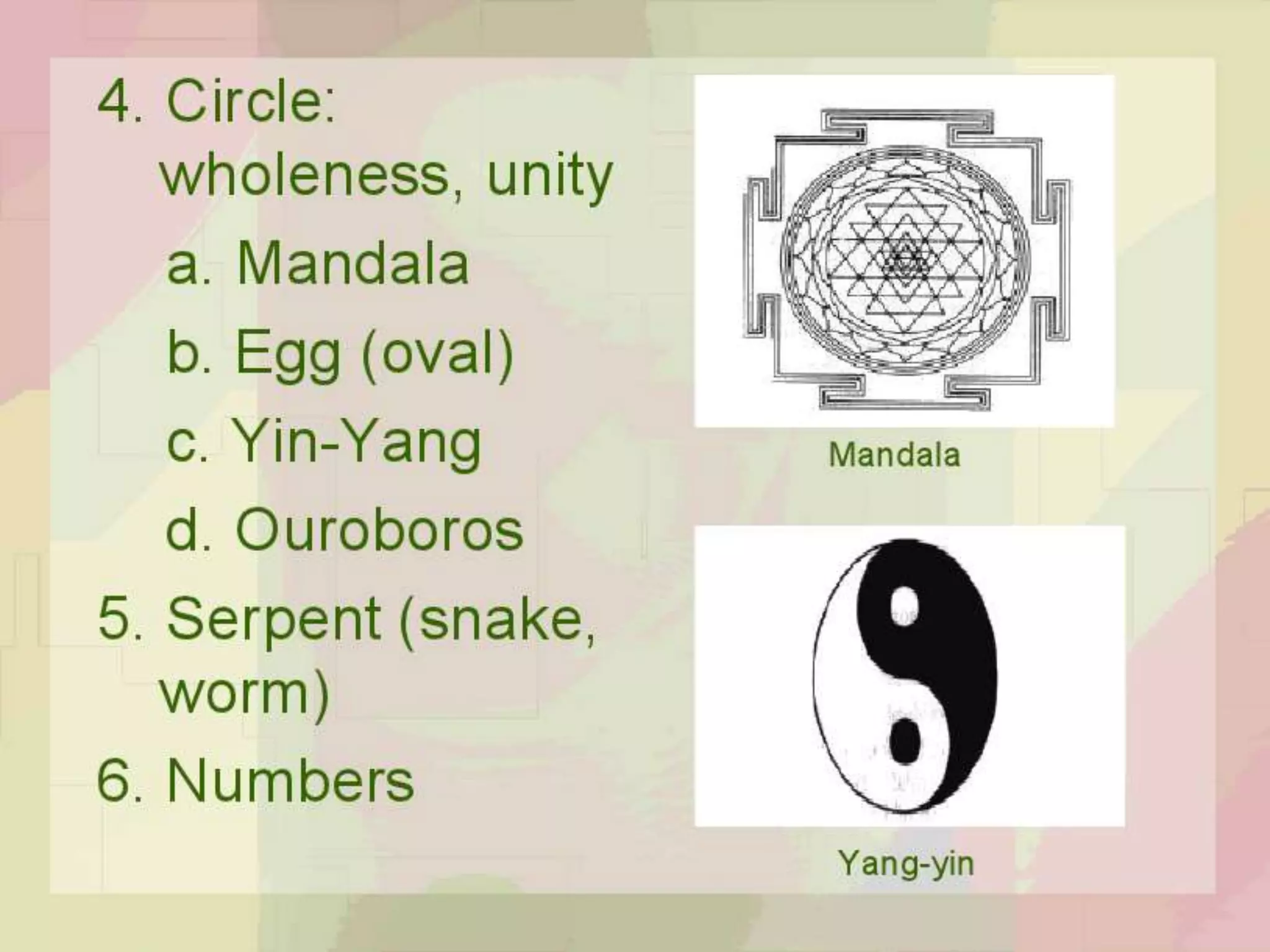
This document discusses archetypal criticism as a type of literary theory. Archetypal criticism examines recurring myths, symbols, and character types in narratives by focusing on patterns embedded in the collective unconscious. It assumes there are universal archetypes that elicit similar responses in all people. Proponents of archetypal criticism like Carl Jung and Northrop Frye believe it can help readers connect with basic human anxieties and desires represented in literature. Archetypal criticism provides a universalistic approach to analyzing works that are highly symbolic.