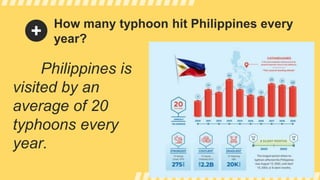
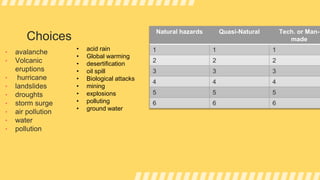
This document provides information about disaster readiness and risk reduction. It includes activities to test recall of disaster-related terms, have students share experiences with hazards, analyze pictures of hazards, and arrange examples of different types of hazards into categories. Natural hazards discussed include typhoons, earthquakes, and tsunamis. Quasi-natural hazards include smog, desertification, and pollution. Technological or man-made hazards include oil spills, biological attacks, mining, and explosions. The document aims to educate students on identifying, categorizing, and mitigating different types of hazards.