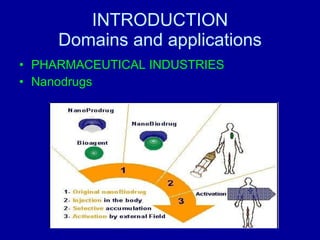
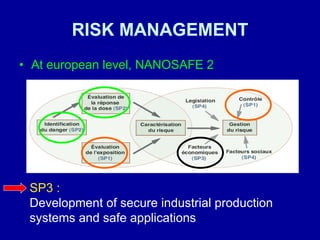
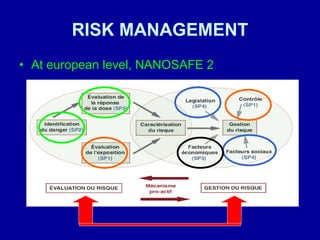
This document discusses the opportunities and risks of nanotechnology. It describes various applications of nanotechnology in fields like food, agriculture, space exploration, the military, energy, electronics and more. However, it also notes health and environmental risks are not yet well understood. There are concerns about nanoparticle toxicity if inhaled or absorbed through skin/digestive tract. Precautionary measures are needed like tracking nanoparticles, safety research, and regulations to protect people and the environment while continuing nanotechnology development.