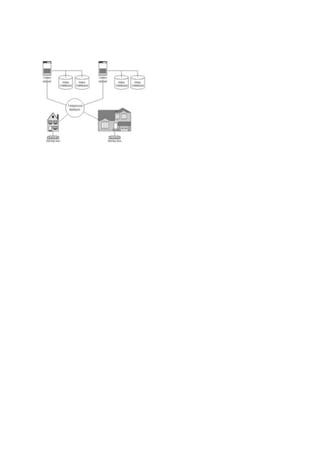
Internet telephony refers to voice, facsimile, and voice messaging applications that are transmitted over the Internet instead of the public telephone network. The basic process involves converting an analog voice signal to digital format and compressing it into Internet packets for transmission. More technically, it is the real-time delivery of voice and other multimedia data types between two or more parties using Internet protocols to control delivery. Common terms for this include Internet telephony, IP telephony, and voice-over-IP. Quality of service parameters like delay, bit rate, packet loss, jitter, and data quality must be considered to ensure desired application quality for users.