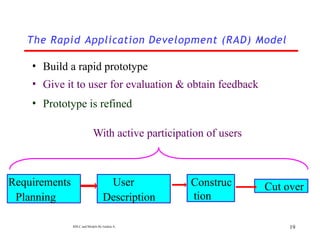
The document outlines the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), detailing its stages such as feasibility, analysis, design, implementation, testing, deployment, and maintenance. It discusses the benefits of SDLC, including better planning, risk management, and customer satisfaction, along with various software development models like Rapid Application Development (RAD) and Prototyping. Additionally, the document emphasizes the importance of user participation, team skills, and appropriate conditions for applying these methodologies.