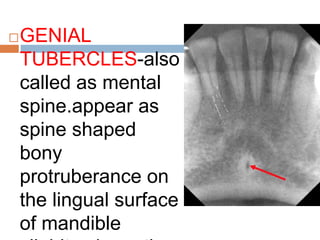
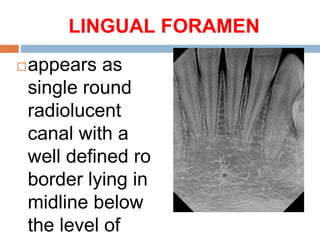
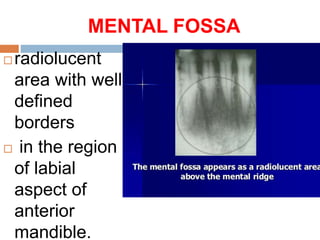
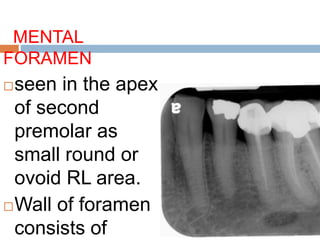
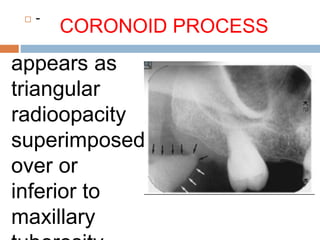
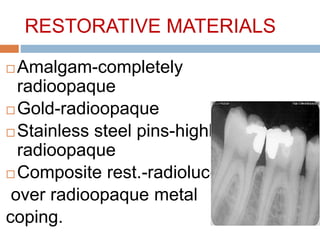
This document discusses normal radiographic landmarks of teeth and supporting structures. It describes the appearance of enamel, dentin, cementum, and pulp chambers. It also outlines landmarks of the maxilla like the zygomatic process, pterygoid plates, maxillary sinus and nasal aperture. For the mandible, it identifies the symphysis, genial tubercles, lingual foramen, mental ridge, and coronoid process. Common restorative materials and their radiopacity are also mentioned. The document is intended as a guide to interpreting normal dental radiographs.