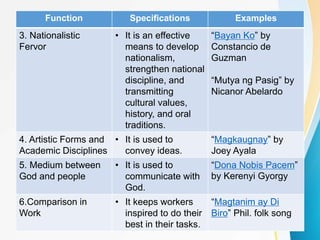
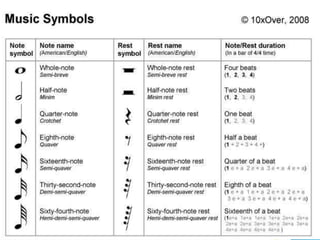
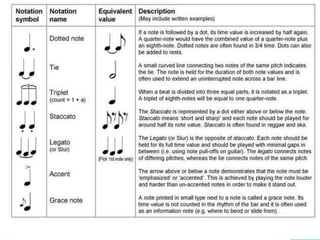
This document defines the basic elements of music and their functions. It discusses that music is organized sound with elements like pitch, duration, timbre, harmony, texture and dynamics. It then explains the various functions of music including aesthetics, emotional appeal, nationalism, entertainment, and marketing. It concludes by describing the key musical elements of rhythm, melody, harmony, texture, timbre, dynamics, form, and musical instruments.