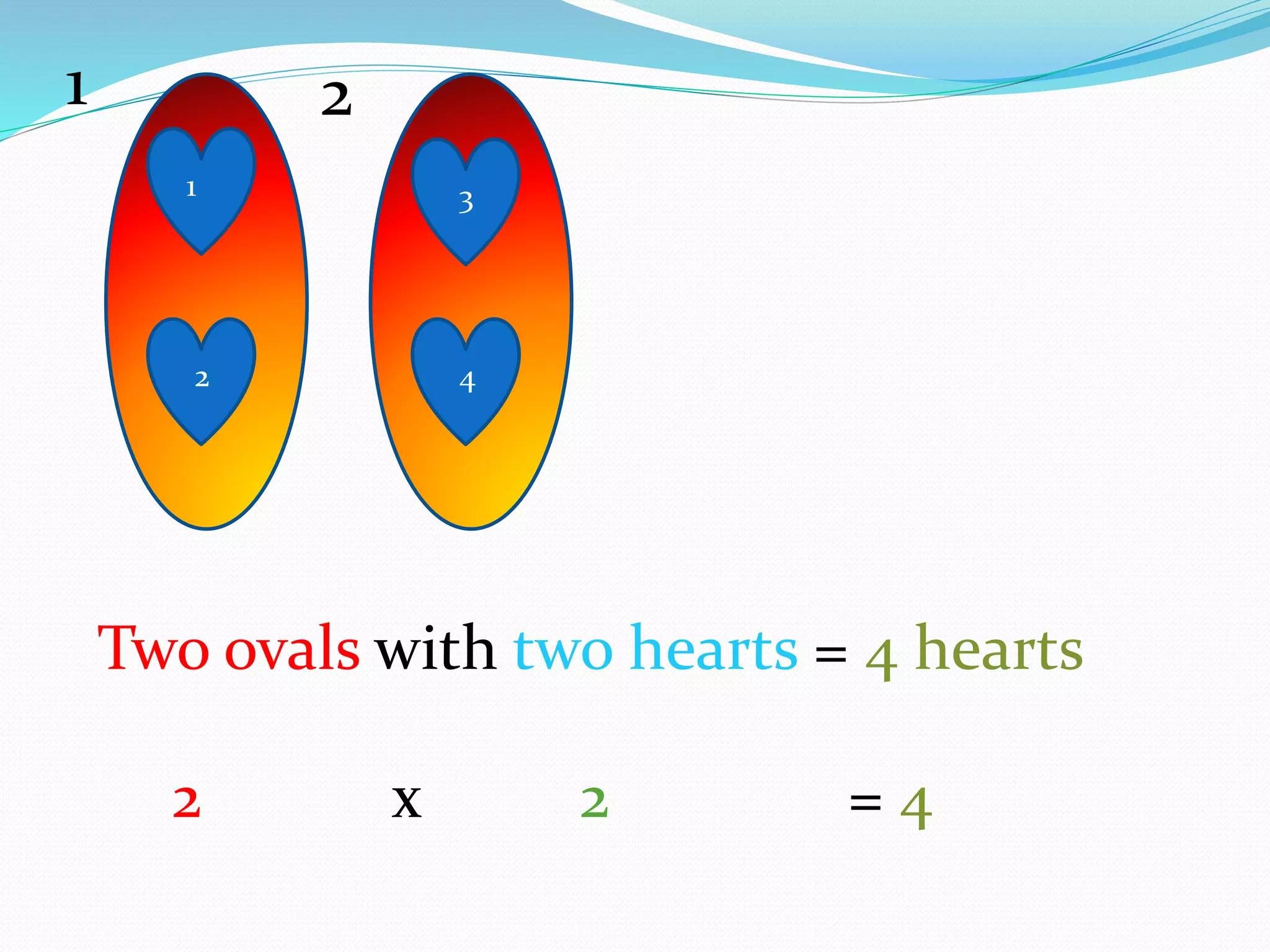
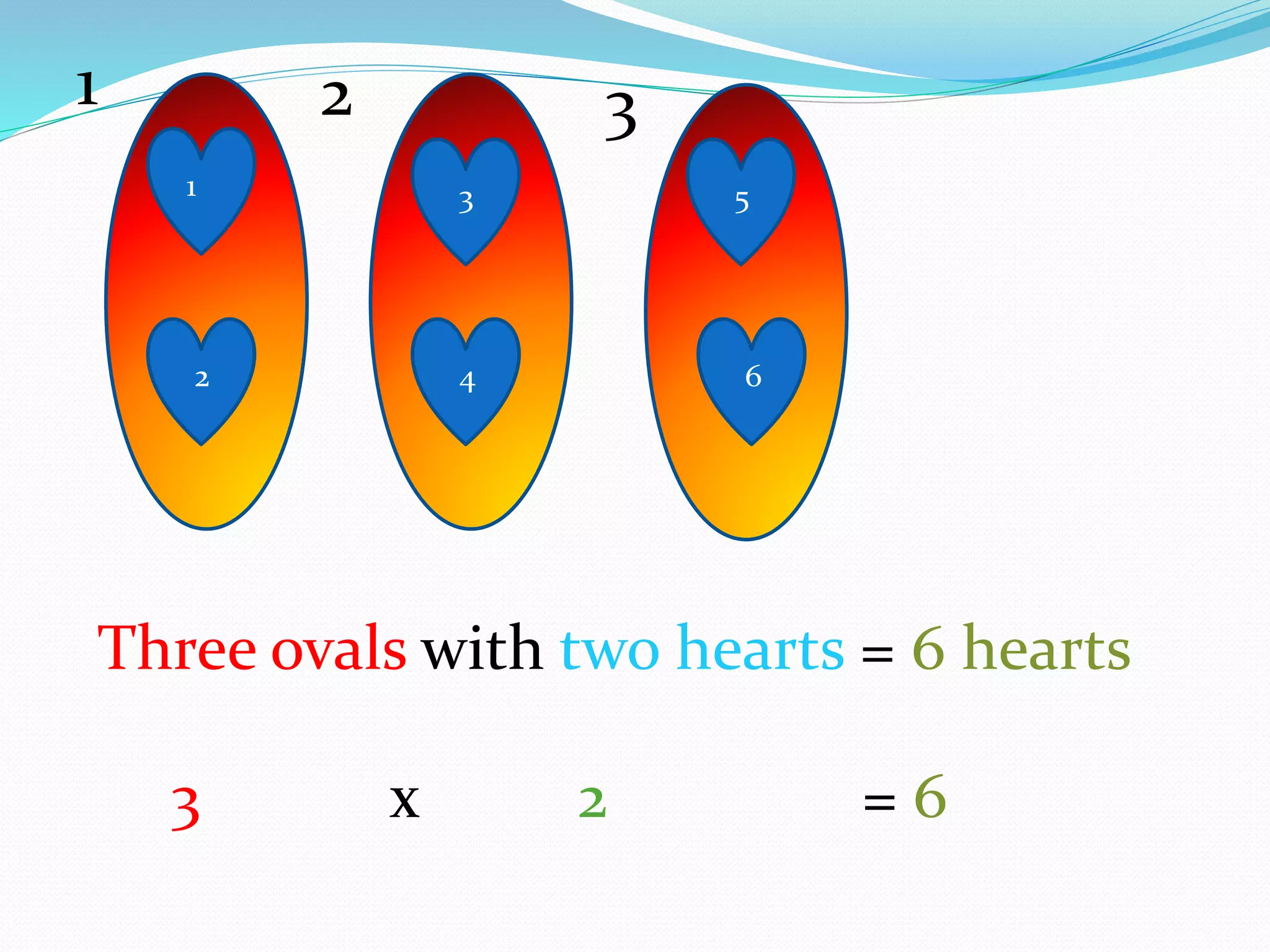
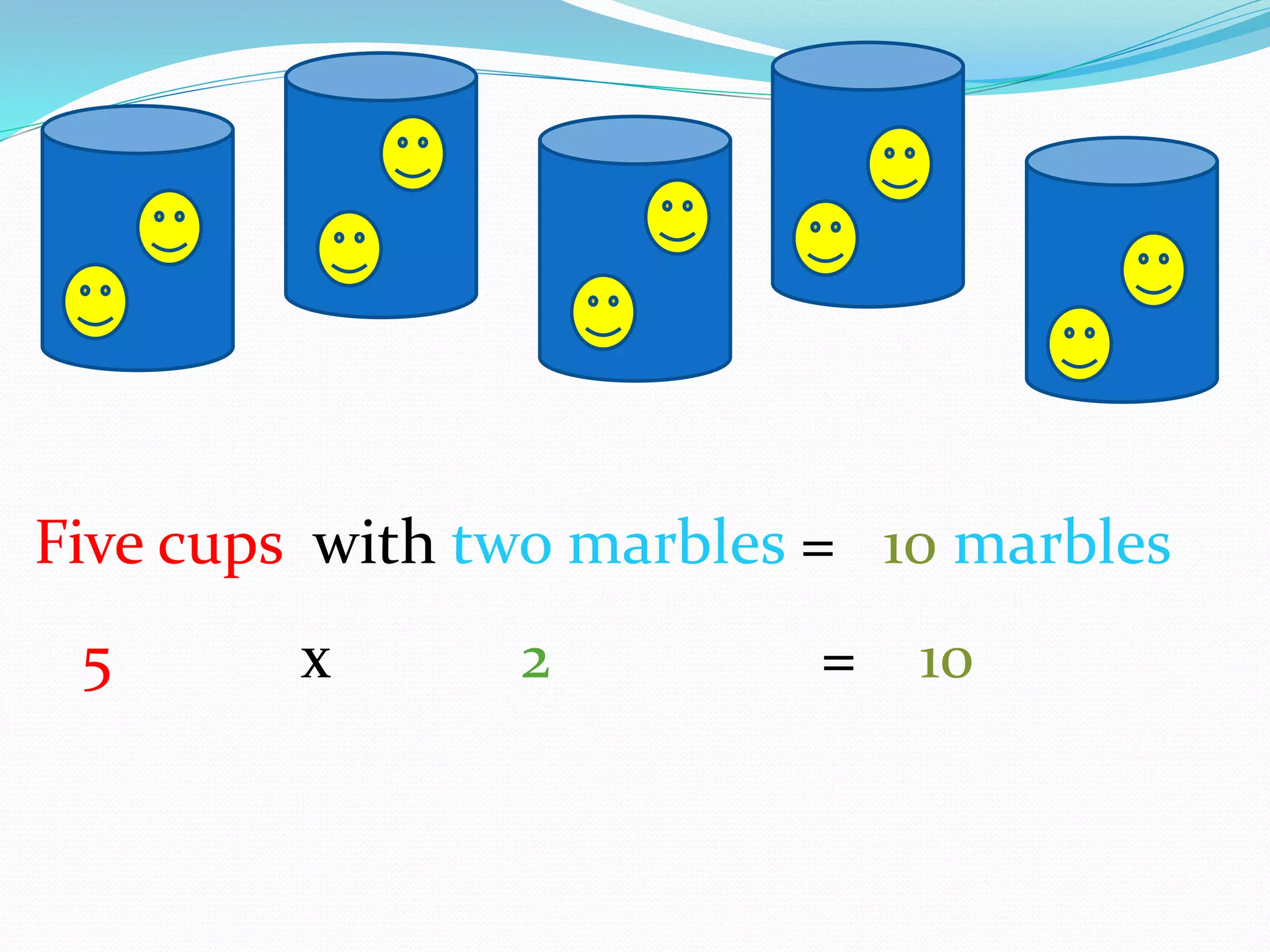
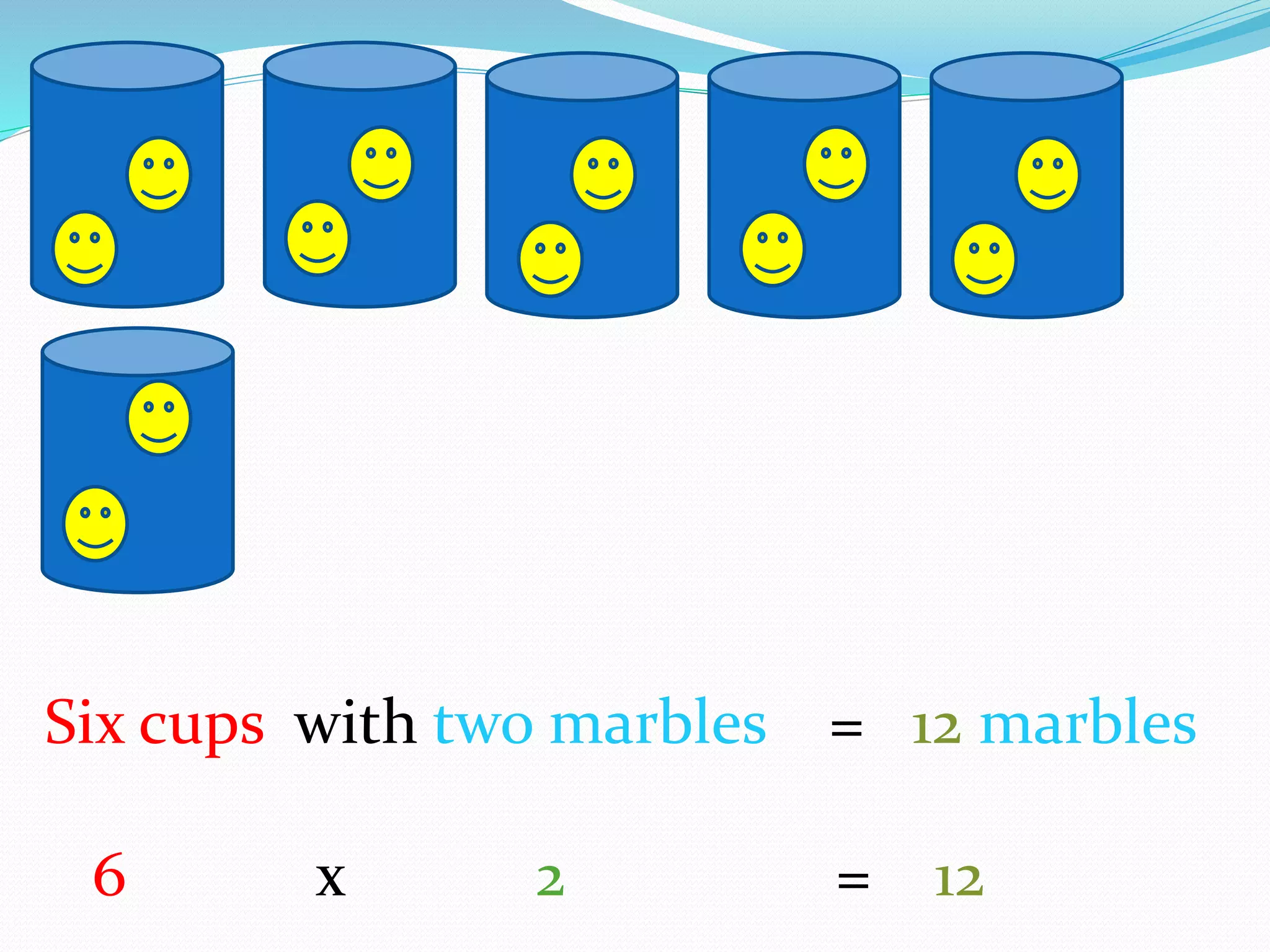
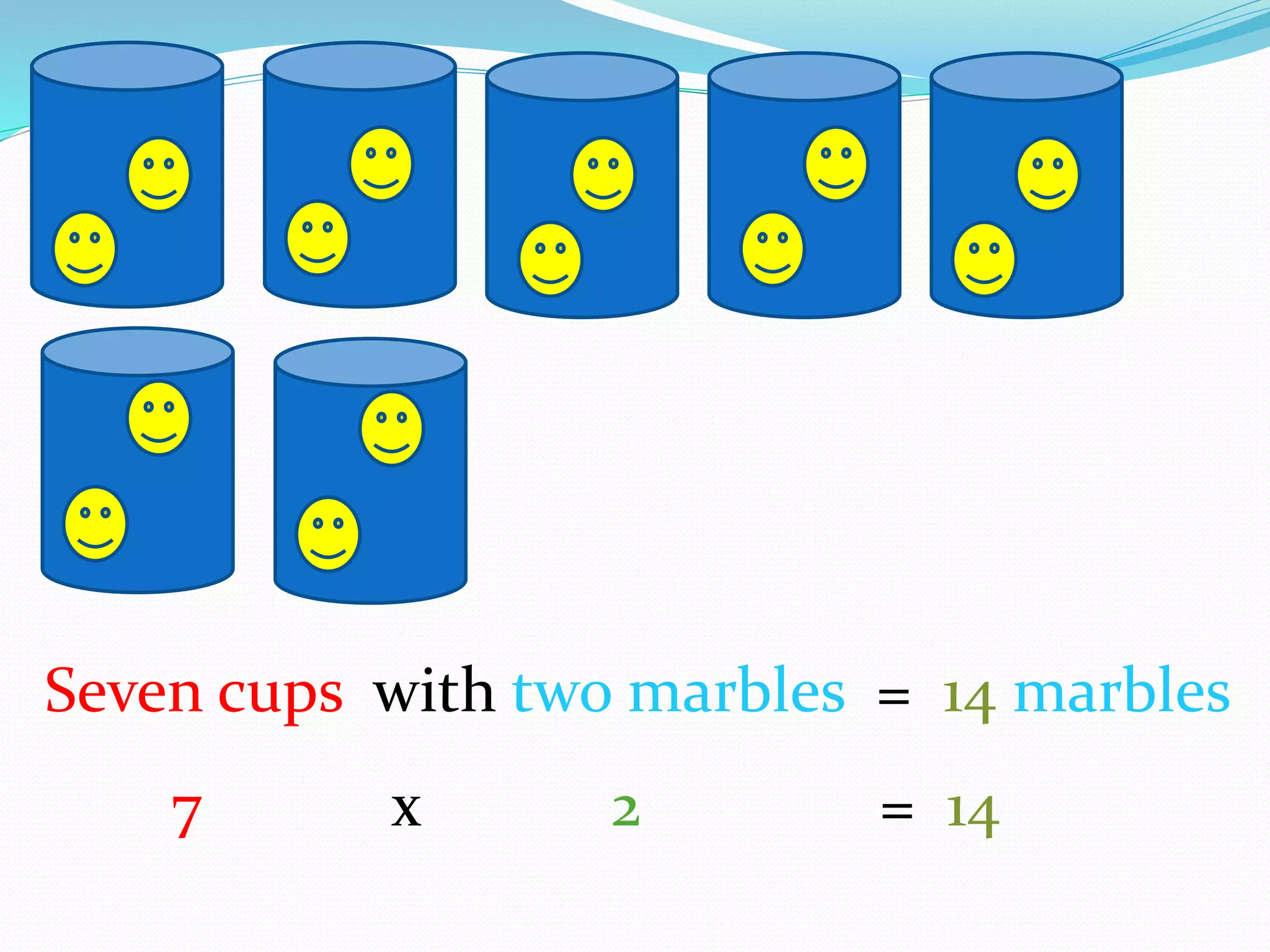
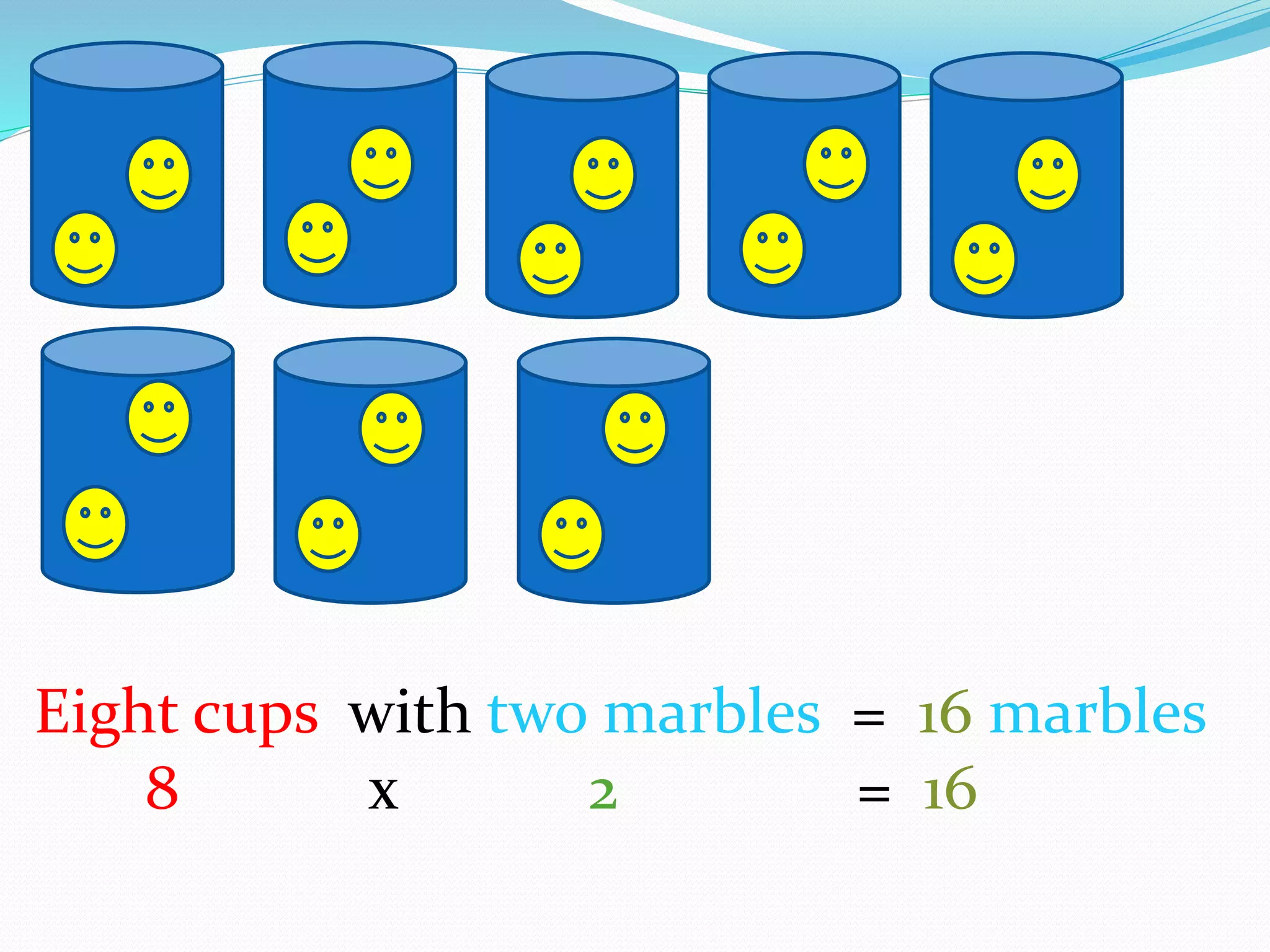
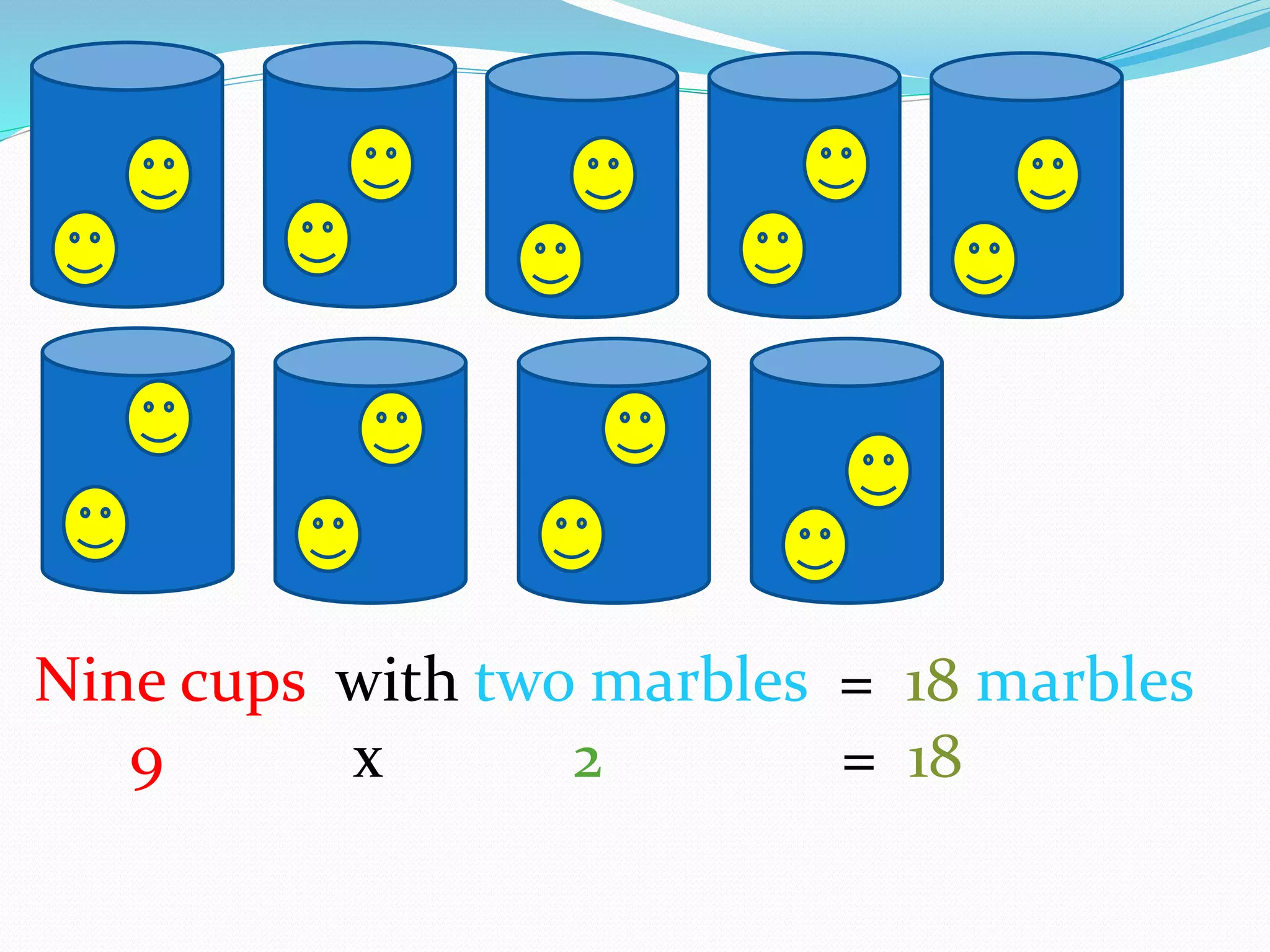
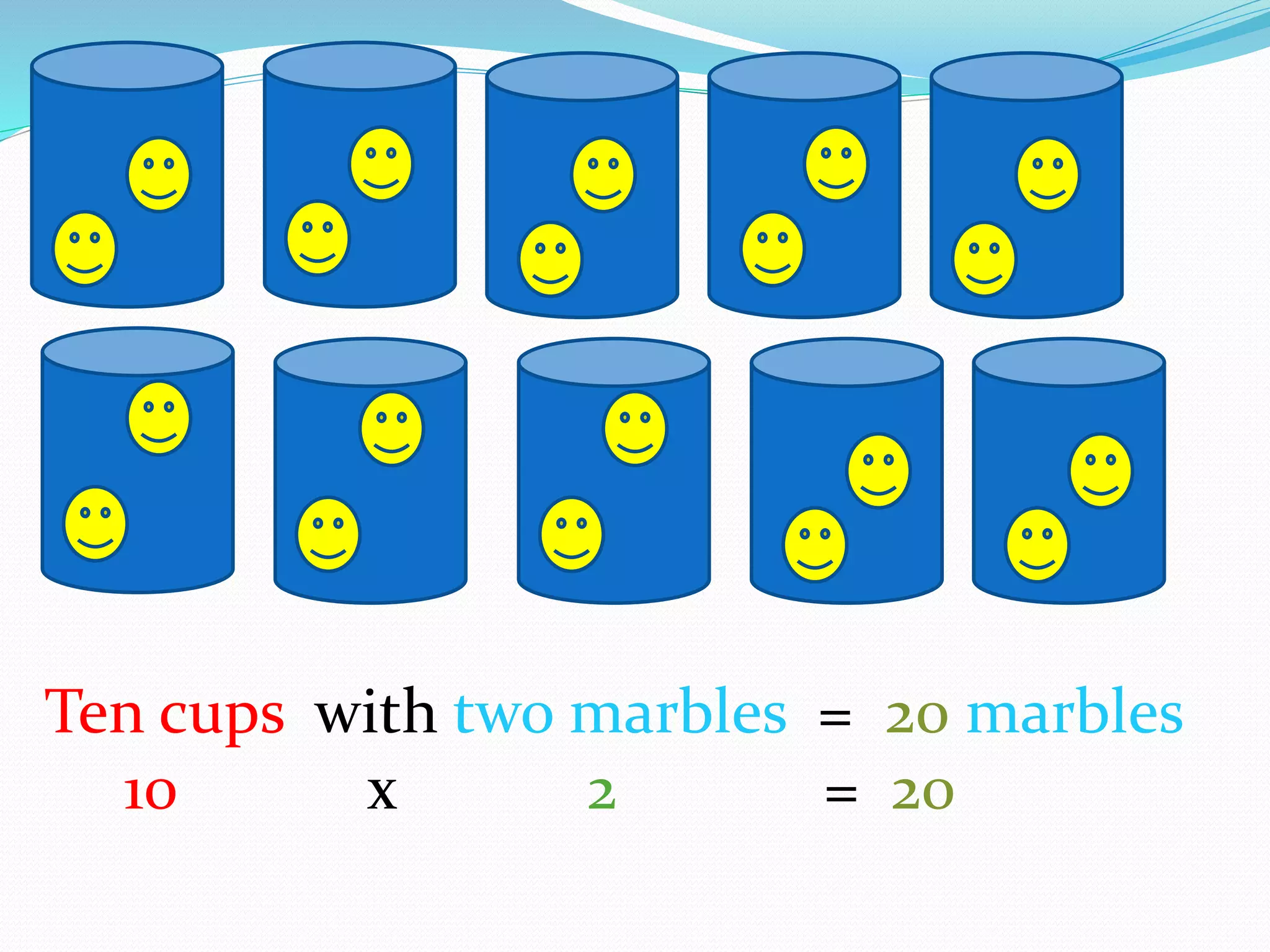
This document provides information for a lesson plan to teach basic multiplication facts to a Standard 1 class of about 20 seven-year-olds. The lesson will last 10-15 minutes and introduce multiplication as repeated addition using manipulatives like crown corks and coins. A PowerPoint presentation with examples in the two times table will be shown. Students will then complete a worksheet and short evaluation of their new understanding that multiplication is the grouping of sets of objects.