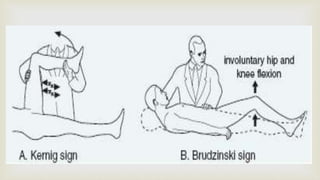
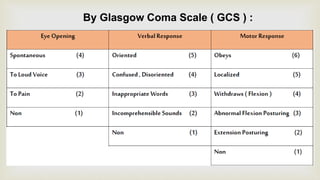
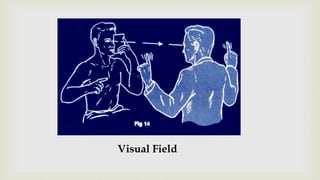
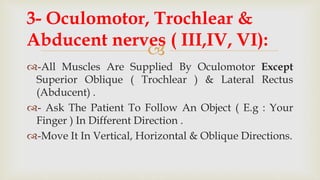
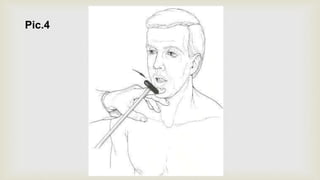
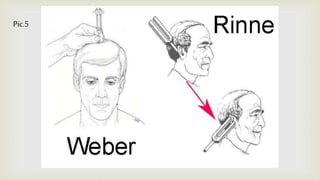
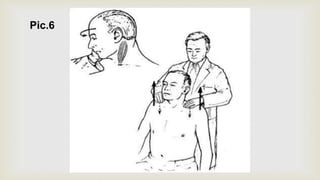
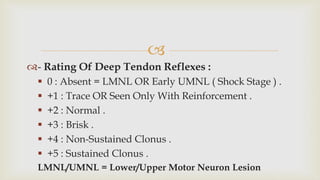
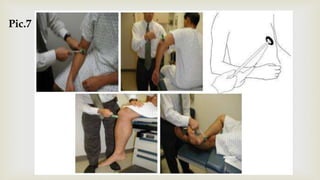
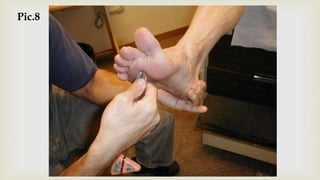
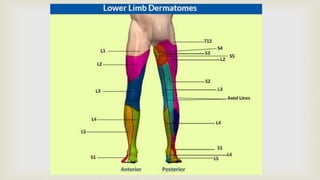
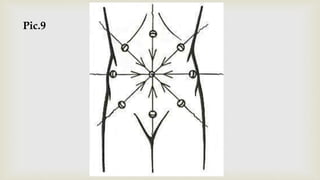
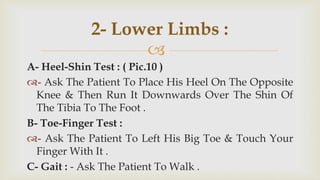
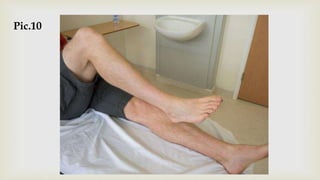
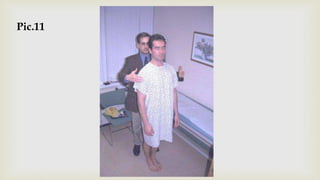
This document provides a summary of how to perform a neurological examination. It begins with an introduction and history taking. It then describes examining the patient's general appearance, vital signs, skin, skull, spine and growth. Tests for meningeal irritation like neck stiffness, Kernig's sign and Brudzinski's sign are outlined. Higher cognitive functions including orientation, memory, speech and handedness are assessed. The rest of the examination involves testing cranial nerves, motor function, reflexes, sensation and cerebellar function.