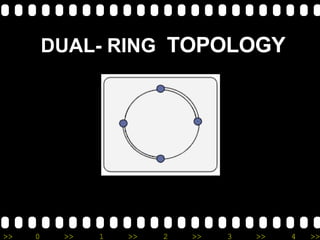
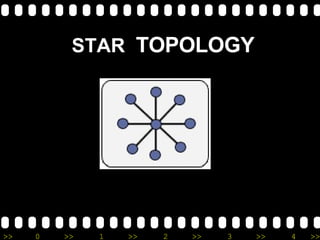
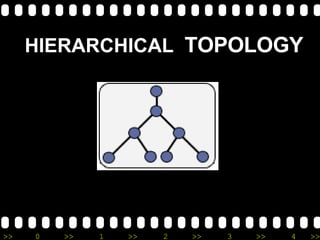
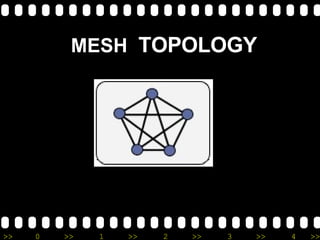
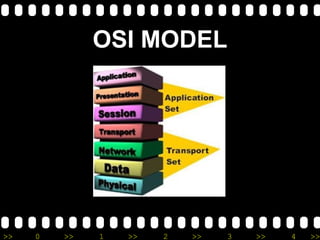
The document provides an overview of basic networking concepts, including:
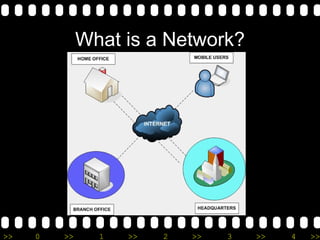
1) It defines what a network is and discusses the benefits of networking such as resource sharing, data sharing, and mobility.
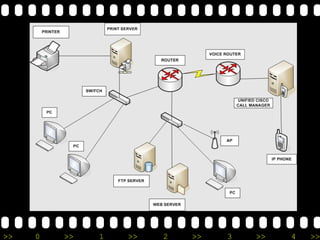
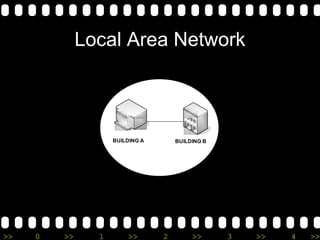
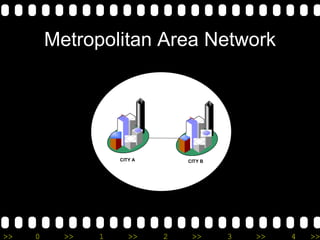
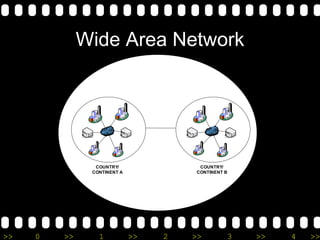
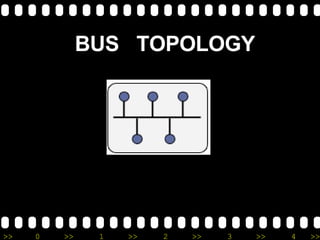
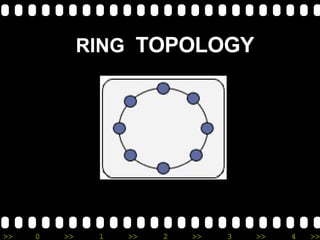
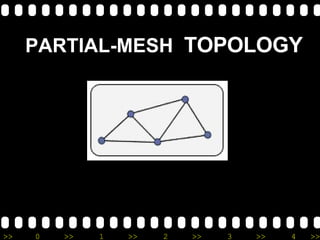
2) It lists different types of networks including personal area networks, local area networks, metropolitan area networks, and wide area networks.
3) It briefly outlines the history of networking, including early networks developed in the 1960s-1970s that helped lay the foundations for the ARPANET and Internet.