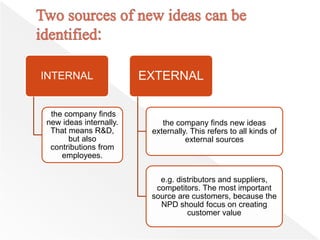
The document outlines the key steps in the new product development process: idea generation, idea screening, feasibility analysis, test marketing, and commercialization. It discusses each step in the process, from initially generating hundreds of ideas internally and externally, filtering them down through screening and feasibility, testing select ideas in realistic market settings, and finally introducing successful new products into the market through manufacturing and marketing efforts. The goal is to guide new product ideas through the process to identify the handful that can become profitable products.