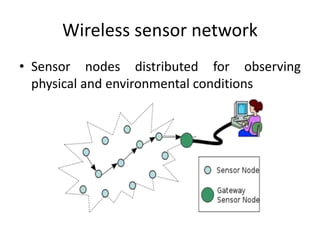
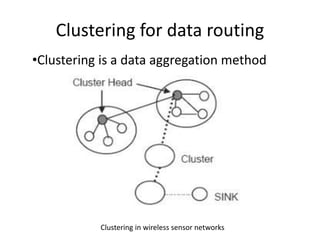
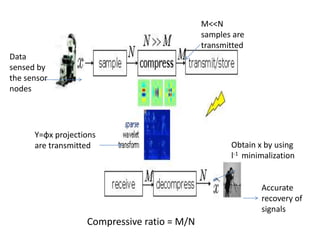
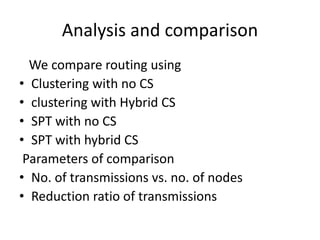
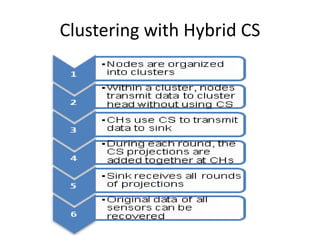
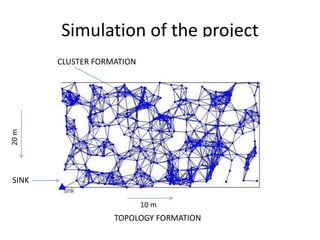
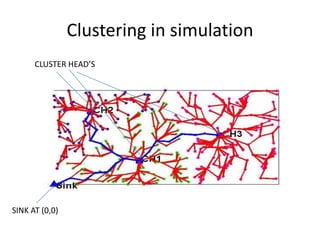
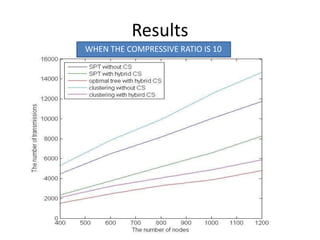
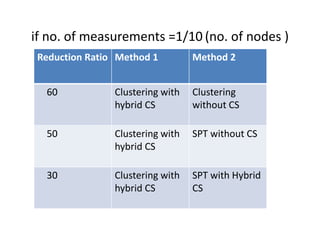
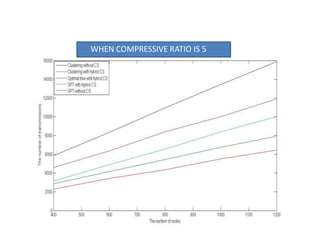
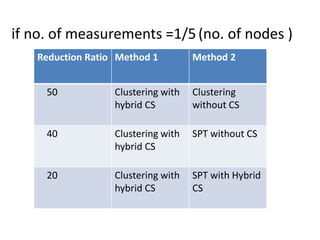
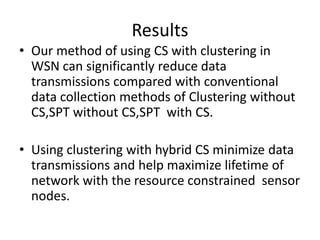
Clustering is commonly used for data routing in wireless sensor networks. This document proposes using compressive sensing (CS) with clustering to further reduce data transmissions. Simulation results show that clustering with hybrid CS can significantly reduce transmissions compared to clustering without CS, shortest path tree routing without CS, and shortest path tree routing with CS. Specifically, when the compressive ratio is 10, clustering with hybrid CS reduced transmissions by 60% compared to clustering without CS and 50% compared to the other methods. When the ratio is 5, reductions were 50%, 40%, and 20% respectively. Thus the proposed method of using CS with clustering minimizes data and helps maximize the lifetime of resource-constrained sensor networks.