The document summarizes key aspects of the National Institute of Standards and Technology's (NIST) definition of cloud computing, including:
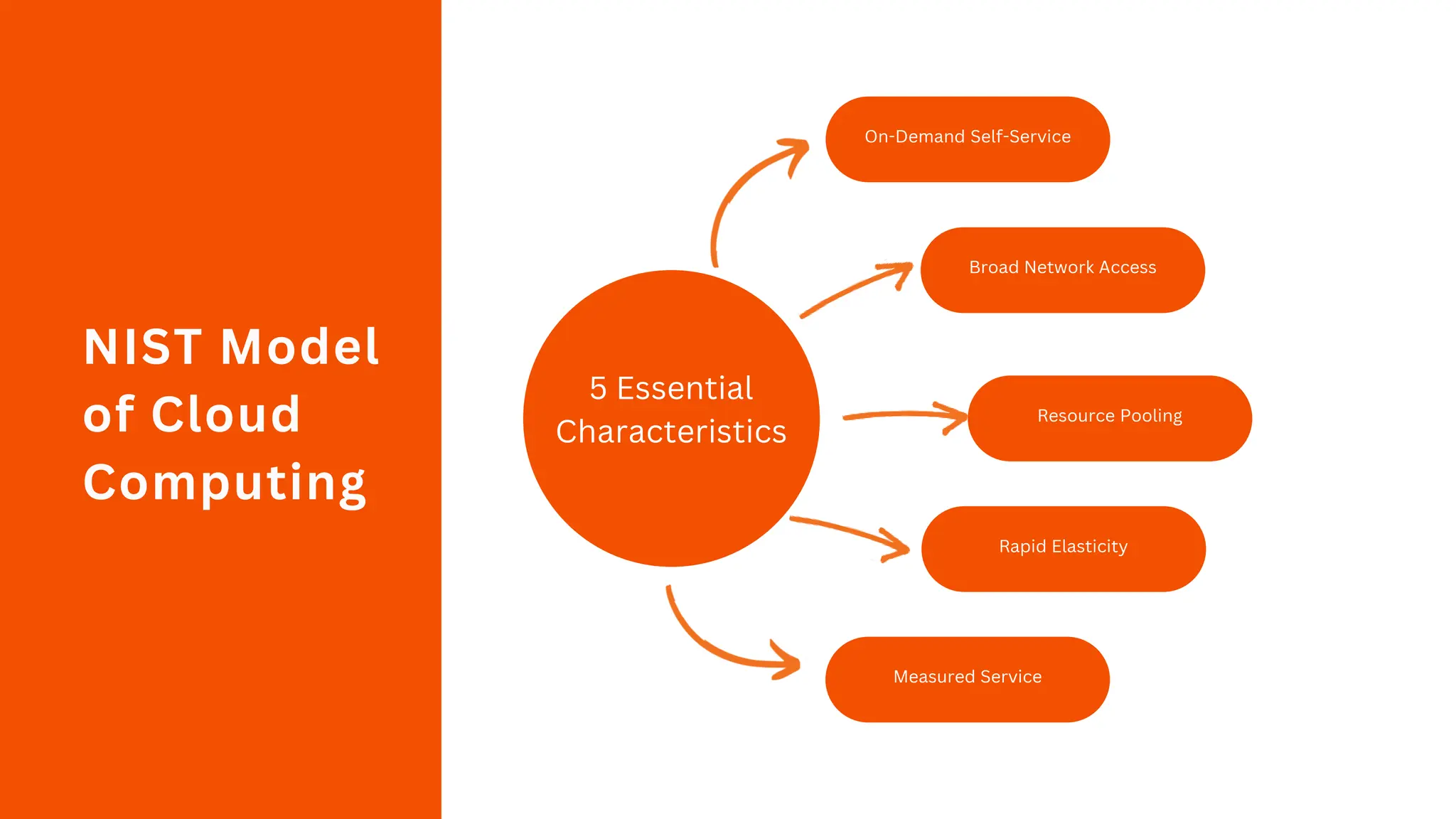
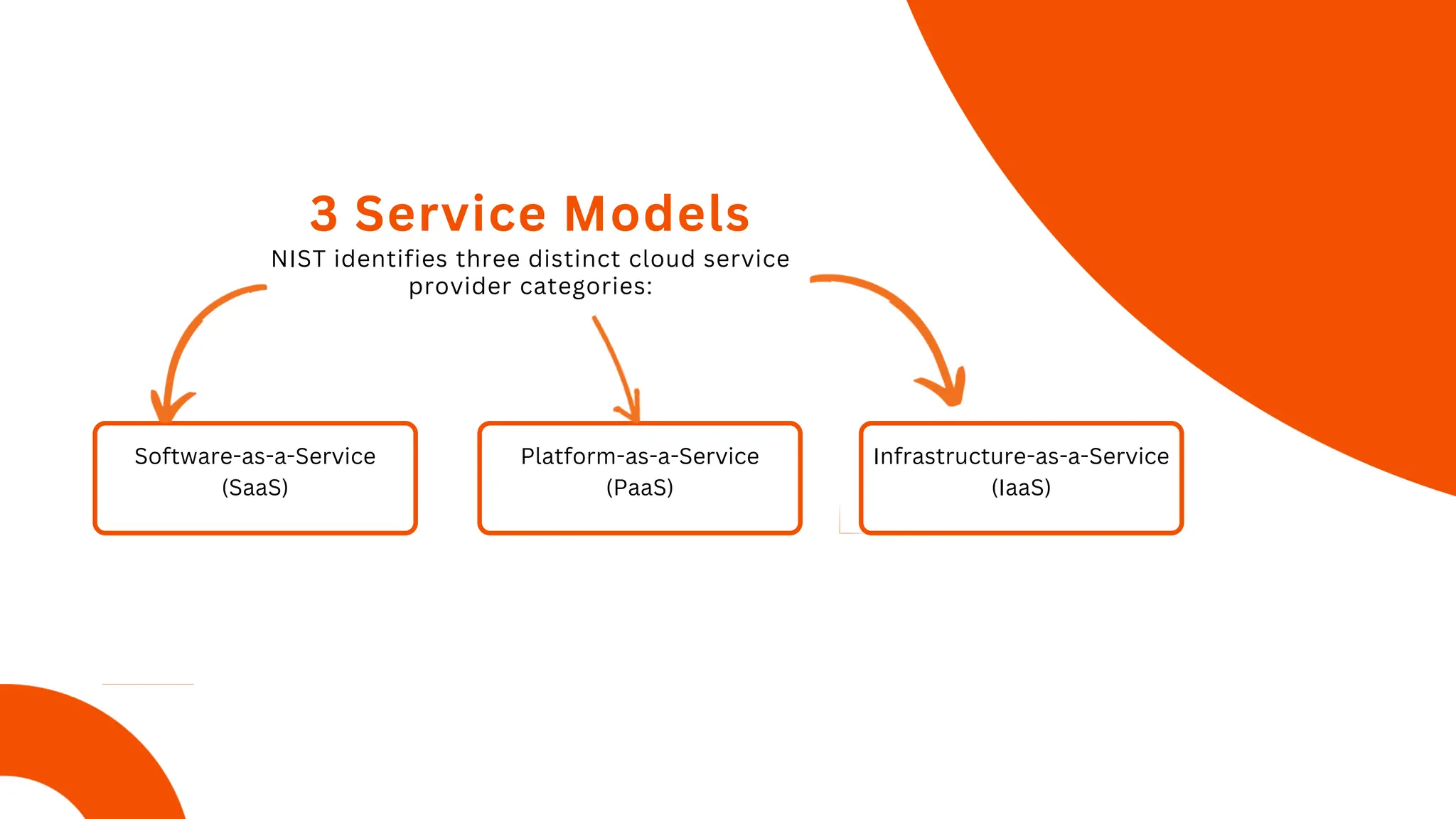
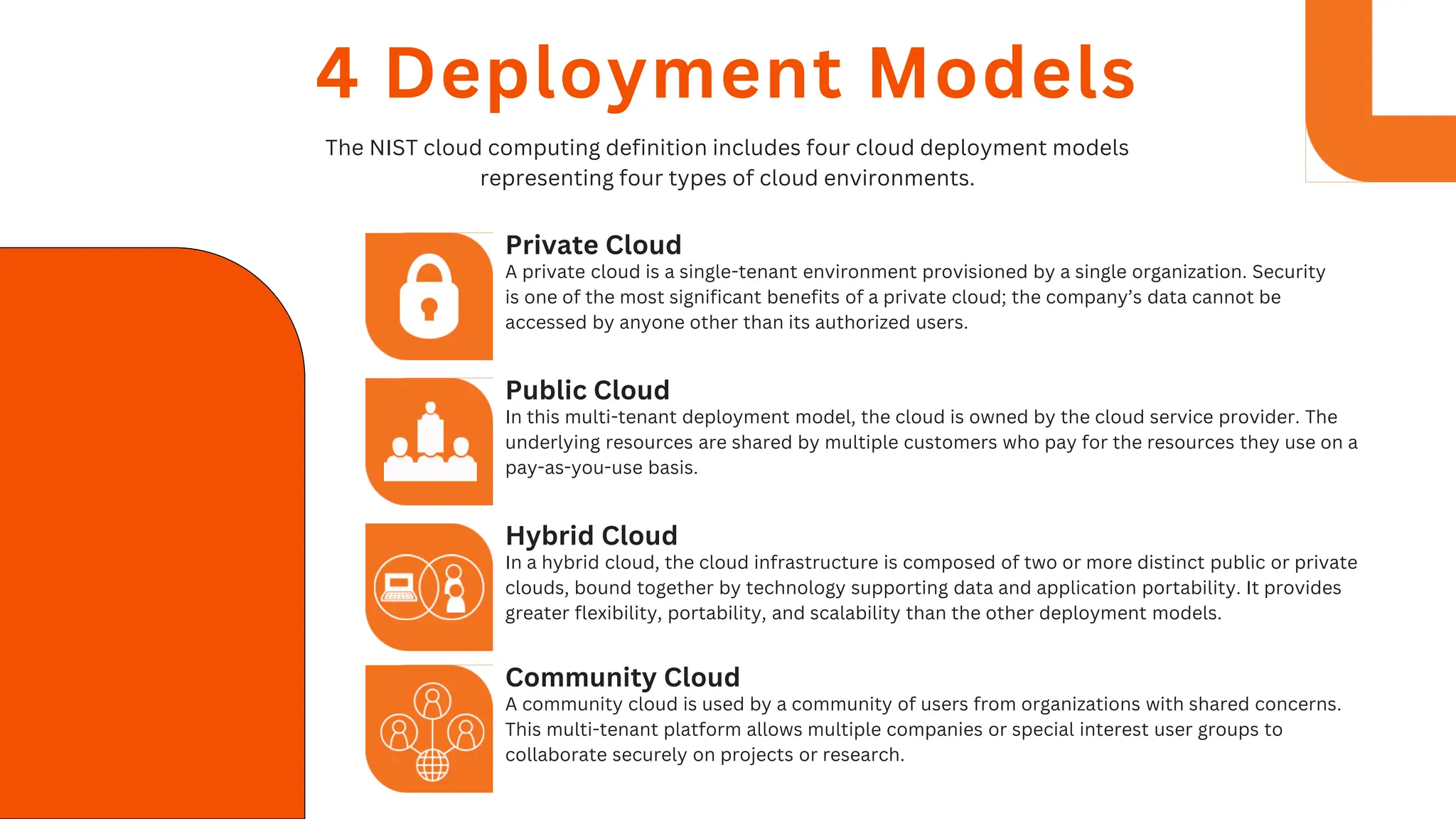
1) NIST defines cloud computing based on 5 essential characteristics (on-demand self-service, broad network access, resource pooling, rapid elasticity, measured service), 3 service models (SaaS, PaaS, IaaS), and 4 deployment models (private, public, hybrid, community cloud).
2) The 5 characteristics describe the essential aspects of cloud computing - on-demand access to configurable resources that can be provisioned with minimal management effort.
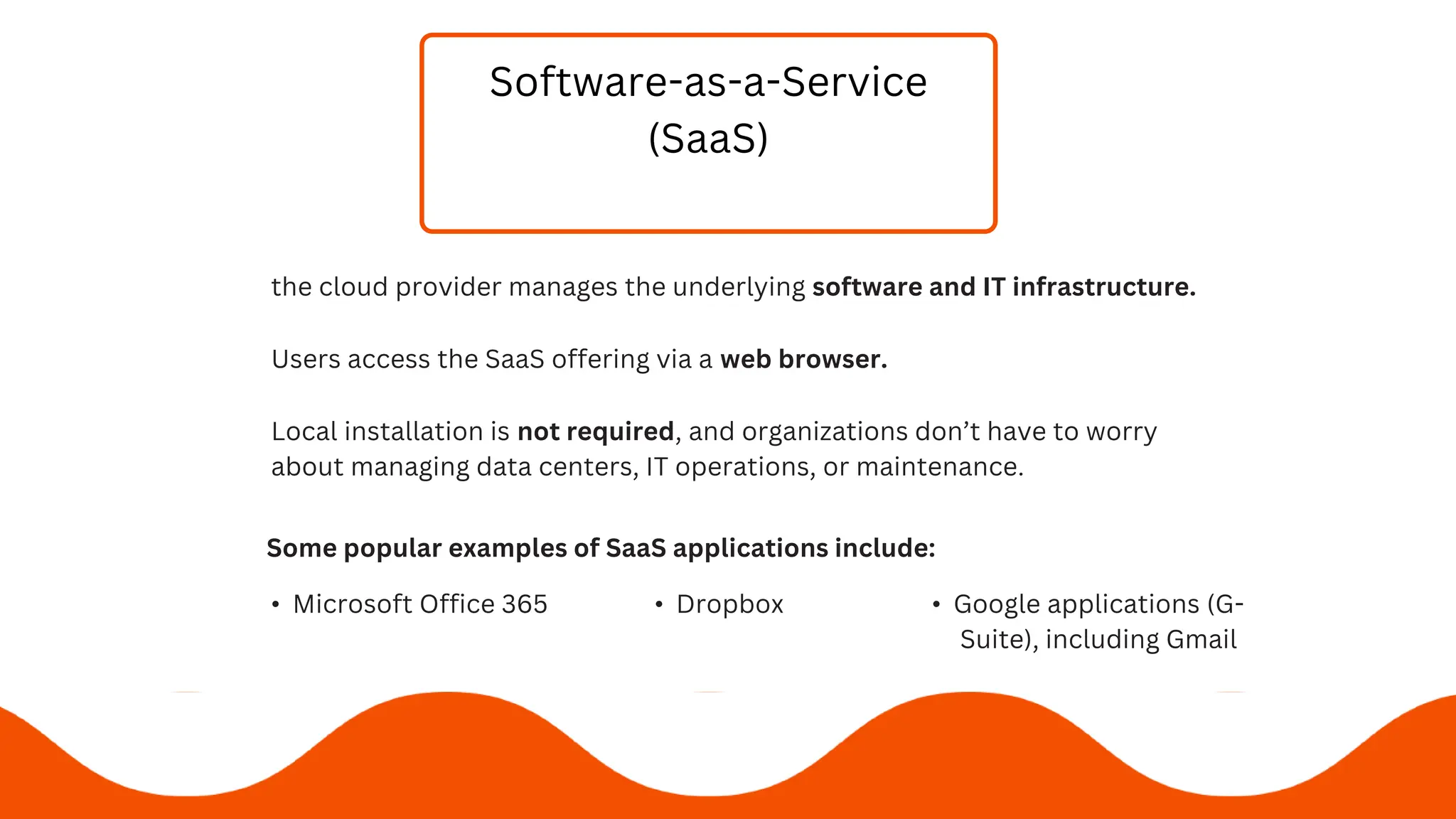
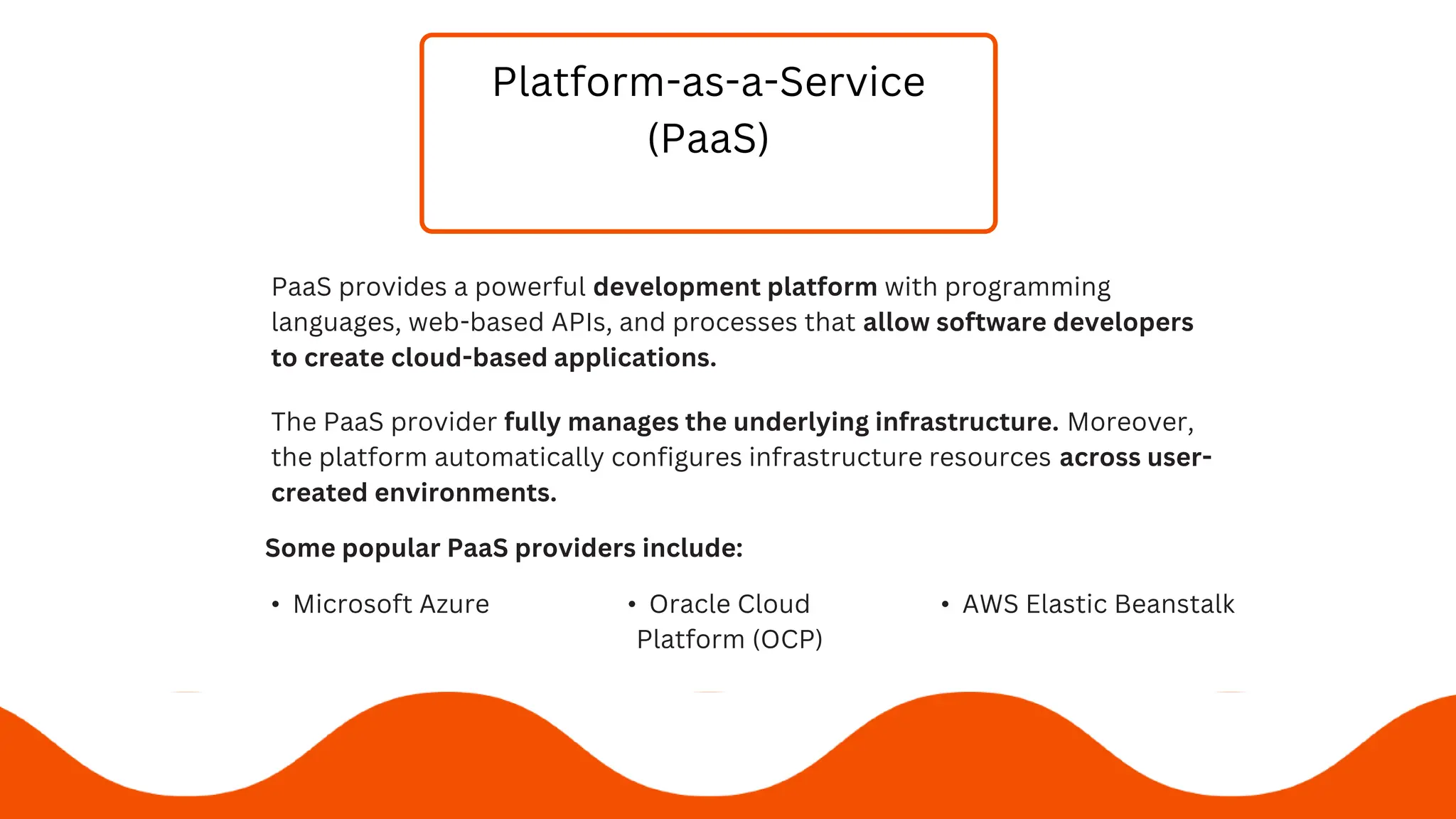
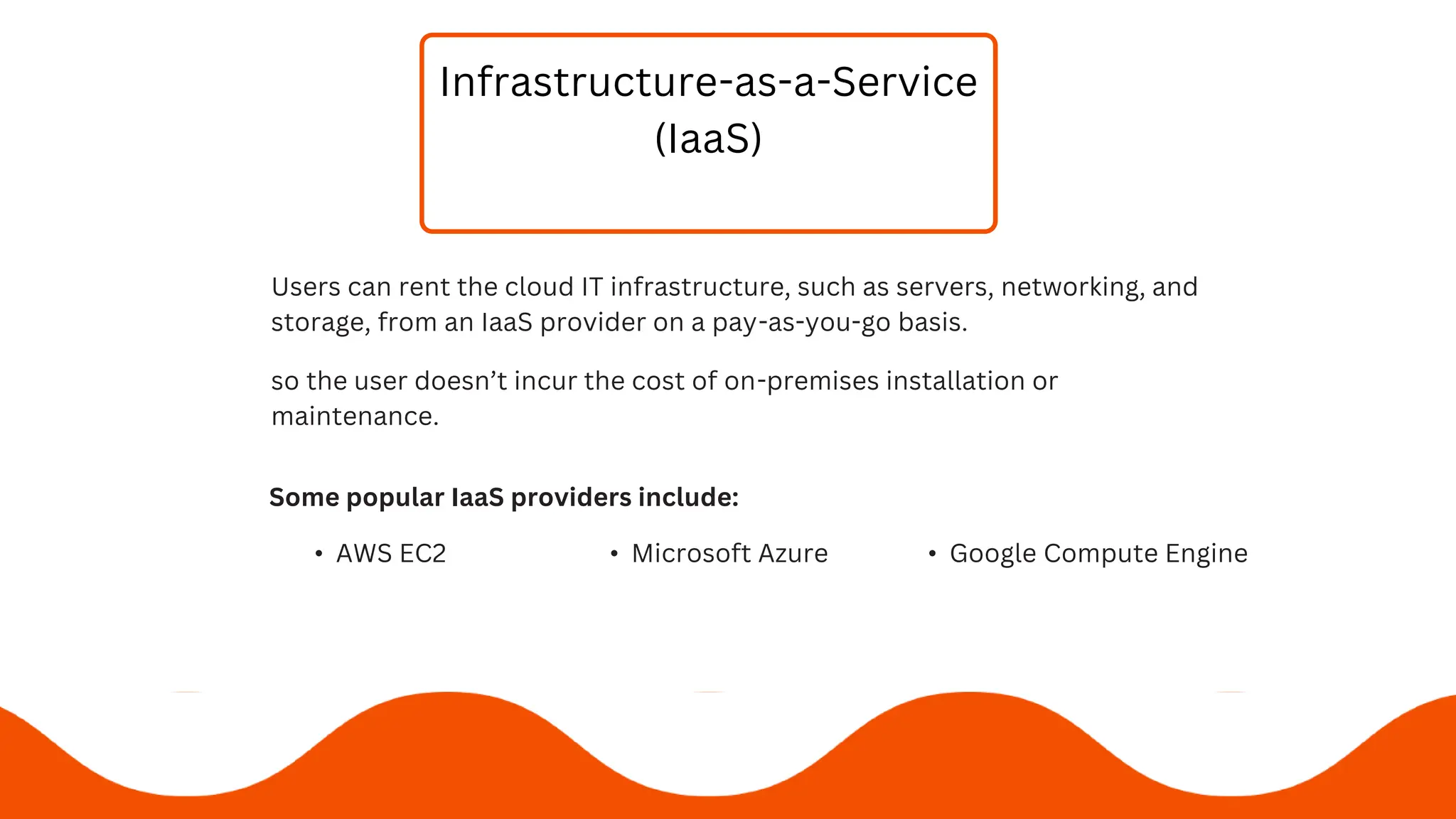
3) The 3 service models are SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS - which respectively