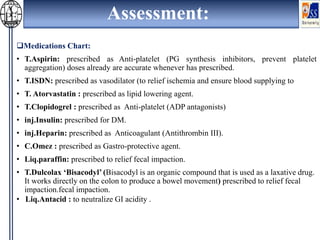
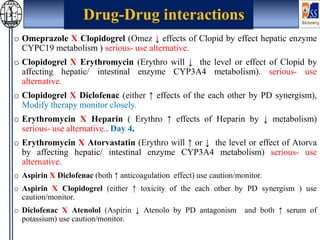
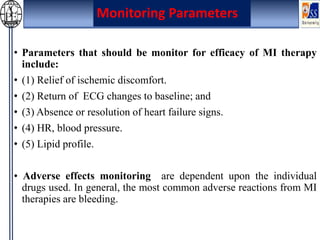
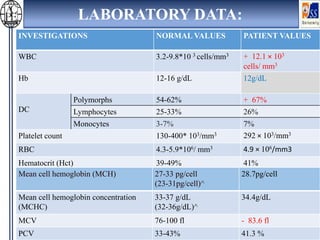
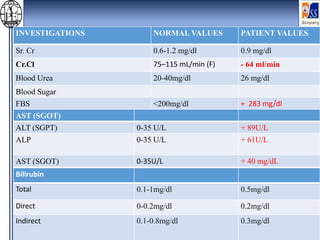
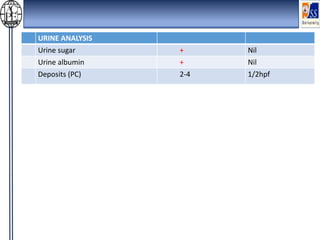
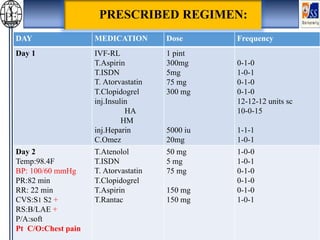
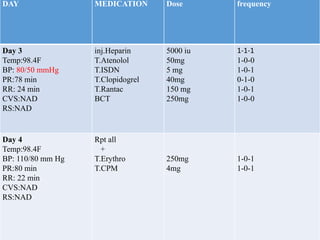
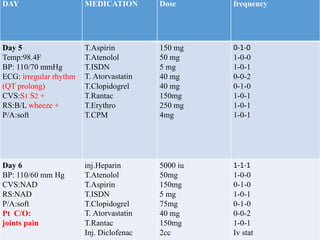
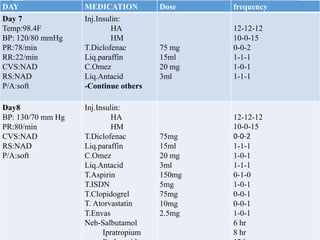
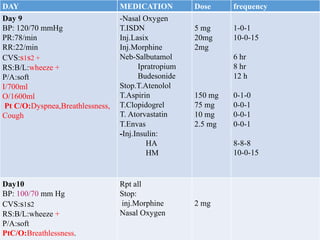
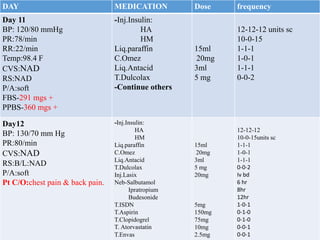
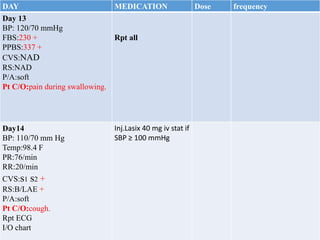
This case presentation describes an 80-year-old female patient admitted to the ICU with a diagnosis of NSTEMI. Her medical history includes diabetes mellitus. On admission, her ECG showed NSTEMI and lab work was notable for elevated WBC and blood sugar. She was started on medications including aspirin, clopidogrel, atorvastatin, ISDN, and insulin. Over her 14-day hospital stay, her medications were adjusted for blood pressure control and management of symptoms like dyspnea and joint pain. Potential drug-drug interactions between her medications including omeprazole and clopidogrel were also assessed.






![• Dose adjustment in Mild renal insufficiency for medications required that.
• Prevent and Monitoring ADRs [ADRs are more common in elderly (20-25%
more then in the young) They are mostly dose related rather than idiosyncratic].
• Poly pharmacy may results in increased drug interaction and drug disease
interaction, ADRs and non compliance.
• Ensure reduce of poly-pharmacy.
• Consider potential drug interactions.
• Treating of only the disorder that need to be treated.
• QAL (quality adjusted lifetime).
• Patient counseling and advice.
• Evaluation and monitoring of therapy.
My Roles :](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mi-190108185712/85/Myocardial-infarction-18-320.jpg)