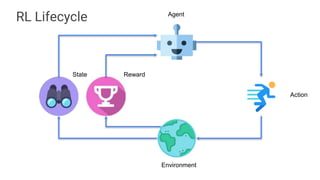
This document discusses using reinforcement learning for autonomous vehicles. It begins with an overview of reinforcement learning and examples of its applications. It then presents a case study of using RL for motion control of autonomous vehicles. The key steps are: 1) identifying the problem, 2) defining the reward function, 3) designing the state space, 4) choosing an algorithm like DDPG or SAC, 5) training the agent, 6) evaluating the trained agent, and 7) considering how to transfer the agent from simulation to the real world. Training requires balancing challenge and success. The document concludes by discussing resources for getting started with reinforcement learning.