The document discusses non-traditional security threats facing South Asia, with a focus on flooding in Bangladesh. Some key points:
- Non-traditional threats include transnational crimes, terrorism, climate change, diseases, and resource scarcity.
- South Asia experiences high levels of insecurity due to national and religious conflicts, weak governments, and lack of regional cooperation.
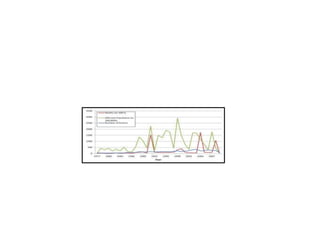
- Bangladesh is highly vulnerable to climate change and natural disasters, experiencing around 200 climate-related disasters in the last 30 years that have killed thousands and caused $16 billion in damages. Major threats are floods, droughts, cyclones, and sea level rise.
- In response to floods, Bangladesh has warning systems, mobilizes










![Response to Floods
• CPP volunteers:
About 42,000 volunteers of Bangladesh Red Crescent Society’s Cyclone Preparedness Program [CPP] were mobilized in
the coastal belt five days before the cyclone made landfall on 15 November 2007,” Abdur Rob, chairman of the Bangladesh
Red Crescent Society explained.
• Warning system :
Once a cyclone appears in the Bay of Bengal, the Storm Warning Centre of the Bangladesh Meteorological Department (BMD) begins
issuing special weather bulletins.
• UNDP:
After the 1991 cyclone, disaster management activities were upgraded through a three-year, US$5 million
technical assistance project of the UN Development Program (UNDP).
• WARPO:
The Ministry of Water Resources created the Water Resources Planning Organization (WARPO), a key organization in dealing
with the nation’s water resources planning and management.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nontraditionalpresentation-170428033919/85/Non-traditional-presentation-12-320.jpg)

