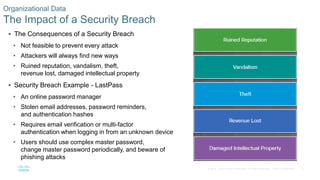
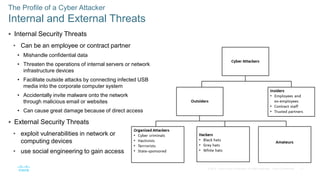
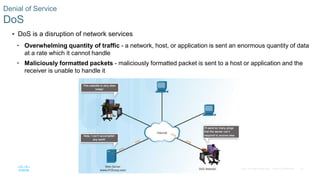
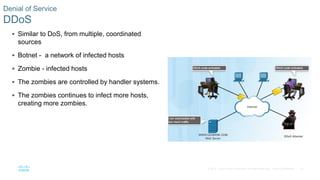
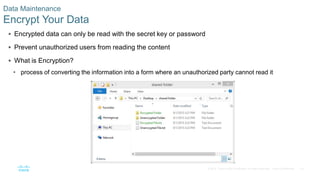
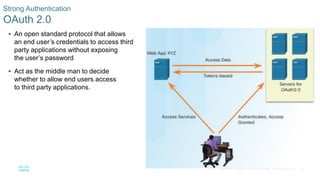
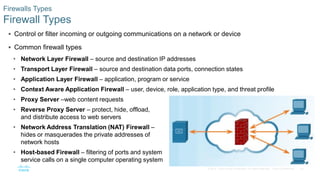
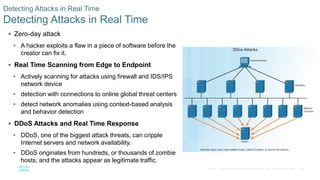
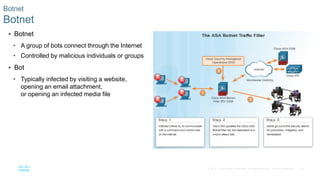
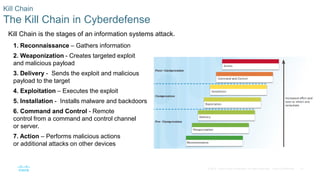
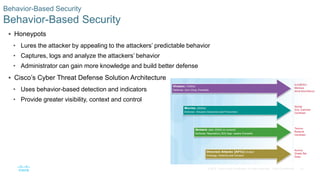
This document discusses the need for cybersecurity and provides an introduction to related topics. It describes what cybersecurity is, the importance of protecting personal and organizational data, and the impact of security breaches. It also profiles different types of cyber attackers, explores common attacks and infiltration methods, and categorizes types of malware and security vulnerabilities.