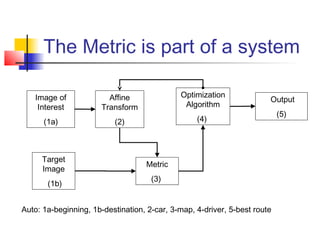
1) The document describes the mutual information metric, which is used to evaluate the similarity between two images after an affine transformation.
2) It discusses evaluating the metric based on factors like execution time, speed, and quality of the optimization. It also examines the relationship between image size and computation time.
3) The document explores sub-pixel resolution with the metric and analyzing histograms of the original and transformed images to evaluate the mapping between them. It considers future directions like using the histogram to determine the next transform.