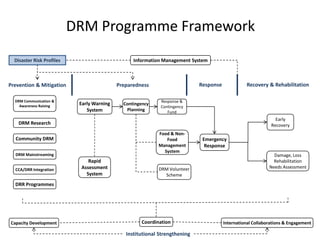
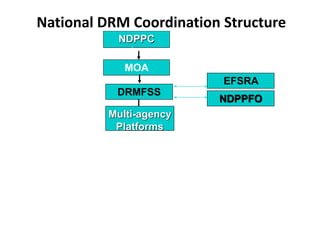
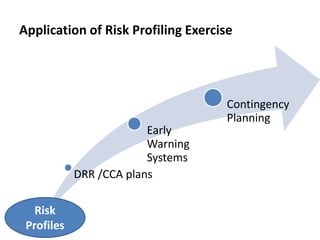
A Disaster Risk Management Strategic Programme and Investment Framework is being designed to translate this new approach into action in a coordinated way across stakeholders. It will help mainstream disaster risk reduction into development planning and maximize resources