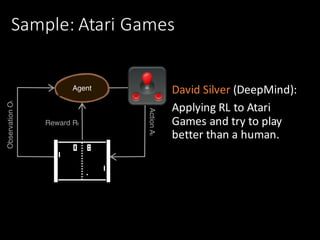
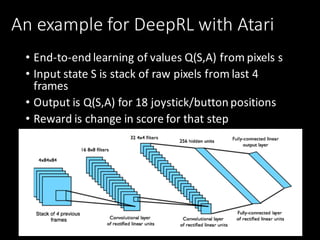
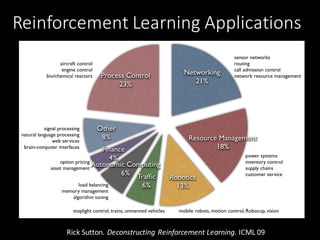
This document provides an introduction to reinforcement learning. It discusses how reinforcement learning agents interact with environments to maximize rewards. It covers key concepts like the reinforcement learning problem, aspects of RL agents including policies and value functions, and popular approaches like value-based, policy-based, and model-based RL. Examples of applying RL to problems like process control, Atari games, and robotics are presented. The document aims to provide context and motivation for using reinforcement learning.



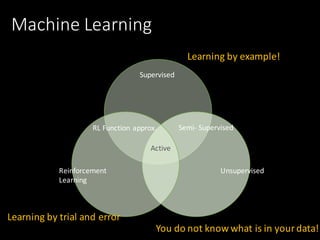
![Machine Learning
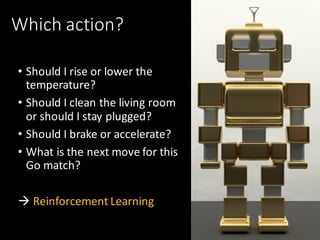
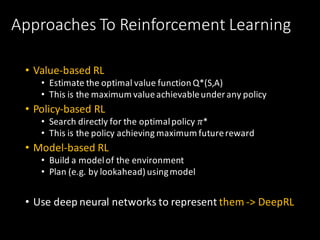
We can answer the 4 major questions:
• How much/How many?
• Which category?
• Which groups? [What is wrong?]
• Which action?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1655tilly-170405112708/85/My-Robot-Can-Learn-Using-Reinforcement-Learning-to-Teach-my-Robot-8-320.jpg)






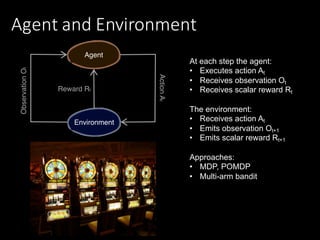

![Components of an RL agent
An RL agent may include one or more of these components:
• Policy: agent's behavior function
• Maps from state to action
• Deterministic policy A=𝜋(S)
• Stochastic policy 𝜋 𝐴 𝑆 = ℙ[𝐴|𝑆]
• Value function: how good is each state and/or action
• How much reward will I get from action
• Optimal Value Function
𝑄∗
𝑆, 𝐴 = 𝔼/0[𝑅 + 𝛾 max 𝑄∗
𝑆0
, 𝐴0
| 𝑆, 𝐴]
• Model: agent's representation of the environment
𝜋
S
A
𝑄
S
V
A
𝑇, 𝑅
S
S’
A
R](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1655tilly-170405112708/85/My-Robot-Can-Learn-Using-Reinforcement-Learning-to-Teach-my-Robot-21-320.jpg)

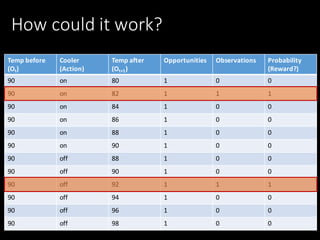
![The result: A model
Temp before Cooler
[Action]
Temp after Opportunities Observations Probability
90 on 80 404 10 0.025
90 on 82 404 134 0.332
90 on 84 404 215 0.532
90 on 86 404 34 0.084
90 on 88 404 9 0.022
90 on 90 404 2 0.005
90 off 88 381 1 0.003
90 off 90 381 23 0.059
90 off 92 381 101 0.261
90 off 94 381 163 0.421
90 off 96 381 75 0.194
90 off 98 381 24 0.062](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1655tilly-170405112708/85/My-Robot-Can-Learn-Using-Reinforcement-Learning-to-Teach-my-Robot-26-320.jpg)
![Now: Take it backward St -> A -> St+1
Temp before Cooler
[Action]
Temp after Opportunities Observations Probability
90 on 80 404 10 0.025
90 on 82 404 134 0.332
90 on 84 404 215 0.532
90 on 86 404 34 0.084
90 on 88 404 9 0.022
90 on 90 404 2 0.005
90 off 88 381 1 0.003
90 off 90 381 23 0.059
90 off 92 381 101 0.261
90 off 94 381 163 0.421
90 off 96 381 75 0.194
90 off 98 381 24 0.062](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1655tilly-170405112708/85/My-Robot-Can-Learn-Using-Reinforcement-Learning-to-Teach-my-Robot-27-320.jpg)