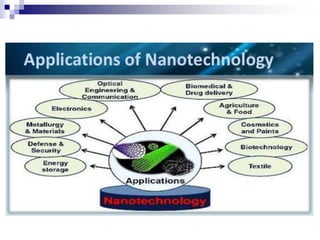
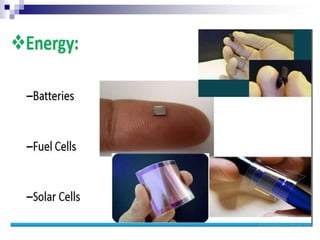
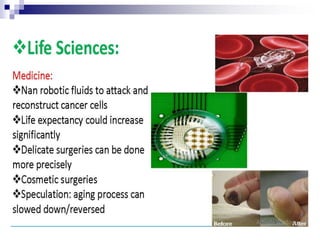
This document provides an overview of nanotechnology. It defines nanotechnology as engineering at the nanoscale level, or the ability to manipulate individual atoms and molecules. The document outlines two main approaches to nanotechnology - top-down, which builds down from larger to smaller structures, and bottom-up, which builds up from individual atoms. It also discusses some potential applications of nanotechnology such as strong fibers, atomic plants to handle radioactive materials, electronics like transistors and diodes, and space applications using small, lightweight machines. Overall, the document serves as an introduction to nanotechnology, its approaches, potential applications, and ability to manipulate matter at the atomic scale.