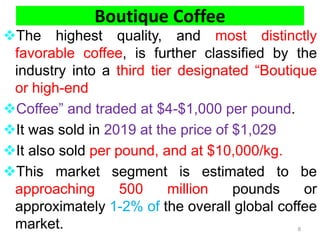
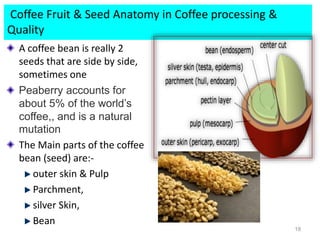
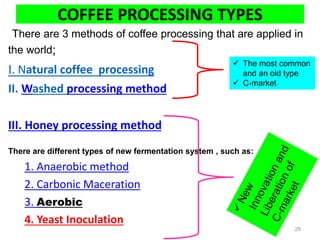
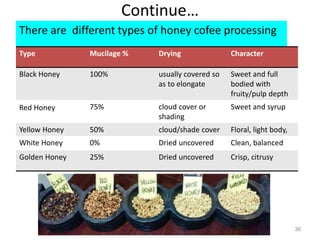
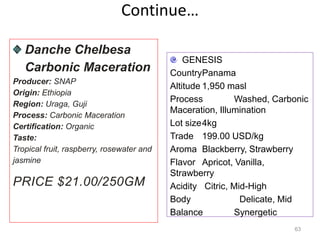
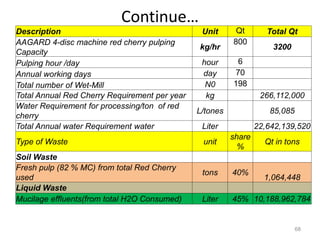
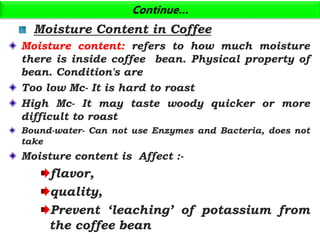
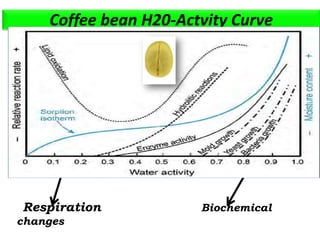
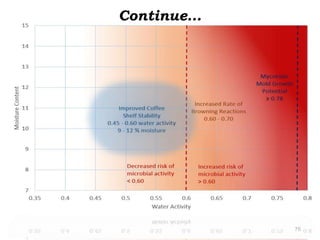
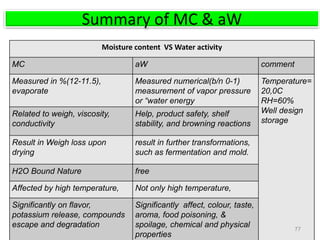
The document discusses the changing landscape of global coffee trade and production, highlighting the importance of processing methods that influence flavor and price. It categorizes coffee into commodity, specialty, and boutique tiers, emphasizing quality and market segmentation. Additionally, it details the science of coffee processing including fermentation and various processing techniques, underscoring the need for careful management of each step to enhance coffee quality.