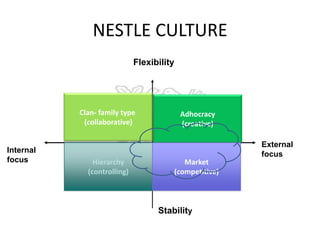
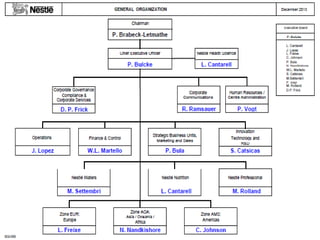
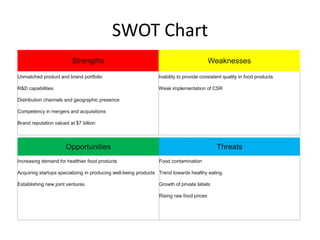
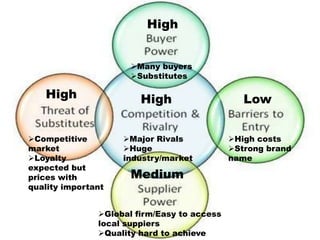
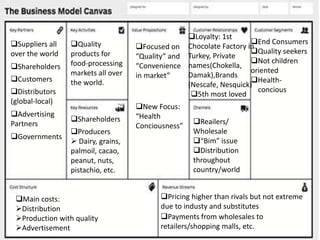
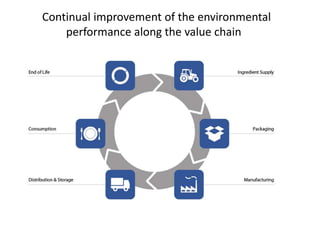
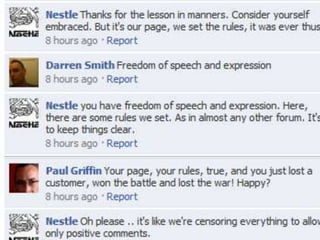
This document provides an overview of Nestlé, the largest food company in the world. It discusses Nestlé's industry analysis, products, corporate culture, strategy, organizational structure, and challenges. Nestlé operates in the food processing industry, producing packaged foods with extended shelf lives. It focuses on health, nutrition and wellness, and differentiates its products through quality and innovation. The company culture emphasizes flexibility, creativity, and responsiveness to markets. Nestlé's corporate strategy involves product differentiation, acquisitions, and creating shared value. It faces challenges around flexibility as a large company, supplier issues, and maintaining a positive public image.