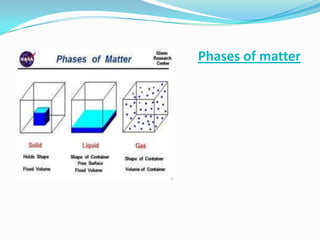
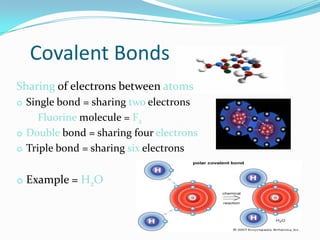
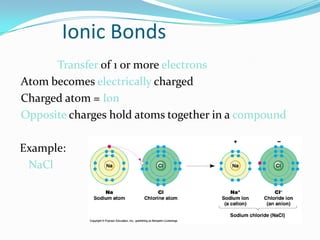
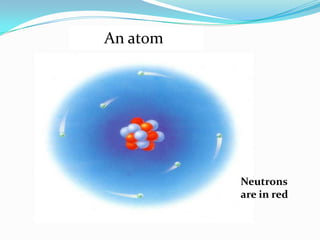
Matter can exist in three states - solid, liquid, and gas. In a solid, the particles are closely packed together with strong intermolecular forces between them, giving the solid a definite shape and volume. In a gas, the particles are far apart with weak intermolecular forces, allowing gases to expand to fill their container. Matter can also be classified as elements, compounds, or mixtures depending on its chemical composition. Elements are made of only one type of atom, while compounds contain different types of atoms bonded together, and mixtures contain elements or compounds not bonded together.