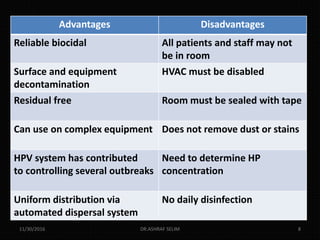
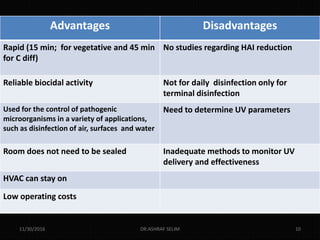
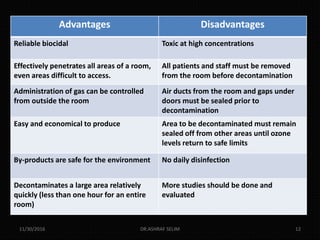
This document discusses new technologies for disinfecting surfaces in hospitals to help prevent healthcare-associated infections. It describes no-touch disinfection technologies like hydrogen peroxide vapor, ultraviolet light, ozone gas, and chlorine dioxide fogging that can disinfect entire rooms. It also discusses self-disinfecting surfaces like those impregnated with copper or silver, coated with light-activated antimicrobials, or having a sharklet pattern that hinders bacterial attachment. Adopting these supplemental methods along with routine cleaning could help reduce recontamination of surfaces between patients and decrease infection risks.