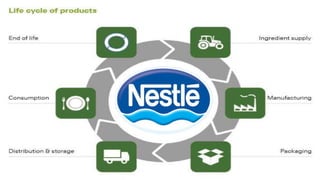
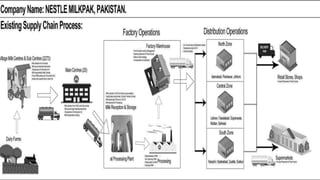
Nestle is the world's largest food and beverage company founded in 1867. It has grown significantly through mergers and acquisitions. To improve efficiency and standardize processes across subsidiaries, Nestle implemented an ERP system from SAP at a cost of $200 million. The ERP system integrated planning, manufacturing, sales and distribution. It helped Nestle achieve savings, better forecasting and standardized operations globally.