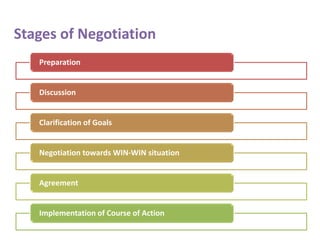
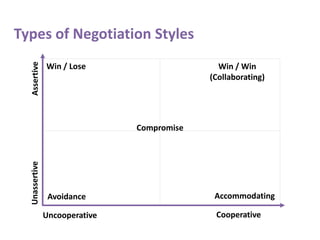
Negotiation is a method to settle differences and reach agreements without conflict or resentment. There are six stages of negotiation: preparation, discussion, clarifying goals, negotiating for a win-win outcome, agreement, and implementing the agreed course of action. Key elements for effective negotiation include having the right attitudes, interpersonal skills like listening and problem solving, and preparation and knowledge. There are five main negotiation styles - win/lose, avoidance, accommodation, compromise, and collaboration which aims for a win-win outcome where both sides' needs are met. Maintaining relationships, focusing on interests not positions, generating options, and clarifying meanings are important for successful negotiation.