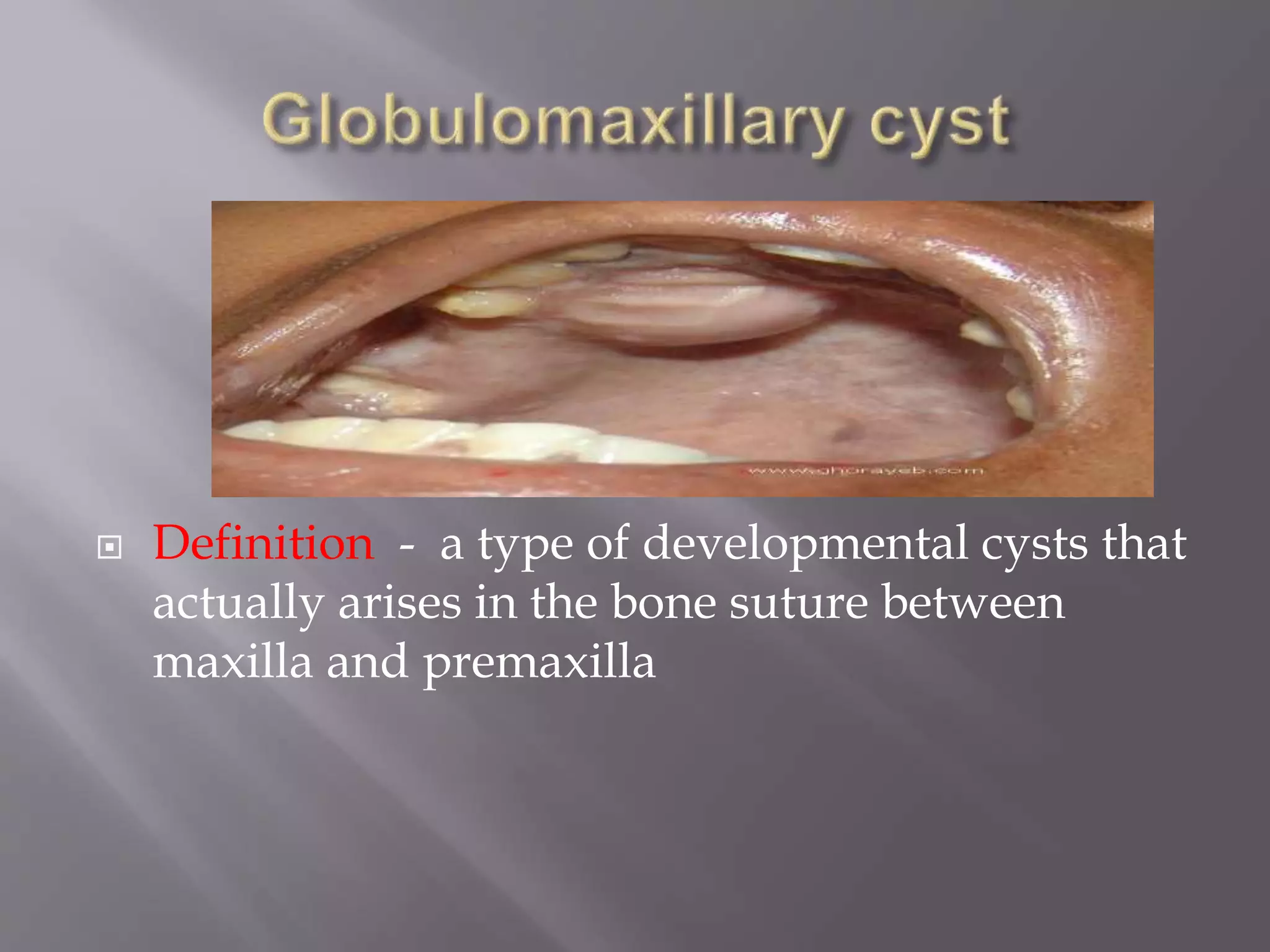
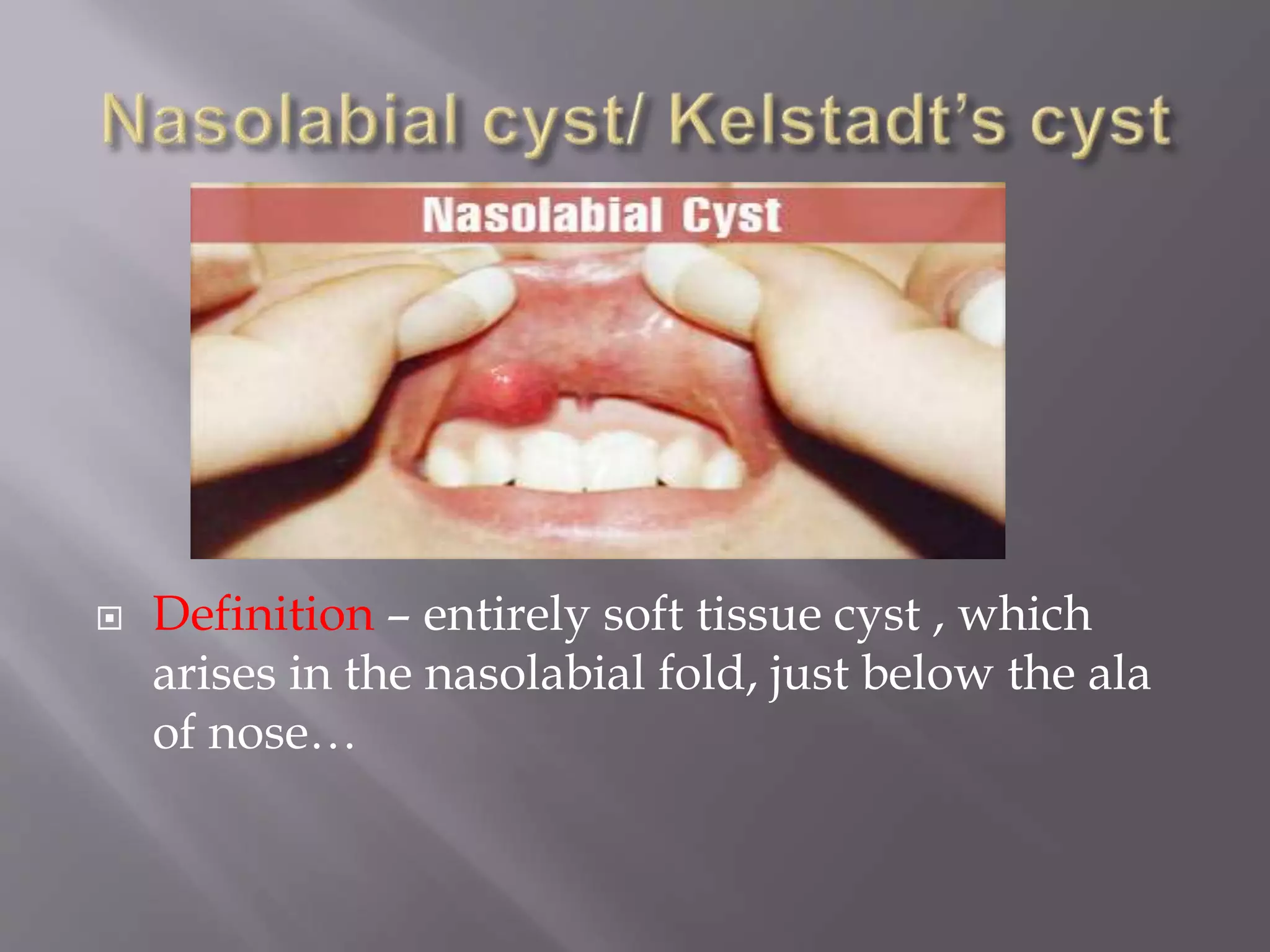
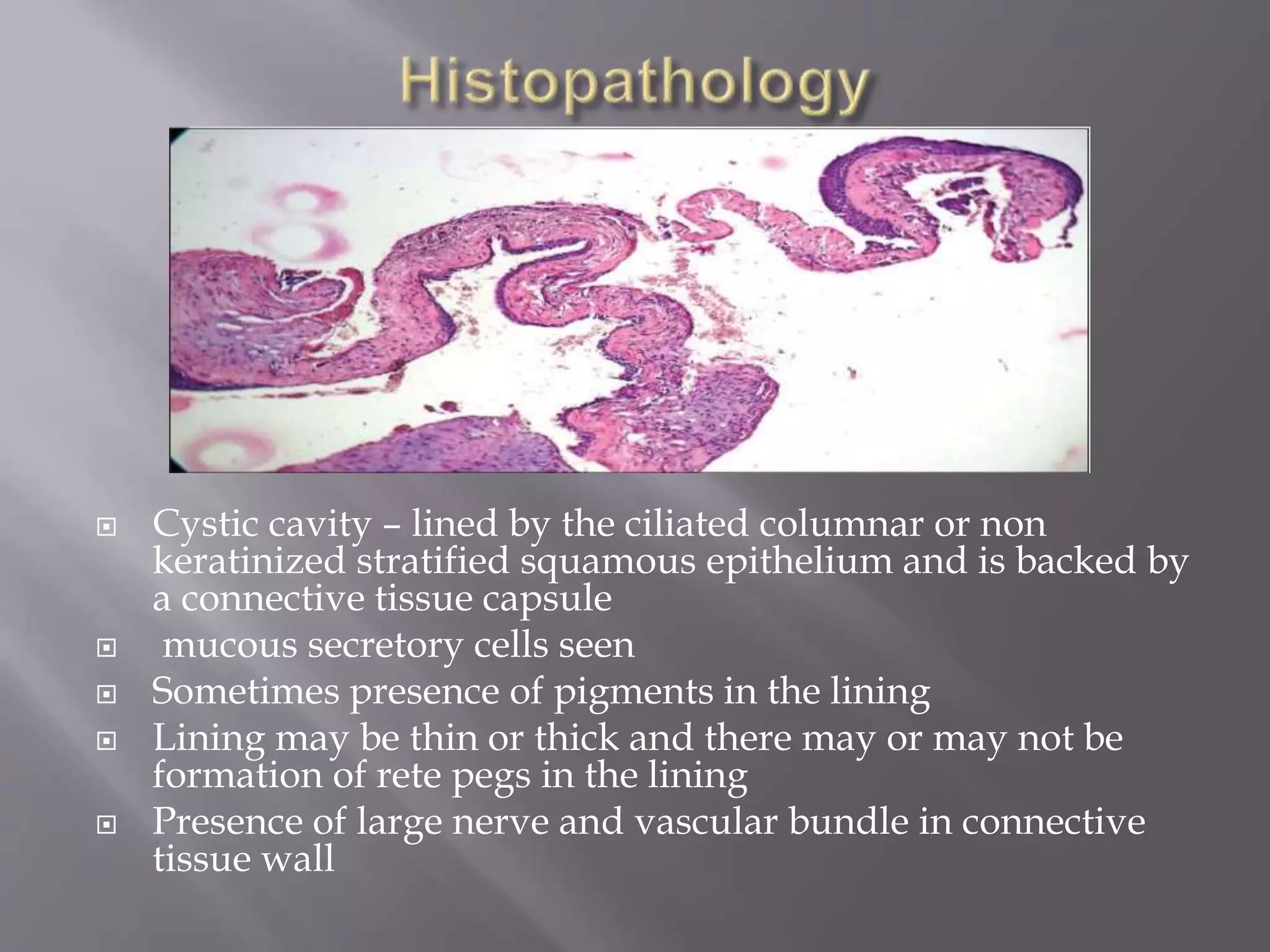
This document discusses various types of cysts found in the oral cavity and jaws. It defines odontogenic cysts as those lined by epithelium from tooth development and non-odontogenic cysts as those arising from epithelial inclusions during facial development. Specific cysts discussed include nasolabial cysts arising from the nasolacrimal duct, nasopalatine duct cysts from remnants of the nasopalatine duct, and globulomaxillary cysts between the maxilla and premaxilla. Clinical features, radiographic appearance, histopathology and treatment are described for each. The document provides an overview of developmental cysts of the oral region.