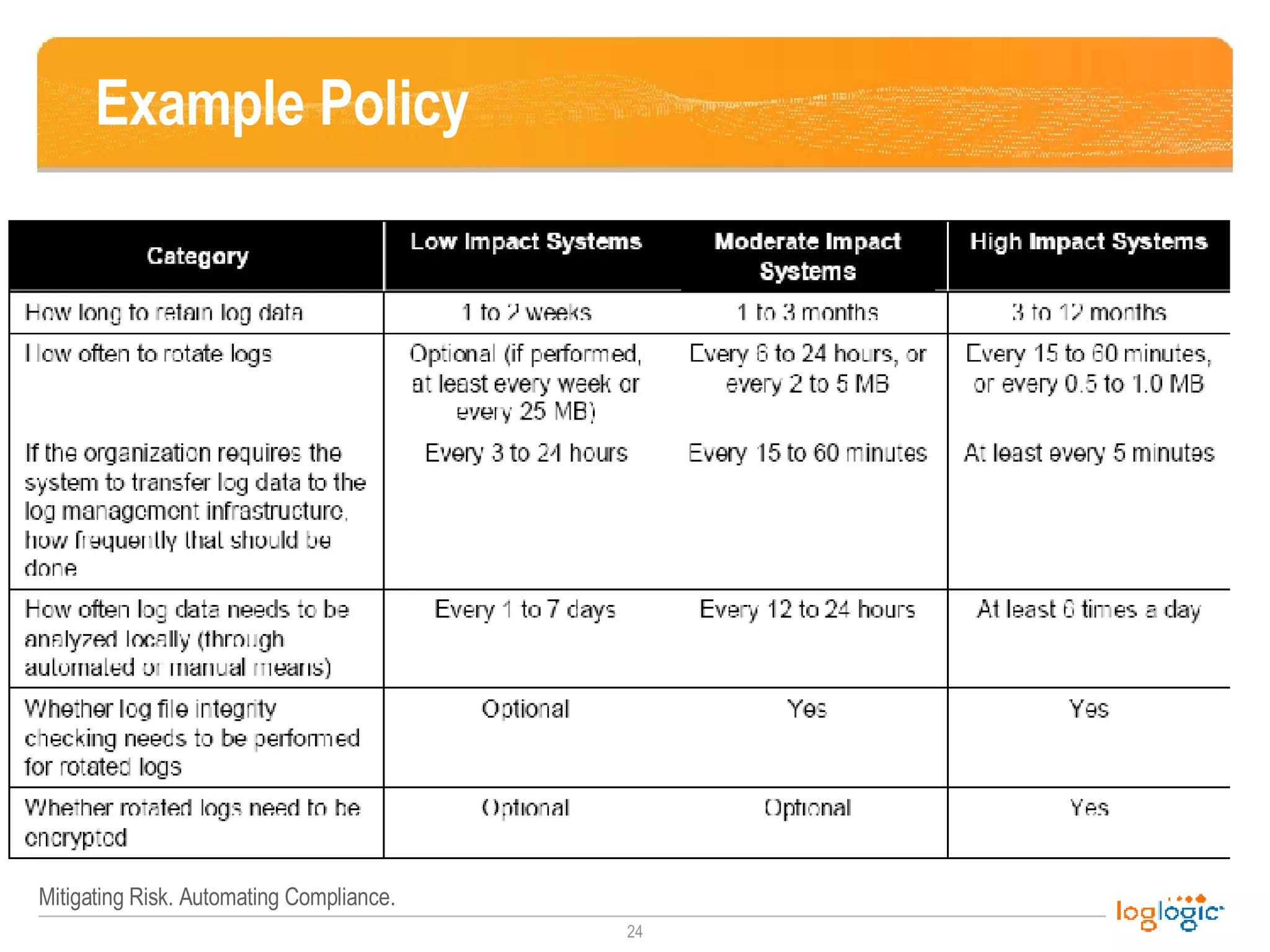
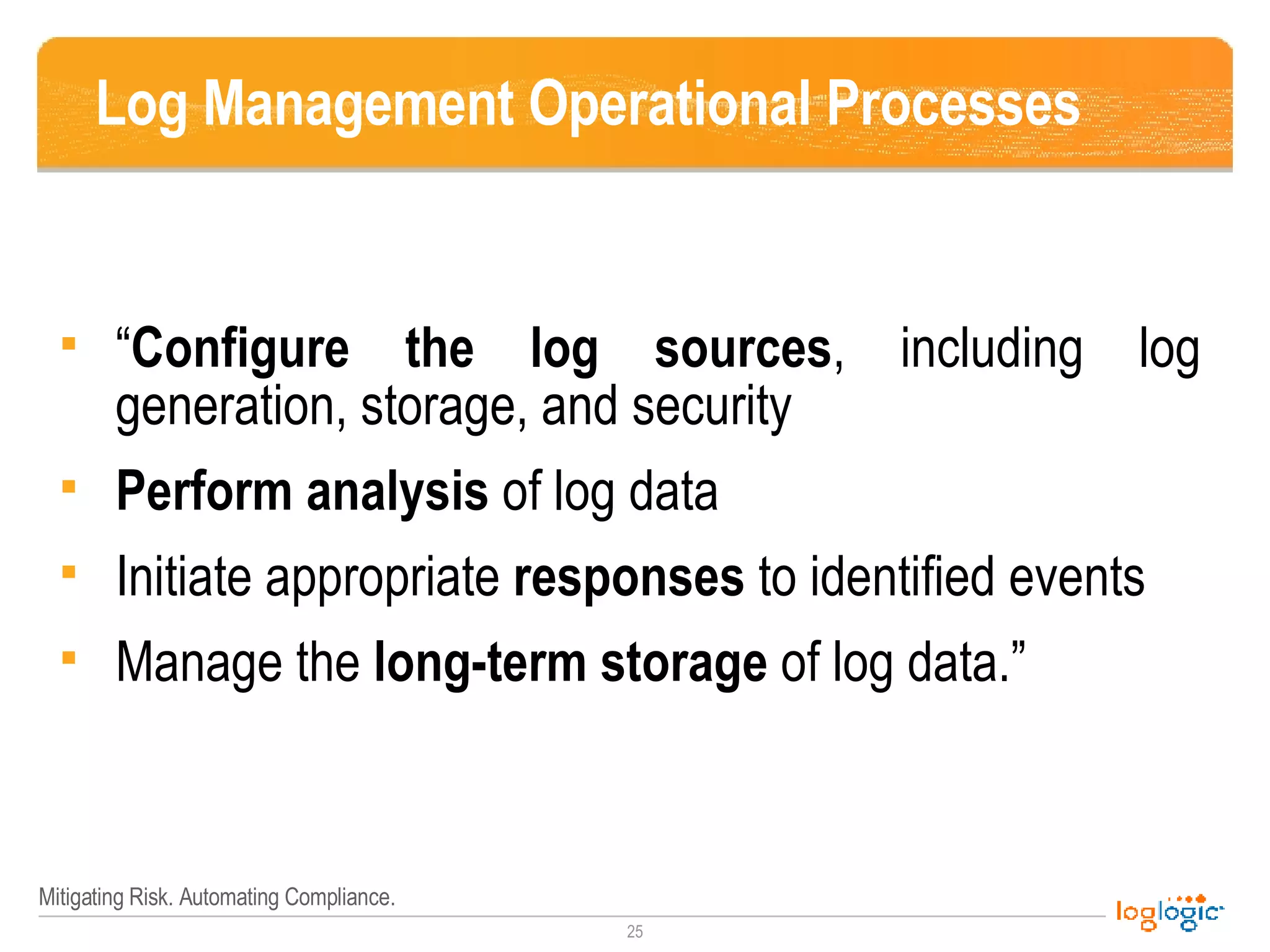
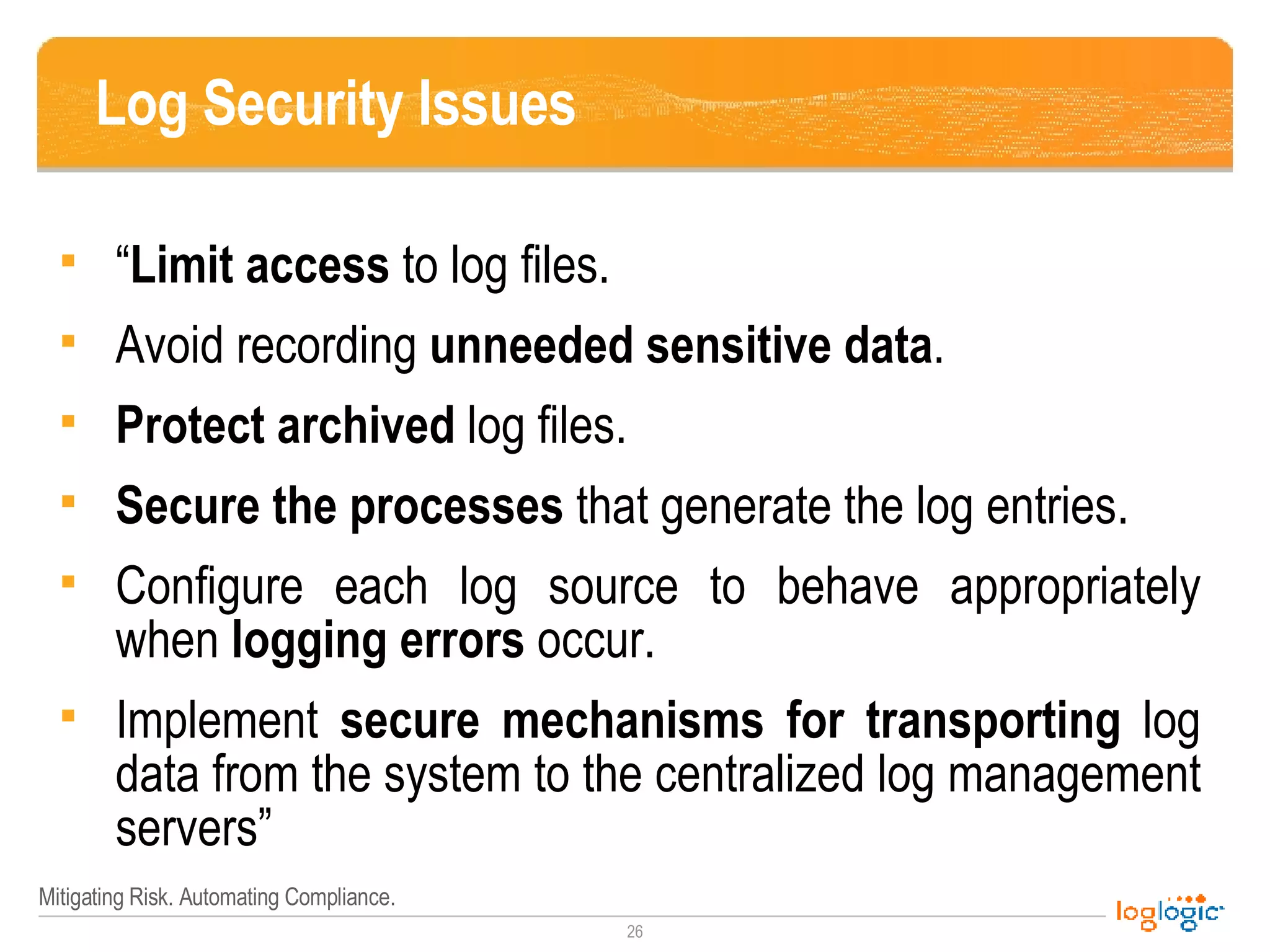
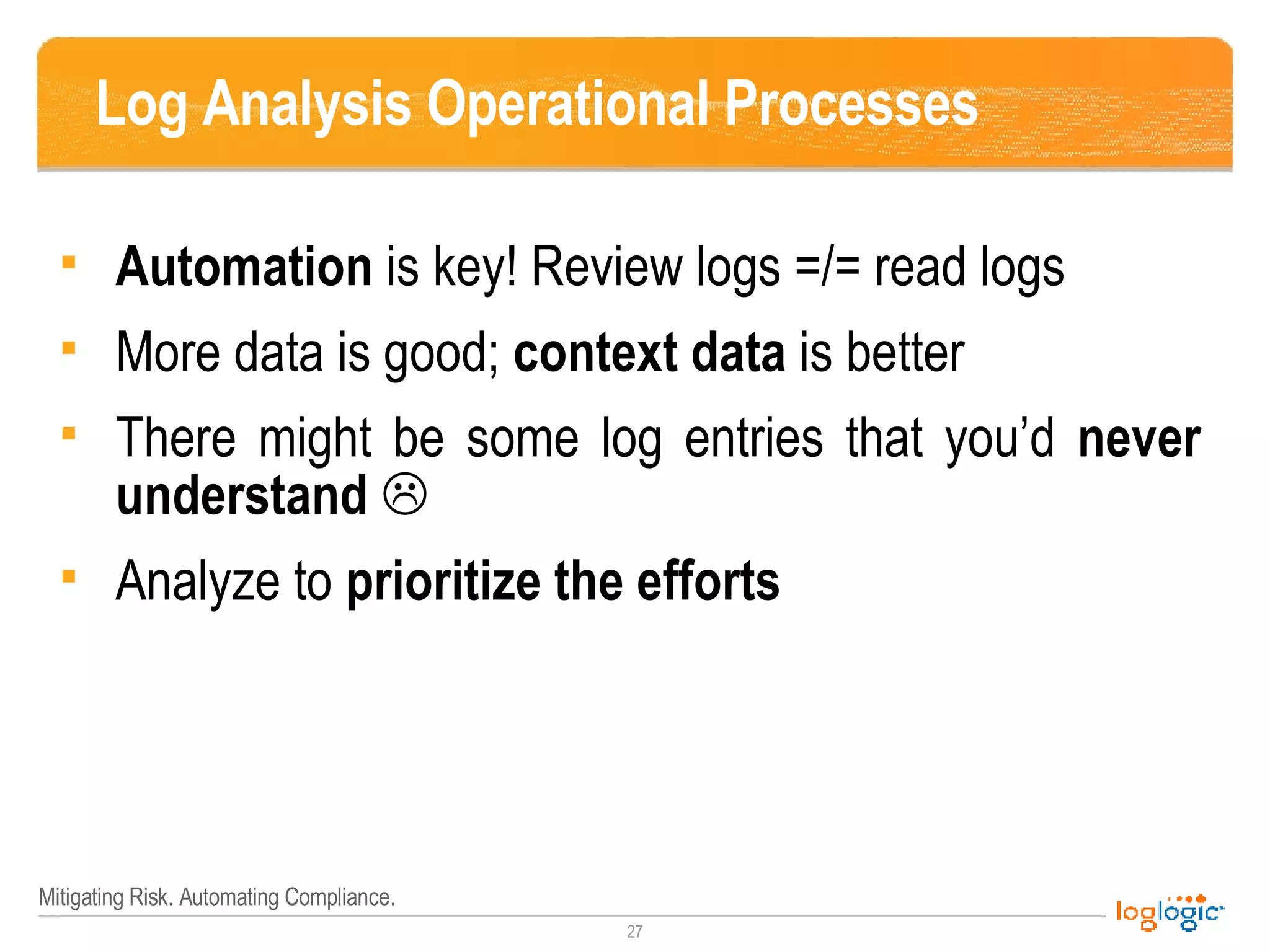
The document outlines the NIST 800-92 Log Management Guide, focusing on effective log management practices for enhancing computer security. It provides a comprehensive overview of log types, their importance in security and compliance, and guidance for implementing log management processes across an organization. The guide emphasizes the value of standardized logging for situational awareness, threat detection, and regulatory compliance, while also addressing the challenges and tools associated with log management.






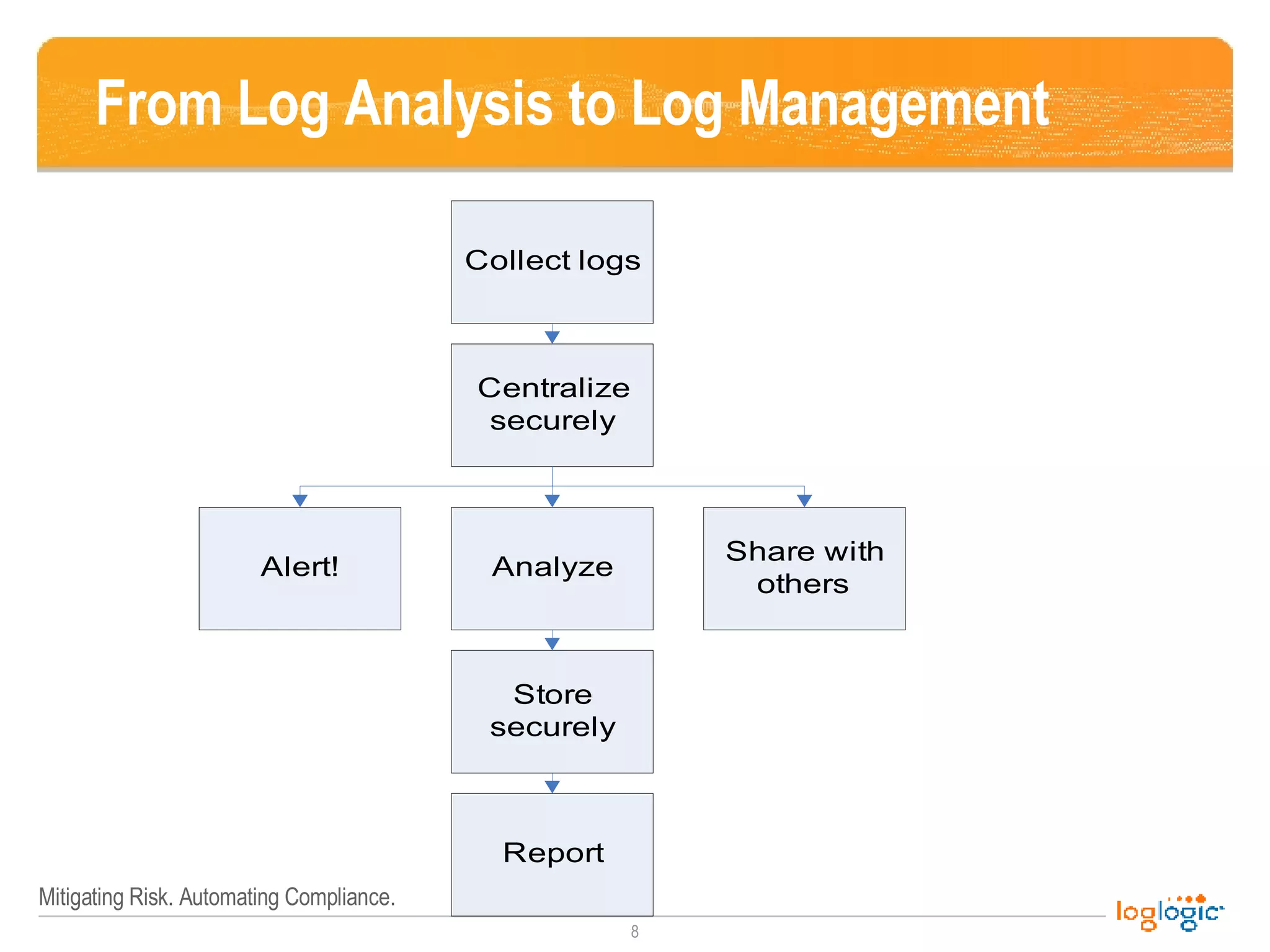





![Computer Security Log Management: Process “ Security log management [is] the process for generating, transmitting, storing, analyzing, and disposing of computer security log data. ”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nist-80092-log-management-guide-in-the-real-world-1195497837416540-3/75/NIST-800-92-Log-Management-Guide-in-the-Real-World-15-2048.jpg)
![Computer Security Log Management: Benefits “ It helps to ensure that computer security records are stored in sufficient detail for an appropriate period of time. Routine log reviews and analysis are beneficial for identifying security incidents, policy violations, fraudulent activity, and operational problems […] Logs can also be useful for performing auditing and forensic analysis , supporting the organization’s internal investigations Establishing baselines, and identifying operational trends and long-term problems .”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nist-80092-log-management-guide-in-the-real-world-1195497837416540-3/75/NIST-800-92-Log-Management-Guide-in-the-Real-World-16-2048.jpg)