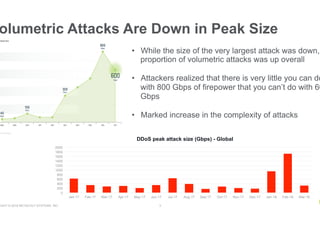
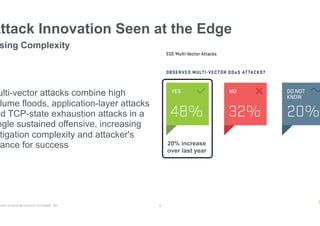
- DDoS attacks are increasing in complexity by combining different attack vectors, though the peak size of volumetric attacks decreased
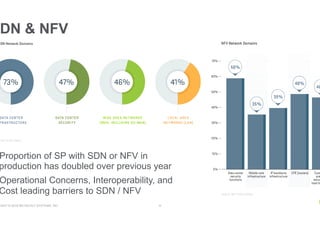
- More service providers are adopting SDN/NFV technologies, with the proportion doubling over the previous year, though interoperability and cost remain barriers
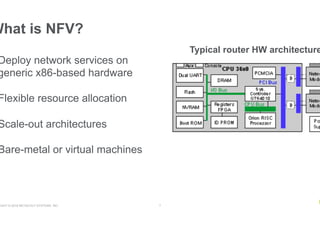
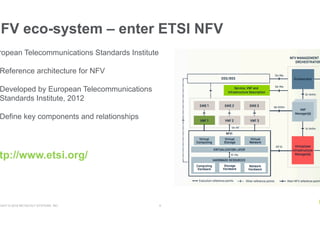
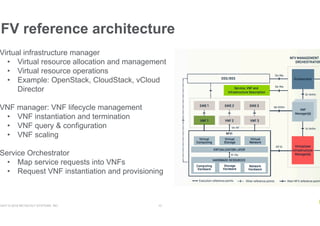
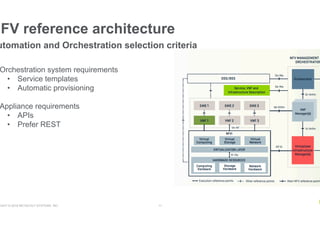
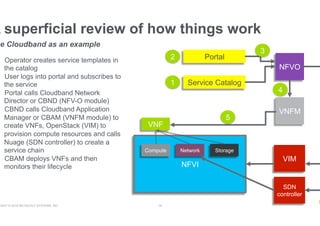
- NFV aims to deploy network services through software on generic hardware rather than proprietary appliances, improving flexibility, but challenges include integration, orchestration, availability, and licensing