The document summarizes the process of an action potential in a neuron. It discusses how:
1) In the resting state, sodium ions are concentrated outside the cell and potassium ions inside, creating a negative charge inside.
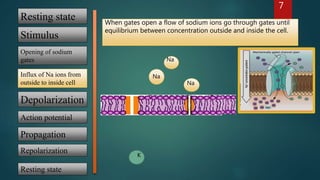
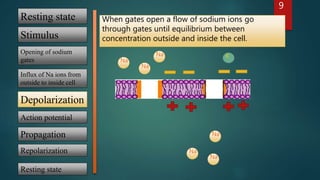
2) A stimulus causes sodium gates to open, allowing sodium ions to rush inside and depolarize the cell.
3) As the cell reaches threshold, an action potential is generated and propagates along the membrane as sodium gates open down the axon.
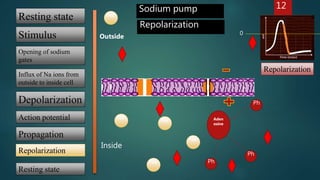
4) The sodium gates then close and potassium gates open, pumping ions out to repolarize the cell back to its resting potential.