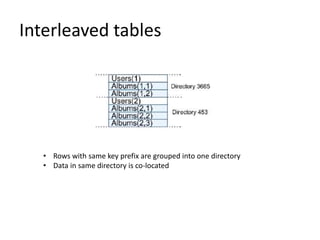
New SQL system called Spanner that can scale like NoSQL databases while providing SQL functions and transaction support. Spanner uses a globally distributed database model across datacenters for high availability. It provides external consistency for reads and writes as well as global snapshot reads. Spanner uses consensus protocol and multi-versioning of rows indexed by timestamp to keep replicas in sync and support snapshot transactions. It also supports schema changes, distributed queries, and sharding to optimize queries across shards.