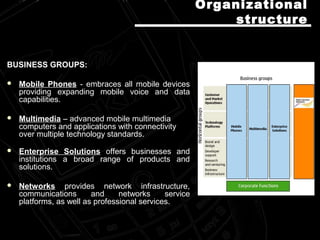
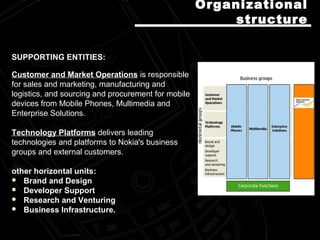
Nokia is a Finnish multinational telecommunications, information technology, and consumer electronics company. It started as a paper mill in 1865 and became the world's largest manufacturer of mobile phones. Nokia has production facilities around the world and sells products in over 130 countries. Its strategic focus is on connecting people through winning devices, consumer internet services, enterprise solutions, networks, and professional services. Nokia emphasizes quality, technological excellence, and understanding customers to differentiate itself and maintain its strong position in the mobile phone market.