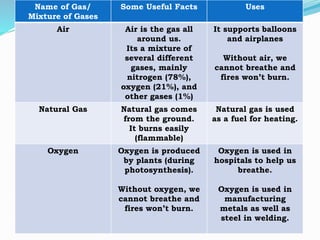
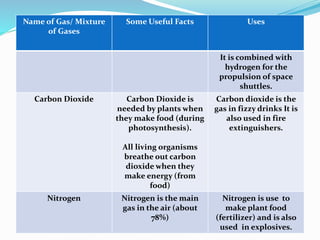
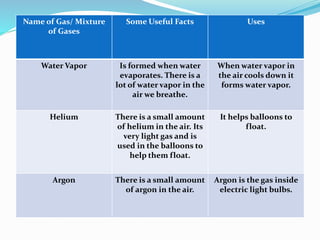
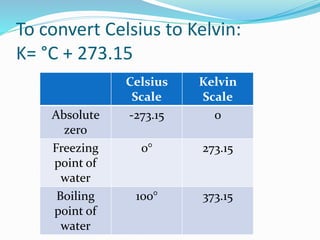
This document provides information about gases and the kinetic molecular theory. It defines 11 common gases, lists their properties and uses. The kinetic molecular theory explains that gases are made of particles that move rapidly in random straight lines and collide elastically. The theory accounts for gas properties like compressibility and the fact that gas density varies with temperature and pressure. Key gas properties like volume, pressure, temperature and amount are also defined.