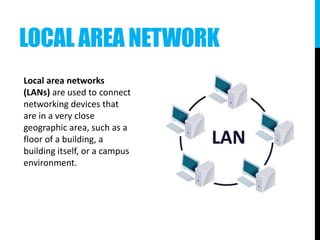
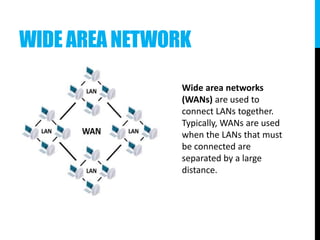
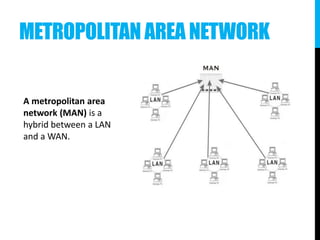
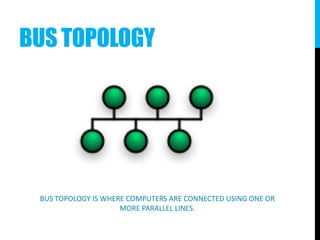
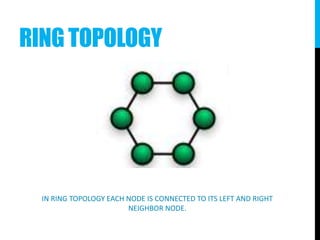
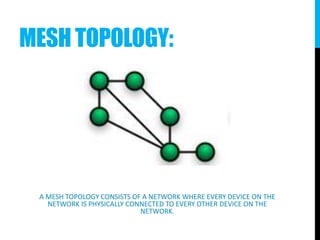
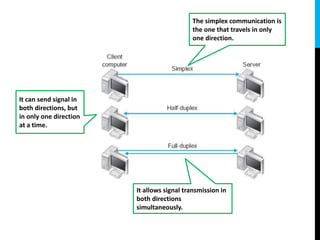
The document provides an introduction to networking, explaining key terms and concepts important for IT professionals, such as types of networks (LAN, WAN, MAN) and network topology (bus, star, ring, tree, mesh). It also outlines the functions of various network devices like routers, switches, and firewalls, and describes the distinctions between intranets, extranets, and the internet. Overall, it serves as a foundational overview of networking principles and applications.