Embed presentation
Downloaded 25 times
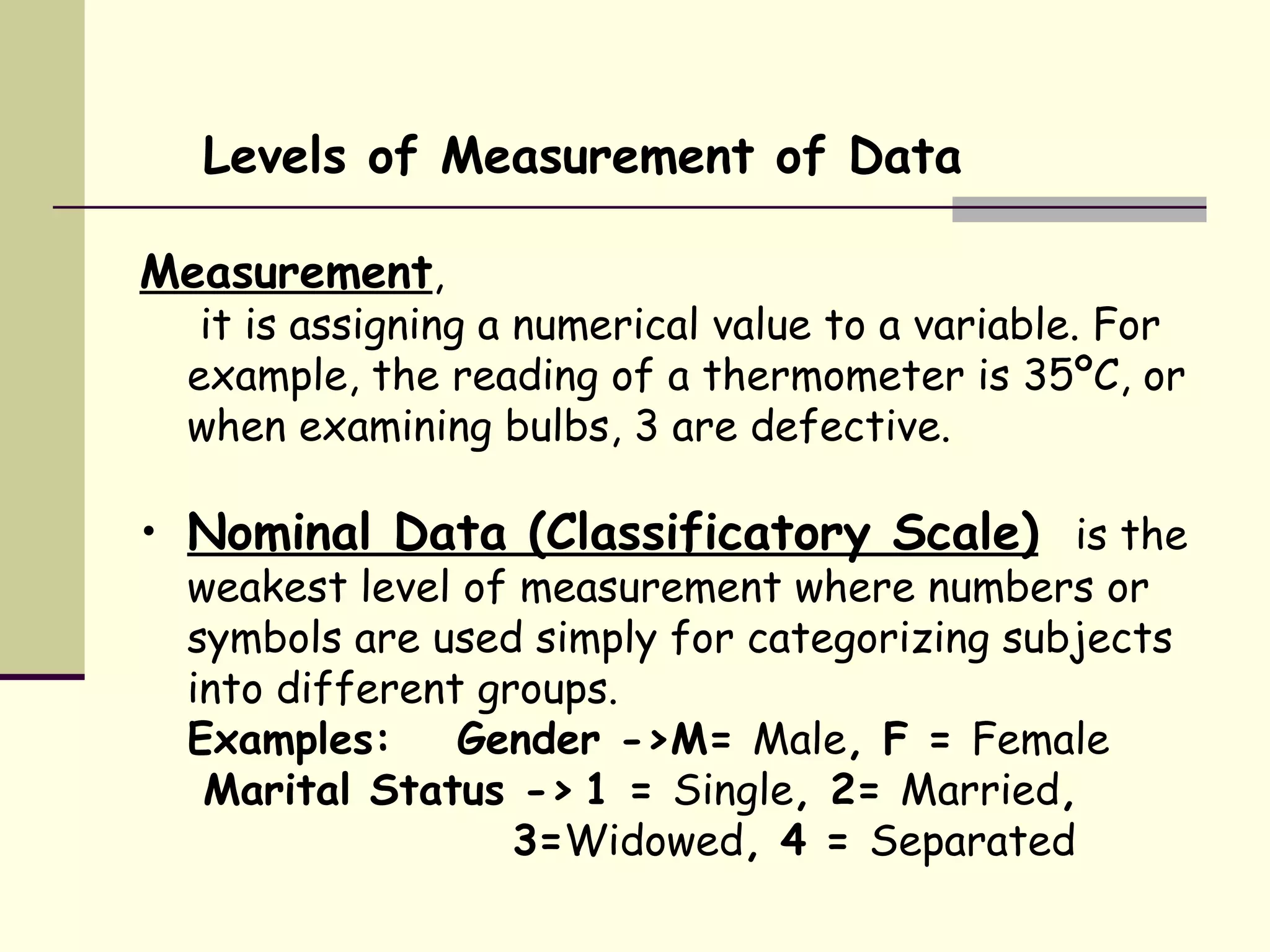
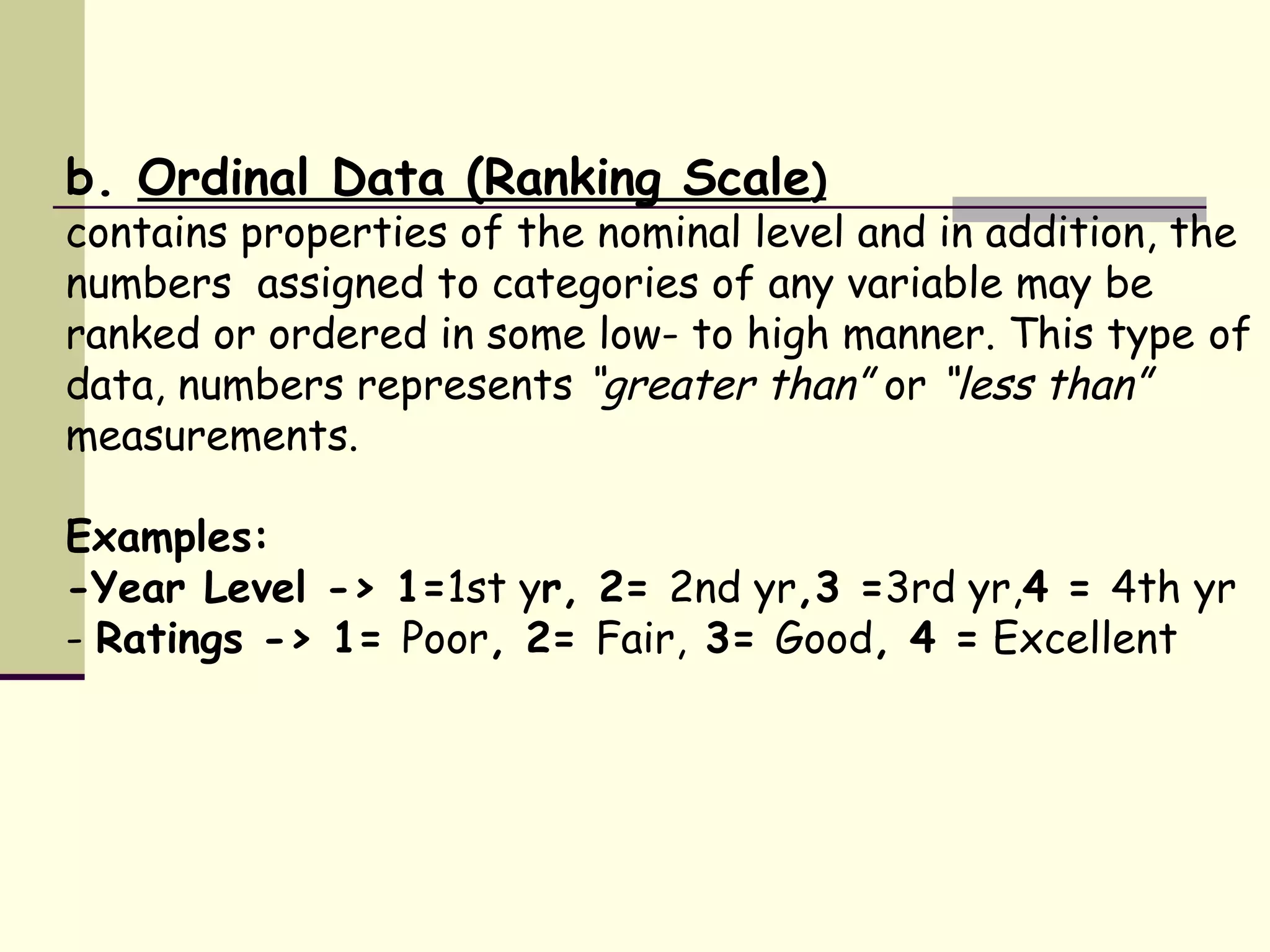


There are four levels of measurement for data: nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio. Nominal data involves categorizing subjects into groups without order. Ordinal data ranks categories in a low-to-high order. Interval data involves distances of equal size between numbers on the scale, but without a true zero point. Ratio data contains all interval properties and has a true zero point, allowing for calculations like percentages.


