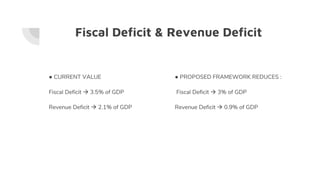
The document outlines NITI Aayog's 3-year action agenda from 2017-2020. It discusses 7 parts: (1) poverty reduction and fiscal management, (2) agriculture and industry growth, (3) rural, urban and regional development, (4) growth enablers like infrastructure and technology, (5) governance reforms, (6) improving social sectors like education and health, and (7) environmental sustainability. However, the summary fails to identify goals, consider financial implications, discuss constraints, and ignores banking/finance sectors in its analysis.