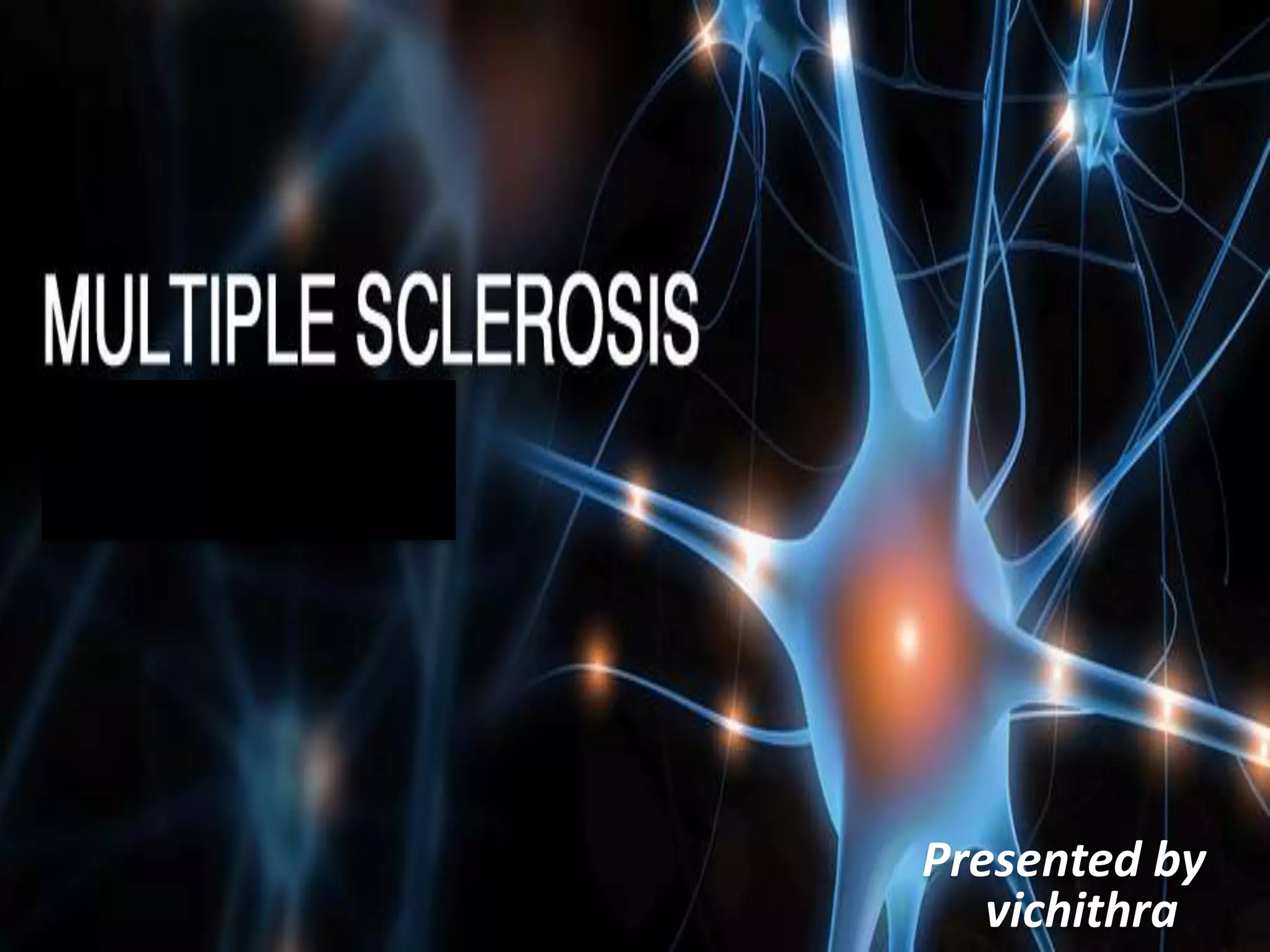
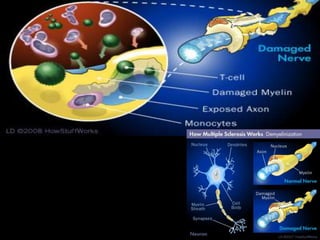
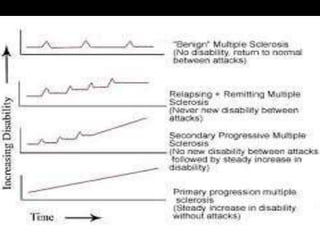
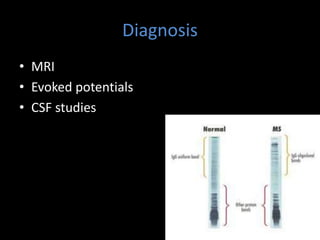
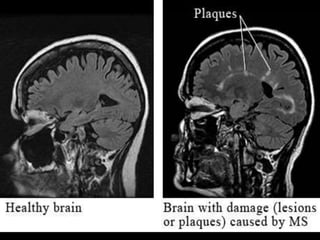
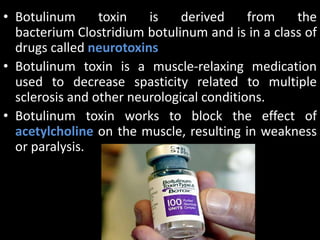
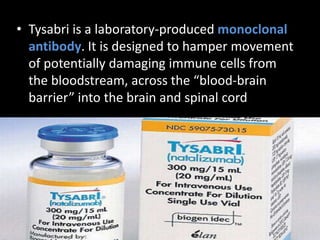
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disease causing inflammation, demyelination, and scarring of the CNS, primarily affecting women aged 20-40. Although there is no cure, various treatment options such as interferons, immunomodulators, and corticosteroids can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression. Diagnosis involves specific signs and MRI, while treatments also address associated symptoms like spasticity and depression.