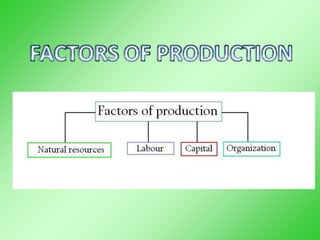
This document provides an overview of economics as a social science. It discusses that economics concerns the production and distribution of wealth between countries and agents. It also explains that economics can be analyzed through microeconomic and macroeconomic models. The document outlines the key agents in an economy as households, firms, government, banks, and the rest of the world. It also discusses the importance of studying economics and the concepts of needs, wants, goods, services, and the factors of production including land, labor, capital and organization. Finally, it describes the primary, secondary, and tertiary sectors of economic activity.